Do you feel something missing!
A ball with the initial velocity u = 3 i + 4 j collides with the smooth wall and rebounds with the final velocity v = 2 i − 3 j . Find the coefficient of restitution for the collision.
Your answer can be represented as e = b a , where a and b are coprime numbers.
Enter your answer as a + b .
Try more here (Level 5 challenges)
Or try this set ...
This is a part of my set Aniket's Mechanics Challenges . (All level questions)
The answer is 50.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Oh ya! By your method the solution will become quite small. Actually I did the long way! I considered a unit vector n ^ = c o s θ i ^ + s i n θ j ^ representing the normal along the line of impact between the body and the wall. I then equated the magnitudes of the components of u and v perpendicular to n ^ as velocity of the body shall change only along the line of impact. From this, I got the value of t a n θ . Now the ratio u . n ^ v . n ^ gives you the value of e
Bhaiyya this is mains or advanced level? I just encountered this problem in my mains practice paper.
Log in to reply
We can say it mains level from the length of sol and the level of q
It is a bit long!
Let n represent the unit vector along the normal to wall, u the initial velocity vector and v the final velocity vector.
Since the velocity component along the wall remains same, we have
u X n = v X n
= > ( u - v ) X n = 0
= > n =k( i +7 j )
To find - v . n u . n = 3 1 1 9
Very nice explanation
Same way...well explained
Same method
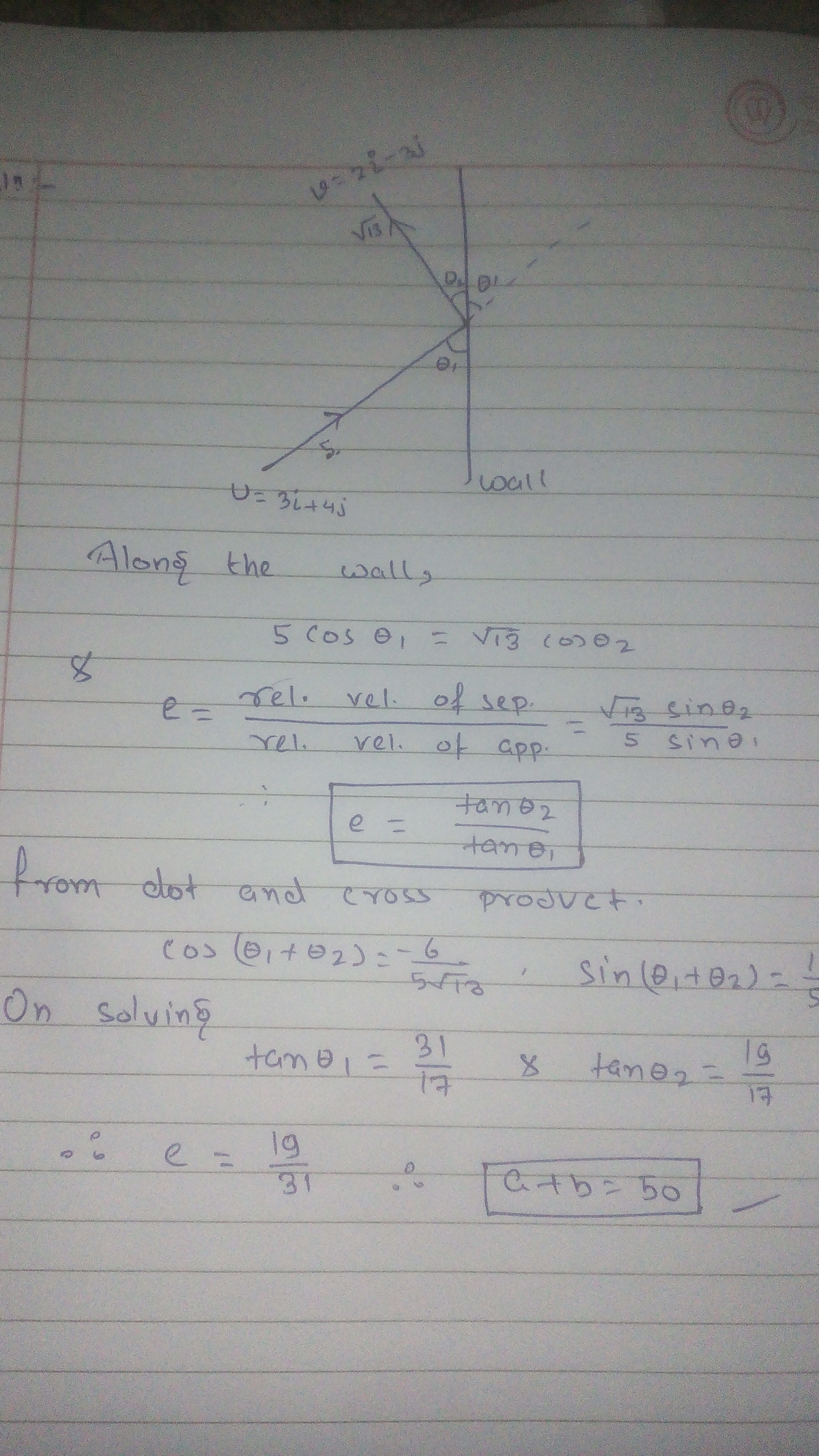
First find the vector for change in velocity. This gives you the direction of impact. Now find the components of initial and final velocity about this direction by taking dot product. Their ratio gives you e.