Dihedral Angle
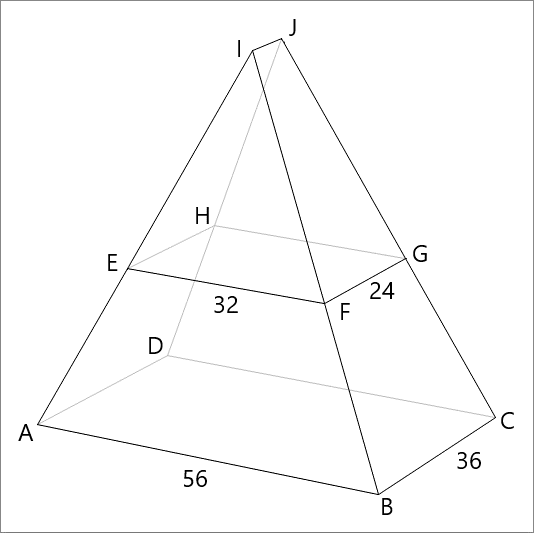
Polyhedron A B C D - E F G H has the bottom rectangle A B C D measuring 5 6 × 3 6 and top rectangle E F G H measuring 3 2 × 2 4 . The two rectangles are aligned, with the longer edges parallel to the x -axis, and the shorter edges parallel to y -axis, and their centers lying on the vertical z -axis with a vertical separation of h = 2 4 .
Find the dihedral angle between face A B F E and face B C G F in degrees.
The answer is 96.2268.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Noting that A B runs parallel to the x -axis and B C runs parallel to the y -axis, the normal to face A B F E is given by:
n 1 = ( 0 , − sin θ 1 , cos θ 1 )
where θ 1 is the angle between face A B F E and the horizontal plane, and is given by
θ 1 = tan − 1 2 1 ( 3 6 − 2 4 ) h = tan − 1 ( 4 )
From which it follows that cos θ 1 = 1 7 1 and sin θ 1 = 1 7 4
Similarly, the normal to face B C G F is given by:
n 2 = ( sin θ 2 , 0 , cos θ 2 )
where θ 2 is the angle between face B C G F are the horizontal plane, and is given by
θ 2 = tan − 1 2 1 ( 5 6 − 3 2 ) h = tan − 1 ( 2 )
From which it follows that cos θ 2 = 5 1 and sin θ 2 = 5 2
Hence, the two normals to the two planes are
n 1 = ( 0 , − 1 7 4 , 1 7 1 ) , and,
n 2 = ( 5 2 , 0 , 5 1 )
Noting that n 1 and n 2 are unit vectors, the angle between them is
ϕ = cos − 1 n 1 ⋅ n 2 = cos − 1 8 5 1 = 8 3 . 7 7 3 1 4 9 7 0 2 8 ∘
Hence the angle between the two planes is 1 8 0 ∘ − ϕ = 9 6 . 2 2 6 8 ∘
Let the center of rectangle A B C D be the origin, so that A is at ( 1 8 , − 2 8 , 0 ) , B is at ( 1 8 , 2 8 , 0 ) , C is at ( − 1 8 , 2 8 , 0 ) , and F is at ( 1 2 , 1 6 , 2 4 ) .
The equation of the plane a 1 x + b 1 y + c 1 z = d 1 containing A , B , and F must fulfill 1 8 a 1 − 2 8 b 1 = d 1 , 1 8 a 1 + 2 8 b 1 = d 1 , and 1 2 a 1 + 1 6 b 1 + 2 4 c 1 = d 1 , which solves to b 1 = 0 , c 1 = 4 1 a 1 , and d 1 = 1 8 a 1 , so that the equation when a 1 = 4 is 4 x + z = 7 2 , which has a normal vector of ( 4 , 0 , 1 ) .
The equation of the plane a 2 x + b 2 y + c 2 z = d 2 containing B , C , and F must fulfill 1 8 a 2 + 2 8 b 2 = d 2 , − 1 8 a 2 + 2 8 b 2 = d 2 , and 1 2 a 2 + 1 6 b 2 + 2 4 c 2 = d 2 , which solves to a 2 = 0 , c 2 = 2 1 b 2 , and d 2 = 2 8 b 2 , so that the equation when b 2 = 2 is 2 y + z = 5 6 , which has a normal vector of ( 0 , 2 , 1 ) .
The dihedral angle between face A B F E and B C G F is equivalent to the obtuse angle between these two normal vectors, which is:
θ = cos − 1 ( − 4 2 + 0 2 + 1 2 ⋅ 0 2 + 2 2 + 1 2 4 ⋅ 0 + 0 ⋅ 2 + 1 ⋅ 1 ) = cos − 1 ( 8 5 − 1 ) ≈ 9 6 . 2 2 6 8 ° .