Circle Fiesta.
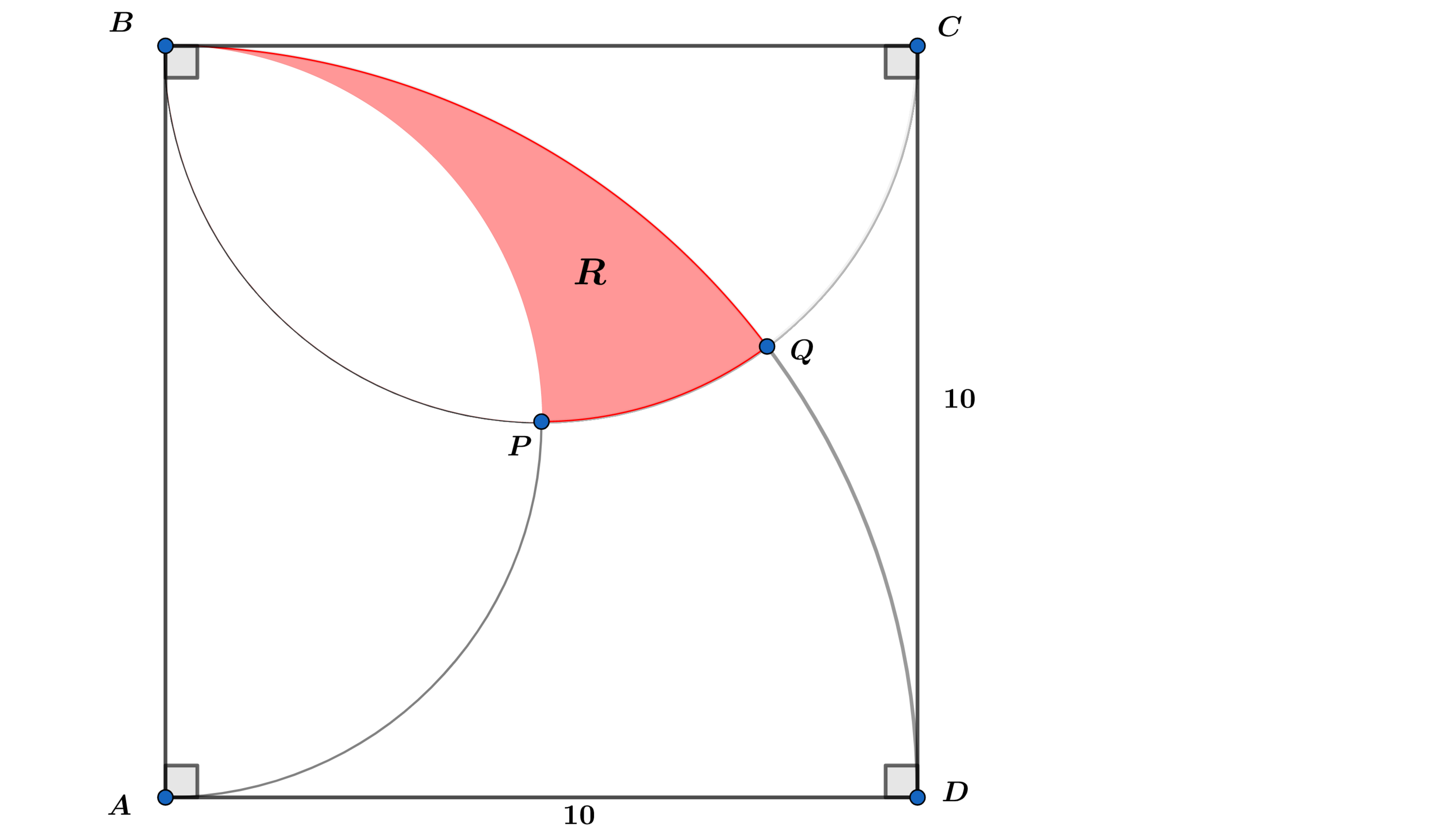
In the above diagram, is a square with side length of , and are semicircles and is a quarter circle.
If the area of the shaded region can be expressed as
, where and are coprime positive integers, find .
The answer is 10.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
The desired area A = A R 2 − A R 1 .
