Displacement = Distance Not all the Time!!!!!!
A particle moves along a horizontal path, such that its velocity is given by v = m/s, where t is the time in seconds. If it is initially located at the origin O, determine the distance covered during t = 0 to t = 3.5.(in m)
The answer is 14.125.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
A particle moves along a horizontal path, such that its velocity is given by v = ( 3 t 2 − 6 t ) m/s, where t is the time in seconds. If it is initially located at the origin O, determine the average speed during t = 0 to t = 3.5.(in m/s)
A v g . s p e e d = t o t a l t i m e t o t a l d i s t a n c e v = 3 t 2 − 6 t v = 0 a t t = 2 s For t < 2 s, velocity is -ve. At t = 2s, velocity is zero and for t > 2 s velocity is +ve. ∴ s 1 = ∫ 0 3 . 5 v d t = ∫ 0 3 . 5 ( 3 t 2 − 6 t ) d t = 6 . 1 2 5 m = d i s p l a c e m e n t u p t o 3 . 5 s s 2 = ∫ 0 2 v d t = ∫ 0 2 ( 3 t 2 − 6 t ) d t = − 4 m = d i s p l a c e m e n t u p t o 2 s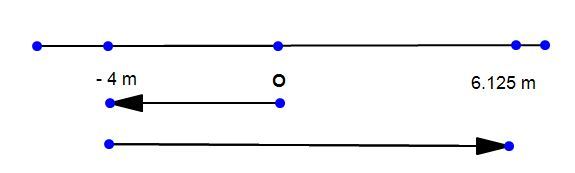 image
d = distance traveled in 3.5s
image
d = distance traveled in 3.5s
= 4 + 4 + 6.125
= 14.125.