Chilly Cardano Curve
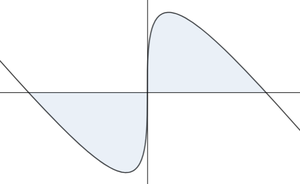
If the area of the blue region bounded by the graph and the horizontal axis can be expressed as
where are positive integers and , input the smallest possible value of the product as your answer.
The answer is 24.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Using polar coordinates, we have x = r cos t , y = r sin t . Substitute these in, you get,
r 3 ( 6 cos 3 t + 1 1 cos 2 t sin t + 6 cos t sin 2 t + sin 3 t ) = r cos t
so that
r 2 = 6 cos 3 t + 1 1 cos 2 t sin t + 6 cos t sin 2 t + sin 3 t cos t
The area is given by
A = 2 ( 2 1 ) ∫ 0 2 π r 2 d t = ∫ 0 2 π 6 cos 3 t + 1 1 cos 2 t sin t + 6 cos t sin 2 t + sin 3 t cos t d t
Multiply top and bottom by sec 3 t
A = ∫ 0 2 π 6 + 1 1 tan t + 6 tan 2 t + tan 3 t sec 2 t d t
Substitute u = tan t , then d u = sec 2 t d t and the integral becomes
A = ∫ 0 ∞ u 3 + 6 u 2 + 1 1 u + 6 d u
By partial fraction expansion we have u 3 + 6 u 2 + 1 1 u + 6 1 = 2 1 ( u + 1 1 − u + 2 2 + u + 3 1 )
The indefinite integral of which is 2 1 ln ( u + 2 ) 2 ( u + 1 ) ( u + 3 )
Finally evaluating this between the limits yields
A = 0 − 2 1 ln 4 3 = 2 1 ln 3 4
Therefore A = 1 , B = 2 , C = 4 , D = 3 and A B C D = 2 4