Comparing Surface Areas
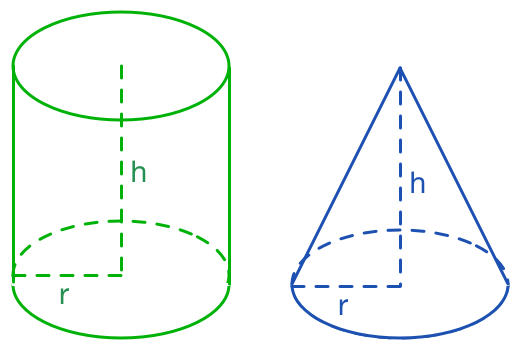
Consider a cone and a cylinder which have the same base radius and height .
Which has a larger surface area?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
r 2 + h 2 < r 2 + h 2 + ( 3 h 2 + 4 r h ) = ( r + 2 h ) ( ∵ 3 h 2 + 4 r h > 0 ) ⟹ r 2 + h 2 < r + 2 h ⟹ π r r 2 + h 2 < π r ( r + 2 h ) ⟹ π r 2 + π r r 2 + h 2 < π r 2 + π r ( r + 2 h ) ⟹ π r 2 + π r r 2 + h 2 < 2 π r 2 + 2 π r h ⟹ Surface area of cone < Surface area of cylinder.
Note : In other words, we want to find the mathematical symbol satisfying the inequation/equation below.
2 π r 2 + 2 π r h = ? π r 2 + π r s ,
where s denote the slant length of the cone. By Pythagorean theorem , s satisfy the equation, r 2 + h 2 = s 2 , so s = r 2 + h 2 .