Centroid of a Cylindrical Wedge
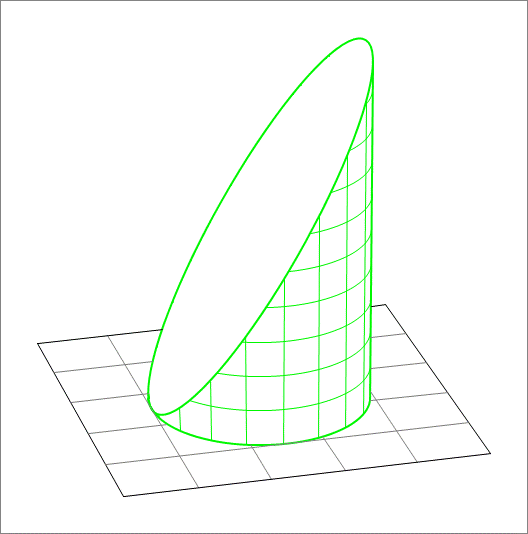
A cylinder of radius and length is placed on the horizontal plane, with the center of it circular base at the origin. The plane cuts the cylinder in two halves. Take the lower half depicted in the figure above and find its centroid. If the centroid , find .
The answer is 28.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Taking a slice of the wedge at x = t , where − 3 ≤ t ≤ 3 of thickness d t , then this slice will be a rectangle of dimensions d t × 2 9 − t 2 × 3 5 ( t + 3 ) , and the centroid of the slice is at ( t , 0 , 6 5 ( t + 3 ) )
The centroid G = ( V 1 ) ∫ t = − 3 3 ( t , 0 , 6 5 ( t + 3 ) ) A ( t ) d t
where A ( t ) is the area of the slice and is equal to 3 1 0 ( t + 3 ) 9 − t 2 . The volume V is half the volume of the cylinder, V = 4 5 π
Using the substitution t = − 3 cos θ , then d t = 3 sin θ d θ , and the integral becomes:
G = ( 4 5 π 1 ) ∫ θ = 0 π ( − 3 cos θ , 0 , 2 5 ( 1 − cos θ ) ) ⋅ ( 9 0 ) ( 1 − cos θ ) sin 2 θ d θ
Simplifying and expanding,
G = ( π 2 ) ∫ θ = 0 π ( − 3 cos θ ( 1 − cos θ ) sin 2 θ , 0 , 2 5 sin 2 θ ( 1 − cos θ ) 2 ) d θ
Now,
∫ θ = 0 π − 3 cos θ ( 1 − cos θ ) sin 2 θ d θ = ∫ θ = 0 π 3 cos 2 θ sin 2 θ d θ = ( 4 3 ) ∫ θ = 0 π sin 2 ( 2 θ ) d θ = ( 4 3 ) ∫ θ = 0 π 2 1 ( 1 − cos ( 4 θ ) ) d θ = 8 3 π
And,
∫ θ = 0 π 2 5 sin 2 θ ( 1 − cos θ ) 2 d θ = 2 5 ∫ θ = 0 π sin 2 θ − 2 cos θ sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ sin 2 θ d θ
= 2 5 ( 2 π − 0 + 8 π ) = ( 2 5 ) ( 8 5 π ) = 1 6 2 5 π
Therefore,
G = ( π 2 ) ( 8 3 π , 0 , 1 6 2 5 π ) = ( 4 3 , 0 , 8 2 5 )
So that x = 4 3 , y = 0 , z = 8 2 5 , making the answer 4 x + 8 z = 3 + 2 5 = 2 8