Division of Square
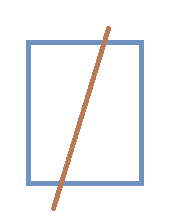
Let a straight line cuts a unit square in two parts such that ratio of their areas is 2:1. This line also passes through the midpoint of one of the intersecting sides of the square. Then find the intercepted length of the line within the square.
If the length comes in the form of b a , where a and b are positive integers and a is square-free, then submit your answer as a + b .
The answer is 13.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Letting the side of the square be 1 , we see that the cutting line cuts one of the sides of the square into two halves. As for the opposite side, it cuts the side into x and ( 1 − x ) . We first determine the value of x as follows:
Considering that one part of the square is twice the area of the other, we have:
2 x + 2 1 = 2 ( 2 1 − x + 2 1 )
x + 2 1 = 2 ( 1 + 2 1 − x )
x + 2 1 = 2 + 1 − 2 x
x + 2 1 = 3 − 2 x
( 1 + 2 ) x = 3 − 2 1
3 x = 2 6 − 1
3 x = 2 5
x = 3 × 2 5
x = 6 5
Now we know one of the sides is divided into 6 5 and 6 1 . Employing Pythagoras' Theorem, the length of the line is ( 3 1 ) 2 + 1 2 = 9 1 + 1 = 9 1 + 9 = 9 1 0 = 3 1 0 .
Then a + b = 1 0 + 3 = 1 3
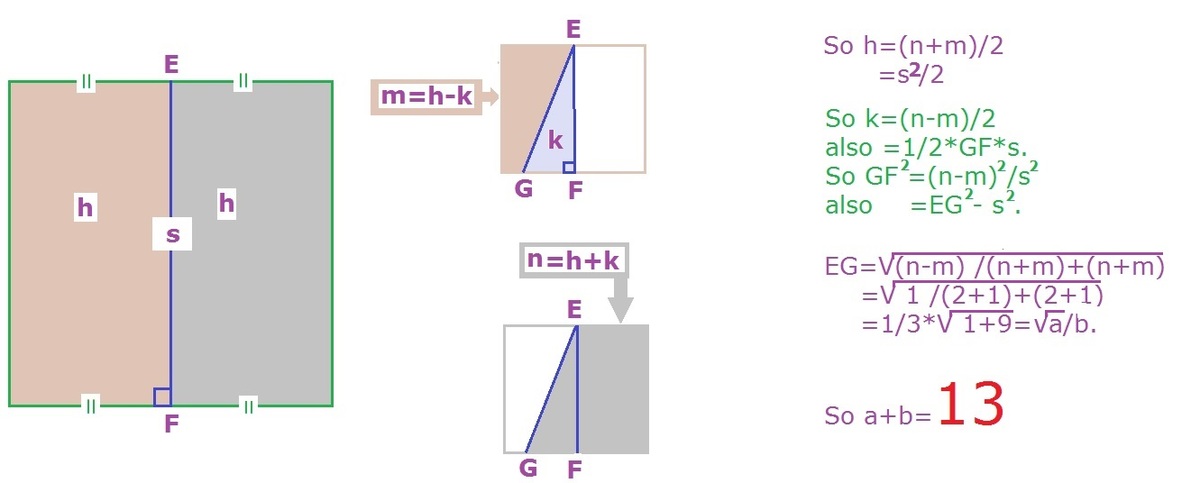
WLOG we first divide the square side 1, into half by joining midpoints of the a pair of opposite sides
say MN
⊥
to side containing N.
If we add 1/6 th of the area to the right partition, and subtract from the left, we get,
1/2+1/6=2/3 on the right and 1/2-1/6=1/3 on the left , the ratio we require.
Let P on the left of N on the same side of the square containing N, such that PN=1/3.
So the area to the left of MP is 1/3 and that to the right is 2/3 and Area of rt. triangle MPN=1/6.
Since MN=1, and PN=1/3,
H
y
.
M
P
=
1
2
+
(
1
/
3
)
2
=
1
0
/
3
=
a
/
b
.
.
a+b=13.
Let the shorter length of the other intersecting side by x . Then the area of the smaller part A s = 2 x + 2 1 × 1 = 4 2 x + 1 and that of the bigger part A B = 2 1 − x + 2 1 × 1 = 4 3 − 2 x . It is given that:
A s A B 2 x + 1 3 − 2 x 3 − 2 x 6 x ⟹ x = 1 2 = 2 = 4 x + 2 = 1 = 6 1
The length of the intercept:
l = ( 2 1 − x ) 2 + 1 2 = ( 2 1 − 6 1 ) 2 + 1 = 3 1 0
⟹ a + b = 1 0 + 3 = 1 3