Coordinates of point F

△ A B C is right at A ( 0 , 0 ) , with vertex B = ( 0 , 4 ) , and vertex C = ( 3 , 0 ) . Segment A C is extended to point D such that the incircles of △ B C D and △ A B C have the same radius. If the incenter of △ B C D is point F ( x , y ) , find x + y .
The answer is 4.5.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
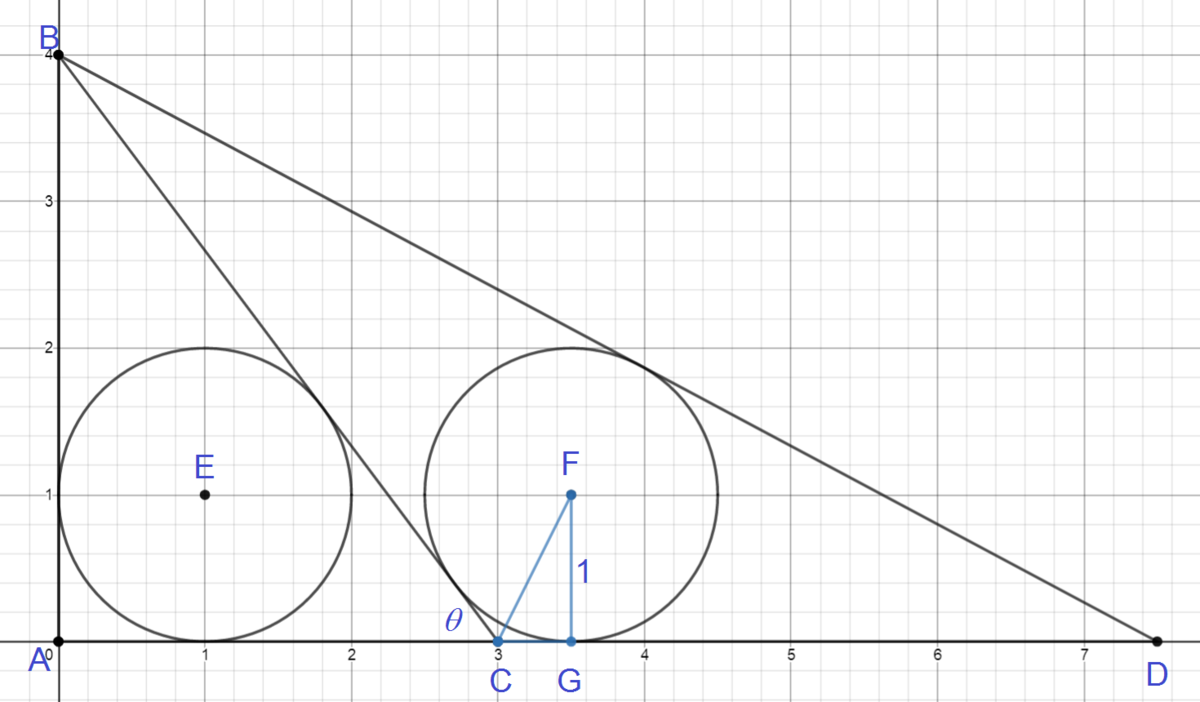
△ A B C is a 3 - 4 - 5 triangle, therefore B C = 5 . Then the area of triangle [ A B C ] = 2 4 × 3 = 6 = s r , where s is the semiperimeter of the triangle and r , the radius of the incircle. Therefore 2 3 + 4 + 5 r = 6 ⟹ r = 1 , Let F G be perpendicular to A D . Then y = F G = 1 . And
x = A G = A C + C G = 3 + F G ⋅ cot ∠ F C D = 3 + cot ( 2 ∠ B C D ) = 3 + cot ( 2 1 8 0 ∘ − ∠ B C A ) = 3 + cot ( 9 0 ∘ − 2 θ ) = 3 + tan 2 θ = 3 + sin θ 1 − cos θ = 3 + 5 4 1 − 5 3 = 3 + 2 1 = 3 . 5 Note that ∠ F C D = 2 ∠ B C D Let ∠ B C A = θ
Therefore x + y = 3 . 5 + 1 = 4 . 5 ,
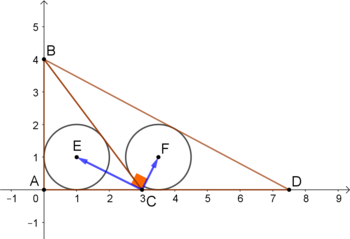 The inradius of the
3
-
4
-
5
right triangle is equal to 1, hence point
E
has coordinates
(
1
,
1
)
. Since the two circles are congruent, the y-coordinate of
F
is equal to 1. Let
x
be the x-coordinate of
F
.
The inradius of the
3
-
4
-
5
right triangle is equal to 1, hence point
E
has coordinates
(
1
,
1
)
. Since the two circles are congruent, the y-coordinate of
F
is equal to 1. Let
x
be the x-coordinate of
F
.
Focusing on the vectors C F = ( x F − x C y F − y C ) = ( x − 3 1 − 0 ) = ( x − 3 1 ) and C E = ( x E − x C y E − y C ) = ( 1 − 3 1 − 0 ) = ( − 2 1 ) , we have
C F ⊥ C E ⇔ C F ⋅ C E = 0 ⇔ ( x − 3 1 ) ( − 2 1 ) = 0 ⇔ − 2 ( x − 3 ) + 1 = 0 ⇔ x = 3 . 5 Hence, x F + y F = 3 . 5 + 1 = 4 . 5 .
From the previous problem, we found that C D = 4 . 5
Therefore, the coordinates of the vertices of △ B C D are
B ( 0 , 4 ) , C ( 3 , 0 ) , D ( 7 . 5 , 0 )
And the side lengths are b = 4 . 5 , c = 4 2 + 7 . 5 2 = 8 . 5 , d = 5
Hence, the coordinates of the incenter F are
F = ( x , y ) = b + c + d b B + b + c + d c C + b + c + d d D
Substituting the numerical values,
( x , y ) = 1 8 4 . 5 ( 0 , 4 ) + 1 8 8 . 5 ( 3 , 0 ) + 1 8 5 ( 7 . 5 , 0 ) = ( 0 , 1 ) + ( 1 2 1 7 , 0 ) + ( 1 2 2 5 , 0 ) = ( 2 7 , 1 ) = ( 3 . 5 , 1 )
Hence x + y = 4 . 5
The inradius is r = 2 3 + 4 − 5 = 1 . Putting an origin at A , the point F lies on the angle bisector of ∠ B C D and on the line y = 1 .
So F has coordinates F ( 3 + cot 2 ∠ B C D , 1 )
We have ∠ B C D = π − ∠ A C B and tan ∠ A C B = 3 4 . Hence cot 2 ∠ B C D = 2 1 and F ( 2 7 , 1 ) giving the answer 4 . 5 .