Cut Cube Volume
A unit cube is to be cut by a plane defined by three points that it passes through. The cube faces are parallel to the coordinate planes, with one vertex at the origin and the opposing vertex at ( 1 , 1 , 1 ) . The cutting plane passes through the points ( 0 . 5 , 0 , 1 ) , ( 0 , 0 . 5 , 1 ) and ( 1 , 1 , 0 . 5 ) . Find the volume of the cube that lies above the cutting plane.
If this volume can be expressed as ( b a ) 2 , for coprime integers a and b , then find a + b .
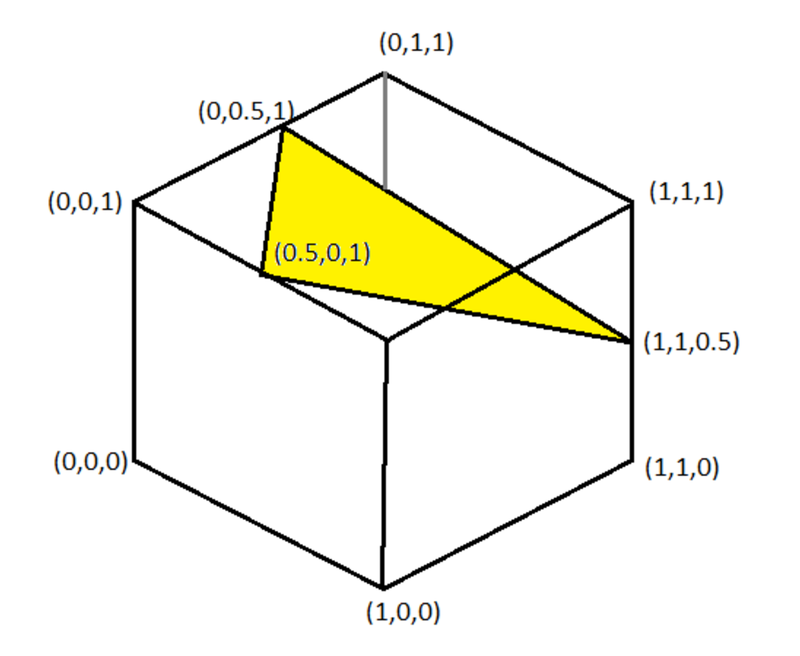
The answer is 17.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Same approach. Except I have done the second step first to confirm the position of point F,G.
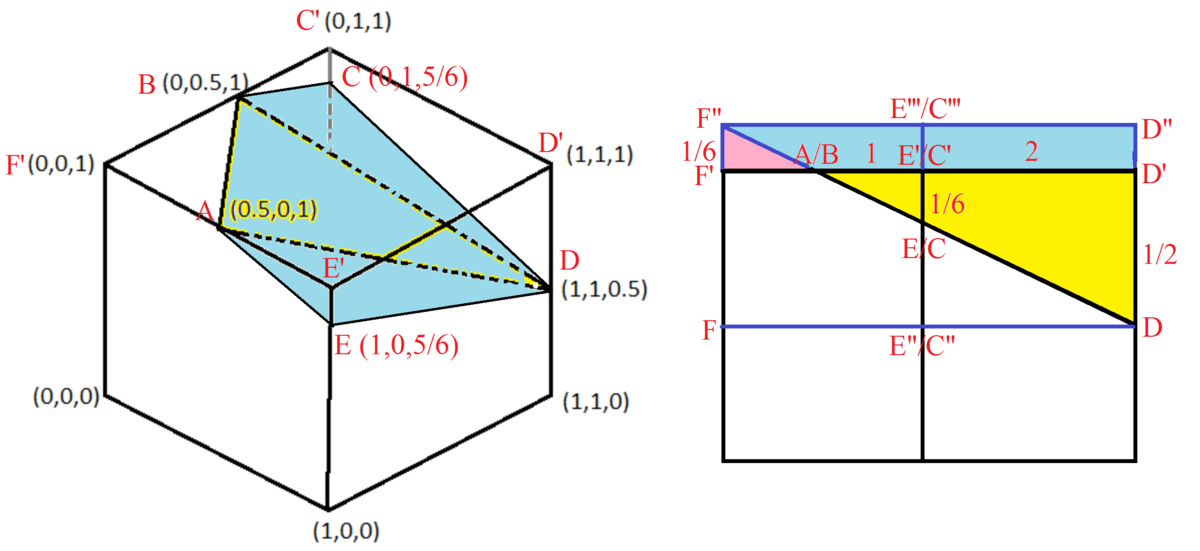
Label the cube as shown. If we look along E ′ C ′ , we note that △ A E E ′ and △ A D D ′ are similar. Then D D ′ E E ′ = A D ′ A E ′ ⟹ E E ′ = A D ′ A E ′ × D D ′ = 3 1 × 2 1 = 6 1 . Then we have C ( 0 , 1 , 6 5 ) and E ( 1 , 0 , 6 5 ) .
