Descartes Sangaku : The Beast part 3
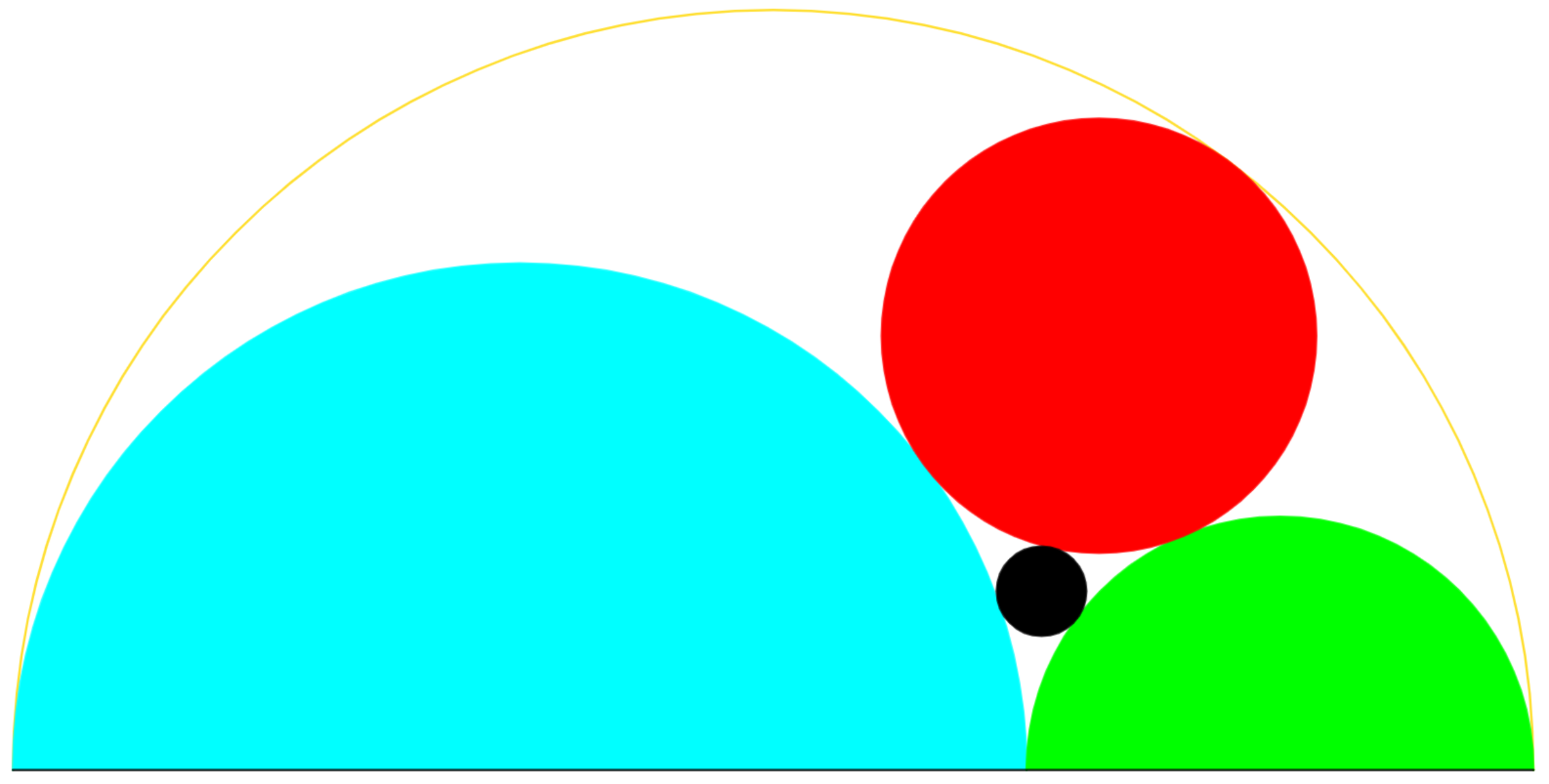
- The diagram shows a semi-circle of radius 1. We place a point on its diameter.
- This point allows us to draw two semi-circles (green and cyan).
- We inscribe a red circle so that this circle is tangent to the other three semi-circles.
- We inscribe a black circle between the red circle, the green semi-circle and the cyan semi-circle.
The question: What is the white area inside the semi-circle of radius 1 if the black circle has a radius equal to 1 7 1 , the answer can be expressed as π ⋅ b a where a and b are positive integers , calculate b − a
The answer is 109972.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Not so foolish after all...
- To solve this problem, we shall denote the radius of the cyan semi-circle as 1 − x , the radius of the green semi-circle as x and the radius of the red circle as R ( x ) .
-
We shall use the Pythagorean theorem to express R ( x ) in terms of x

-
We shall write three equations using the diagram:
- ( 1 − R ( x ) ) 2 = l ( x ) 2 + h ( x ) 2
- ( 1 − x + R ( x ) ) 2 = ( x − l ( x ) ) 2 + h ( x ) 2
- ( x + R ( x ) ) 2 = ( 1 − x + l ( x ) ) 2 + h ( x ) 2
- After combining the equation and using minor algebra skills we find:
- R ( x ) = x 2 − x + 1 x − x 2
- Now using Descartes Circle's theorem whe can express the radius of the black circle in terms of x :
- B ( x ) 1 = R ( x ) 1 + x 1 + 1 − x 1 + 2 R ( x ) ⋅ x 1 + R ( x ) ⋅ ( 1 − x ) 1 + x ⋅ ( 1 − x ) 1
- Whe can solve then B ( x ) 1 = 1 7
- We find x = 3 2
- We evaluate : R ( 3 2 ) = 7 2
- Knowing all radii needed when find that the white area is : π ⋅ 1 2 7 4 4 9 1 7 4 7 7
- 1 2 7 4 4 9 − 1 7 4 4 7 = 1 0 9 9 7 2
Let the radius of the red circle be R . Then, applying Descartes's circle's theorem we get
R 1 = a 1 + 1 − a 1 − 1 + 2 a ( 1 − a ) 1 − a 1 − 1 − a 1
= a ( 1 − a ) a 2 − a + 1
where a and 1 − a are the radii of the cyan and the green semicircles respectively.
And,
1 7 = a 1 + 1 − a 1 + a ( 1 − a ) a 2 − a + 1 + 2 a ( 1 − a ) 1 + a ( 1 − a ) 2 a 2 − a + 1 + a 2 ( 1 − a ) a 2 − a + 1
= a − a 2 a 2 − a + 4
⟹ 9 a 2 − 9 a + 2 = 0 ⟹ a = 3 1 , 1 − a = 3 2
⟹ R = 7 2
Total area of the cyan and green semicircles, red circle and black circle is
2 π ( 9 1 + 9 4 + 4 9 8 + 2 8 9 2 )
= 2 π × 1 2 7 4 4 9 9 2 4 9 5
Hence area of the white region is
2 π ( 1 − 1 2 7 4 4 9 9 2 4 9 5 ) = π × 1 2 7 4 4 9 1 7 4 7 7
Therefore a = 1 7 4 7 7 , b = 1 2 7 4 4 9 , b − a = 1 0 9 9 7 2 .