Coffin Problem No.1
A positive real number x satisfies the inequality x ( 8 1 − x + 1 + x ) ≤ 1 1 1 + x − 1 6 1 − x . Find the minimum value of x .
The answer is 0.6.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
Let a = 1 − x , b = 1 + x . Then x = b 2 − 1 , a 2 + b 2 = 2 , and the equation becomes ( b 2 − 1 ) ( 8 a + b ) b 2 ( 8 a + b ) 8 a ( b 2 + 1 ) 6 4 a 2 ( b 2 + 1 ) 2 6 4 ( 2 − b 2 ) ( b 2 + 1 ) 2 0 0 ≤ 1 1 b − 1 6 a ≤ 1 2 b − 8 a ≤ 1 2 b − b 3 ≤ b 2 ( 1 2 − b 2 ) 2 ≤ b 2 ( 1 2 − b 2 ) 2 ⋮ ≤ 6 5 b 6 − 2 4 b 4 − 4 8 b 2 − 1 2 8 ≤ ( 5 b 2 − 8 ) ( 1 3 b 4 + 1 6 b 2 + 1 6 ) . The second term is always positive, so the inequality is equivalent to 5 b 2 − 8 ≥ 0 , or 5 ( x + 1 ) − 8 ≥ 0 , or x ≥ 3 / 5 . Hence the minimum value for x is 0 . 6 .
Using the substitution
y = 1 + x 1 − x a n d x = 1 + y 2 1 − y 2
The inequality reduces to
( 1 − y 2 ) ( 8 y + 1 ) ≤ ( 1 1 − 1 6 y ) ( 1 + y 2 )
expanding and rearranging the terms we get
( 2 y − 1 ) ( 2 y 2 − 2 y + 5 ) ≤ 0
and because 2 y 2 − 2 y + 5 = 0 has no real solutions, we know that y ≤ 2 1
and finally, solving
1 + x 1 − x ≤ 2 1
we have x ≥ 5 3
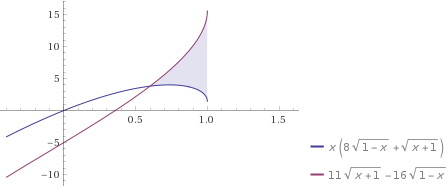 I found it convenient to plot it and we can see the solution is at
x
=
0
.
6
.
I found it convenient to plot it and we can see the solution is at
x
=
0
.
6
.
x ( 8 1 − x + 1 + x ) ( 8 x + 1 6 ) 1 − x ( 6 4 x 2 + 2 5 6 x + 2 5 6 ) ( 1 − x ) − 6 4 x 3 − 1 9 2 x 2 + 2 5 6 6 5 x 3 + 1 7 1 x 2 + 9 9 x − 1 3 5 ( 5 x − 3 ) ( 1 3 x 2 + 4 2 x + 4 5 ) ⟹ x ≤ 1 1 1 + x − 1 6 1 − x ≤ ( 1 1 − x ) 1 + x ≤ ( x 2 − 2 2 x + 1 2 1 ) ( 1 + x ) ≤ x 3 − 2 1 x 2 + 9 9 x + 1 2 1 ≥ 0 ≥ 0 ≥ 5 3 = 0 . 6 Squaring both sides 1 3 x 2 + 4 2 x + 4 5 has no real root.