Cyclic Regular Polygon Fractals
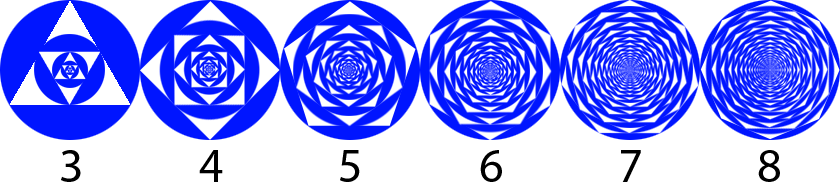
The n th figure in the above sequence is constructed by the following procedure:
- Draw a blue disc of radius π 2 0 1 6
- Remove a regular n -gon area from the (smallest) disc
- Inscribe a blue disc inside the empty n -gon space
- Repeat steps 2-4
Let A n be the total blue area of the n th figure in the sequence.
Compute n → ∞ lim A n .
The answer is 1344.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
1 solution
Easiest way would be use series expansion. Atleast I did it that way. Lhopital is still available on taking common denominator though.
Try L'Hospitals' rule. It works with a bit of manipulation. A very nice problem though.
Hey, @Kerry Soderdahl n → ∞ lim A n = n → ∞ lim π r 0 2 ⎝ ⎛ sin 2 n π 1 − n 2 π sin n 2 π ⎠ ⎞
Now, using the power series of sin upto third order terms, and simplifying, n → ∞ lim A n = 3 2 π r 0 2
Use could also put n π = α so that, α → 0 as n → ∞ and then use L'Hospitals' rule (but you'll have to use it twice or thrice, which is labourious for the given expression).
I got the expression but I do not know how to evaluate the limit
I used a spreadsheet to find the limit as n tends to a big value, nut then to check I found a similar formula for the white areas, and found the ratio of white to blue was 2:1, so the limit is 2/3 the area of the circle.
Relevant wiki: Regular Polygons - Problem Solving - Medium
I'll write a better and more complete solution as soon as I have the time to.
The radius of the outer circle is r 0 = π 2 0 1 6
The blue area after steps 1 and 2 is π r 0 2 − n r 0 2 cos ( n π ) sin ( n π )
This area is repeated through a geometric sequence with a ratio of cos 2 ( n π ) to construct the entire figure:
n → ∞ lim k = 0 ∑ ∞ ( cos 2 k ( n π ) ) ( π r 0 2 − n r 0 2 cos ( n π ) sin ( n π ) )
= r 0 2 n → ∞ lim 1 − cos 2 ( n π ) π − n cos ( n π ) sin ( n π ) = r 0 2 n → ∞ lim sin 2 ( n π ) π − n cos ( n π ) sin ( n π )
= r 0 2 n → ∞ lim π csc 2 ( n π ) − n cot ( n π )
I don't actually know how to evaluate this limit -- I'd really appreciate if someone could post how to do it. According to Wolfram Alpha, lim n → ∞ π csc 2 ( n π ) − n cot ( n π ) = 3 2 π .
r 0 2 ∗ 3 2 π = 1 3 4 4