Now extend the top of the cube until the cut meet the extended edge of F F ′ at F ′ ′ . From similar triangle we have F ′ F ′ ′ = 6 1 . Color the block whose volume V we need to find yellow; and the volume of extended blocked of height 6 1 to top red V 1 and blue V 2 .
We note that V + V 2 is half the volume of the cuboid C ′ ′ ′ D ′ ′ E ′ ′ ′ F ′ ′ C D E ′ ′ F ′ ′ which has a height of F F ′ ′ = 6 1 + 2 1 = 3 2 . Since the volume of the cuboid is 1 × 1 × 3 2 = 3 2 , then V + V 2 = 2 1 × 3 2 = 3 1 .
We also note that V 1 + V 2 = 1 × 1 × 6 1 = 6 1 or a unit cuboid of height 6 1 .
And that V 1 is a pyramid with a base area 2 1 × 2 1 × 2 1 = 8 1 and height 6 1 . That is V 1 = 3 1 × 8 1 × 6 1 = 1 4 4 1
Then we have:
V = ( V + V 2 ) − ( V 1 + V 2 ) + V 1 = 3 1 − 6 1 + 1 4 4 1 = 1 4 4 2 5 = ( 1 2 5 ) 2
Therefore a + b = 5 + 1 2 = 1 7 .
The last number on the last line should be corrected to ( 1 2 5 ) 2 .
Label the diagram as follows:
The plane has an equation of x + b y + c z = d , and since it goes through A ( 0 , 2 1 , 1 ) , B ( 2 1 , 0 , 1 ) , C ( 1 , 1 , 2 1 ) , we know that 0 + 2 1 b + c = d , 2 1 + 0 + c = d , and 1 + b + 2 1 c = d , which solves to b = 1 , c = 3 , and d = 2 7 , and gives an equation of x + y + 3 z = 2 7 or 2 x + 2 y + 6 z = 7 .
G is also on the plane 2 x + 2 y + 6 z = 7 with x = 1 and y = 0 , so its coordinates solve to ( 1 , 0 , 6 5 ) , which means E G = 1 − 6 5 = 6 1 .
Now extend A B , D H , and F C to meet at I and A B , E H , and G C to meet at J to form right-angled tetrahedron I J H C :
J is on the plane 2 x + 2 y + 6 z = 7 with y = 1 and z = 1 , so its coordinates solve to ( − 2 1 , 1 , 1 ) , which means J E = 2 1 . By symmetry, I D = J E = 2 1 .
The volume of the cube that lies above the cutting plane is V = V I J H C − V B J E G − V I A D F = 6 1 ⋅ H I ⋅ H J ⋅ H C − 6 1 ⋅ E B ⋅ E J ⋅ E G − 6 1 ⋅ D I ⋅ D A ⋅ D F = 6 1 ⋅ 2 3 ⋅ 2 3 ⋅ 2 1 − 6 1 ⋅ 2 1 ⋅ 2 1 ⋅ 6 1 − 6 1 ⋅ 2 1 ⋅ 2 1 ⋅ 6 1 = 1 4 4 2 5 = ( 1 2 5 ) 2 . Therefore, a = 5 , b = 1 2 , and a + b = 1 7 .