cos 3 6 ∘
What is cos 3 6 ∘ ?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
5 solutions
It's a easy one
Consider a pentagram with an exterior regular pentagon A B C D E with unit sides and an interior regular pentagon F G H I J with x sides:
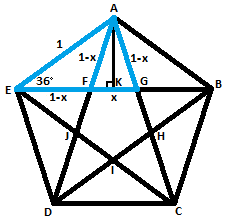
By symmetry, A E = E G = 1 , so E F = E G − F G = 1 − x . Also by symmetry, E F = A F = A G = 1 − x .
As interior angles of a regular pentagon, ∠ J F G = ∠ E A B = 1 0 8 ° , so by vertical angles ∠ E F A = 1 0 8 ° , and as base angles of an isosceles △ E F A , ∠ A E F = ∠ E A F = 2 1 ( 1 8 0 ° − 1 0 8 ° ) = 3 6 ° . Also by symmetry, ∠ G A B = ∠ E A F = 3 6 ° , so ∠ G A F = ∠ E A B − ∠ E A F − ∠ G A B = 1 0 8 ° − 3 6 ° − 3 6 ° = 3 6 ° . Therefore, △ E A G ∼ △ A F G by SAS similarity.
Since △ E A G ∼ △ A F G , A G A E = F G A G or 1 − x 1 = x 1 − x , which solves to x = 2 3 − 5 for x < 1 .
From right △ A E K , cos ∠ A E K = A E E K , or cos 3 6 ° = 1 1 − x + 2 1 x . Substituting x = 2 3 − 5 from above and simplifying gives cos 3 6 ° = 4 1 + 5 .
Using the identity: k = 1 ∑ n cos ( 2 n + 1 2 k − 1 π ) = 2 1 ,
cos 5 π + cos 5 3 π cos 5 π − cos 5 2 π cos 5 π − 2 cos 2 5 π + 1 4 cos 2 5 π − 2 cos 5 π − 1 ⟹ cos 5 π = 2 1 = 2 1 = 2 1 = 0 = 4 1 + 5 Note that cos ( π − θ ) = − cos θ and cos 2 θ = 2 cos 2 θ − 1 Since cos 5 π > 0
In a 3 − 4 − 5 right triangle, the smallest angle is 3 7 ∘
So, c o s 3 7 ∘ = 5 4 = 0 . 8
As c o s x decreases with increase in x ( 0 ∘ ≤ x ≤ 9 0 ∘ ) and 3 6 ∘ < 3 7 ∘ , the only option greater than 0 . 8 is 4 1 + 5
To be precise it’s arccos 0 . 8 = 3 6 . 8 6 9 8 9 7 6 4 ∘
Really clever. If you work smart you don't have to work hard.
cos 3 6 ° ≈ 0 . 8 , so we have to just find its approximation.
Then, it is 4 1 + 5 .
Let θ = 1 8 ∘ so that 2 θ = 3 6 ∘ and 3 θ = 5 4 ∘ so, cos 5 4 ∘ = cos ( 9 0 ∘ − 3 6 ∘ ) = sin 3 6 ∘ Or we can write it as cos 3 θ = sin 2 θ Let’s see sin 2 θ = 2 sin θ cos θ = 2 cos θ 1 − cos 2 θ Denote cos θ = x We have sin 2 θ = 2 x 1 − x 2 And we have cos 3 θ = 4 c o s 3 θ − 3 cos θ = 4 x 3 − 3 x Then, 2 x 1 − x 2 = 4 x 3 − 3 x 1 6 x 4 − 2 0 x 2 + 5 = 0 We denote y = x 2 1 6 y 2 − 2 0 y + 5 = 0 So we get x 2 = y 1 , 2 = 8 5 ± 5 We discard the smaller root. And by double angle formula cos 2 θ = 2 cos 2 θ − 1 = 2 x 2 − 1 = 4 1 + 5