Centroid of a conical wedge
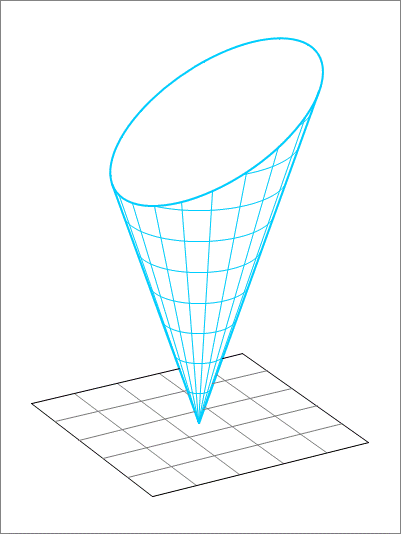 Fig. 1 Right circular cone cut by a plane
Fig. 1 Right circular cone cut by a plane
A right circular solid cone with a semi-vertical angle of and its vertex at the origin opening in the positive axis direction is depicted in the figure above. The semi-vertical angle is defined as the angle between the axis of the cone and its surface. As shown in the figure, this solid cone is cut by the plane , where , and . The figure depicts the part of the cone under this cutting plane. If the solid cone is made of a material of uniform density, find the centroid of this part of the cone, and submit the value of .
Details and Assumptions:
- You may need the following formulas for the semi-minor and semi-major axes lengths of the ellipse of intersection between the cone and the plane:
Where is the distance between the apex and the intersection point of the axis with the intercepting plane. is the semi-vertical angle of the cone, i.e. the angle between the axis of the cone and its surface. Finally, is the acute angle between the axis of the cone and the normal vector to the intersecting plane. And most importantly (actually this is the only formula you will need), the distance between the center of the ellipse and the point where the axis of the cone meets the cutting plane is given by ,
These formulas were derived in the solution of this problem .
The answer is 1649.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
The center of the elliptical "base" of the given cone is as discussed above given by
C = ( 0 , 0 , z 0 ) + v 0 ( cos ϕ , 0 , sin ϕ )
The centroid of the cone is simply G = 4 3 C
Substituting the given values, we get v 0 = 0 . 7 2 9 4 9 0
From which C = ( 0 . 6 3 1 7 5 7 , 0 , 1 0 . 3 6 4 7 4 5 )
and therefore, G = 4 3 C = ( 0 . 4 7 3 8 1 7 , 0 , 7 . 7 7 3 5 5 8 )
which makes the answer ⌊ 2 0 0 ( 0 . 4 7 3 8 1 7 + 7 . 7 7 3 5 5 8 ) ⌋ = 1 6 4 9