R 2 :
x 2 + ( y − 5 ) 2 = 2 5
x 2 + y 2 = 1 0 0
Finding points of intersection:
( x − 5 ) 2 + ( 1 0 0 − x 2 − 1 0 ) 2 = 2 5 ⟹ 2 0 − x = 2 1 0 0 − x 2 ⟹ 5 x ( x − 8 ) = 0 ⟹ x = 0 , x = 8
y 2 ( x ) = 1 0 0 − x 2 and y 1 ( x ) = − 2 5 − ( x − 5 ) 2 + 1 0 ⟹
A R 2 = ∫ 0 8 y 2 ( x ) − y 1 ( x ) d x = ∫ 0 8 1 0 0 − x 2 + 2 5 − ( x − 5 ) 2 − 1 0 d x
For I 1 = ∫ 2 5 − ( x − 5 ) 2 d x
Let x − 5 = 5 sin ( θ ) ⟹ d x = 5 cos ( θ ) d θ ⟹
I 1 = 2 2 5 ∫ ( 1 + cos ( 2 θ ) ) d θ = 2 2 5 ( θ + sin ( θ ) cos ( θ ) ) =
2 2 5 ( arcsin ( 5 x − 5 ) + ( 5 x − 5 ) 5 2 5 − ( x − 5 ) 2 )
⟹ I 1 ∣ 0 8 − ∫ 0 8 1 0 d x = ( ⟹ I 1 ∣ 0 8 − 8 0 = 2 2 5 arcsin ( 5 3 ) + 4 2 5 π − 7 4 .
Let I 2 = ∫ 1 0 0 − x 2 d x
Let x = 1 0 sin ( θ ) ⟹ d x = 1 0 cos ( θ ) d θ ⟹
I 2 = 5 0 ∫ ( 1 + cos ( 2 θ ) ) d θ = 5 0 ( θ + sin ( θ ) cos ( θ ) ) =
5 0 ( arcsin ( 1 0 x ) + ( 1 0 x ) 1 0 1 0 0 − x 2 ) ⟹
I 2 ∣ 0 8 = 5 0 arcsin ( 5 4 ) + 2 4
⟹ A R 2 = 2 2 5 arcsin ( 5 3 ) + 5 0 arcsin ( 5 4 ) + 4 2 5 π − 5 0 .
R 1 :
x 2 + ( y − 5 ) 2 = 2 5
( x − 5 ) 2 + ( y − 1 0 ) 2 = 2 5
Finding points of intersection:
y = 2 5 − x 2 + 5 ⟹ ( x − 5 ) 2 + ( 2 5 − x 2 − 5 ) 2 = 2 5 ⟹
⟹ 5 − x = 2 5 − x 2 ⟹ x ( x − 5 ) = 0 ⟹ x = 0 , 5
y 2 ( x ) = + 2 5 − x 2 5 and y 1 ( x ) = − 2 5 − ( x − 5 ) 2 + 1 0 ⟹
A R 1 = ∫ 0 5 y 2 ( x ) − y 1 ( x ) d x = ∫ 0 5 2 5 − x 2 + 2 5 − ( x − 5 ) 2 − 5 d x
I 1 = ∫ 0 5 2 5 − ( x − 5 ) 2 − 5 d x =
2 2 5 ( arcsin ( 5 x − 5 ) + ( 5 x − 5 ) 5 2 5 − ( x − 5 ) 2 ) ∣ 0 5 − 2 5 = 4 2 5 π − 2 5
For I 2 = ∫ 0 5 2 5 − x 2 d x
Let x = 5 sin ( θ ) ⟹ d x = 5 cos ( θ ) ⟹
I 2 = 2 2 5 ∫ 0 2 π ( 1 + cos ( 2 θ ) ) d θ =
2 2 5 ( θ + sin ( θ ) cos ( θ ) ) ∣ 0 2 π = 4 2 5 π
⟹ A R 1 = 4 5 0 π − 2 5
⟹ The desired area A = 2 2 5 arcsin ( 5 3 ) + 5 0 arcsin ( 5 4 ) − 4 2 5 π − 2 5 =
2 5 2 arcsin ( 5 3 ) + 5 2 ∗ 2 arcsin ( 5 2 2 ) − 2 2 5 2 π − 5 2 =
b a b arcsin ( a c ) + a b ∗ b arcsin ( a b b ) − b b a b π − a b
⟹ a + b + c = 1 0 .