Circle And Chords
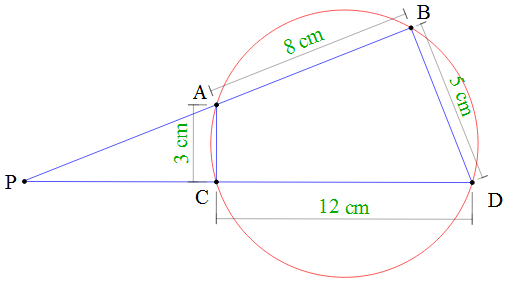
Diagram above shows a circle of radius , with two non-parallel chords and . When extended, these chords intersect outside the circle at point .
Find the distance correct up to 2 decimal places.
Note : Figure not drawn up to scale.
The answer is 15.75.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Let ∣ P A ∣ = a and ∣ P C ∣ = b . Then by the Intersecting Secant theorem we have that
∣ P A ∣ ∣ P B ∣ = ∣ P C ∣ ∣ P D ∣ ⟹ a ( a + 8 ) = b ( b + 1 2 ) , (i).
Next, since A B C D is a cyclic quadrilateral we know that ∠ A B D + ∠ A C D = 1 8 0 ∘ . But as ∠ A C D + ∠ A C P = 1 8 0 ∘ as well we have that ∠ A B D = ∠ A C P . Similarly ∠ C D B = ∠ C A P . Thus triangles Δ P C A and Δ P B D are similar, in which case
∣ A C ∣ ∣ P A ∣ = ∣ D B ∣ ∣ P D ∣ ⟹ 3 a = 5 b + 1 2 ⟹ b + 1 2 = 3 5 a .
Combining this with the equation (i) gives us that
a 2 + 8 a = ( 3 5 a − 1 2 ) ( 3 5 a ) ⟹ 9 a 2 + 7 2 a = ( 5 a − 3 6 ) ( 5 a )
⟹ 9 a + 7 2 = 5 ( 5 a − 3 6 ) ⟹ 9 a + 7 2 = 2 5 a − 1 8 0
⟹ 1 6 a = 2 5 2 ⟹ a = 1 6 2 5 2 = 4 6 3 = 1 5 . 7 5 .