Cutting Territory
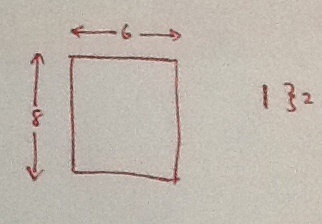 Consider a block of wood of dimensions
. Also, consider support rods of length
, and negligible cross-section. Now, the wooden board can be
cut
, only if the cut is not obstructed by a support. Also, any successful cut must result in two pieces. If the smaller of the two pieces must always have an area less than
, find the minimum number of supports required.
Consider a block of wood of dimensions
. Also, consider support rods of length
, and negligible cross-section. Now, the wooden board can be
cut
, only if the cut is not obstructed by a support. Also, any successful cut must result in two pieces. If the smaller of the two pieces must always have an area less than
, find the minimum number of supports required.
Details and Assumptions:
-
A cut starts for one edge, and must end at another edge. No cut can be made solely in the interior of the board
-
A cut must be linear, and cannot curve around supports
-
Supports can be placed back-to-back, side-to-side, but not one superimposing the other
-
The arrangement of the supports must allow cuts, and not completely eradicate the possibility of cuts
The answer is 10.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
0 solutions
No explanations have been posted yet. Check back later!