Demand And Supply?
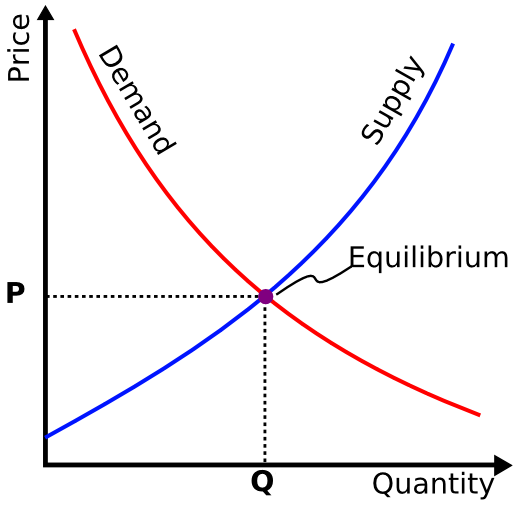
In a market economy , the price of a product is determined solely by its demand and supply.
When a new product is launched in a market economy, it has high demand and supply. As time passes, it becomes outdated, and its demand decreases. As the company introduces newer products, its supply decreases too.
What effect does a decrease in both the demand and the supply have on the price of the product?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
In each of the diagrams above, the red lines show demand, and the blue lines show supply. In each case, demand as well as supply decreases.
In the first diagram, supply decreases more as compared to demand, so the equilibrium price decreases.
In the second diagram, demand decreases more as compared to supply, so the equilibrium price increases.
In the third diagram, the equilibrium price remains constant.
Unless we know the extent of decrease of both demand and supply, we cannot conclude what happens to the equilibrium price of the product. □
Note: We can see that the quantity of goods traded certainly decreases.