Cube Resistance Network
Form a resistance network with the following steps:
1)
Start with a wire frame cube consisting of
line segments, each with resistance
2)
From a point inside the cube, draw
line segments to the vertices of the cube, each with resistance
3)
Connect the interior point (colored red) to the positive terminal of a battery
4)
Connect all of the cube vertices (colored green) to the negative terminal of the same battery
What equivalent resistance does the network present to the battery?
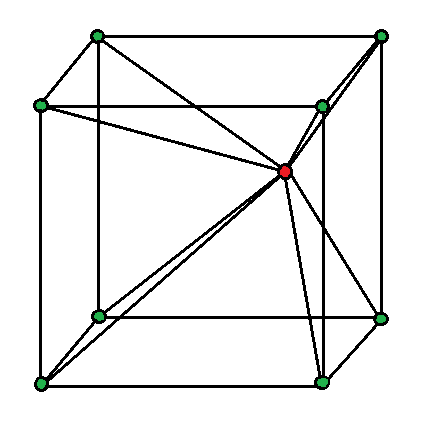
The answer is 0.125.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
The twelve vertices of the cube are all equipotentials, and so can be shorted together, and the wires connecting them ignored. Thus the circuit described is equivalent to eight 1 Ω resistors connected in parallel between the red and green nodes, for an equivalent resistance of 8 1 Ω .