Dynamic Geometry: P39
 The diagram shows a cyan circular sector with radius
1
. Its angle varies between
0
°
and
1
8
0
°
. The pink circle is the largest circle we can inscribed inside the circular sector. When the ratio of the
x
coordinate to the
y
coordinate of the pink circle's center (green) is equal to
7
2
4
, the distance between the green point and the origin (red point) can be expressed as
b
a
where
a
and
b
are coprime positive integers. Find
2
a
−
5
b
.
The diagram shows a cyan circular sector with radius
1
. Its angle varies between
0
°
and
1
8
0
°
. The pink circle is the largest circle we can inscribed inside the circular sector. When the ratio of the
x
coordinate to the
y
coordinate of the pink circle's center (green) is equal to
7
2
4
, the distance between the green point and the origin (red point) can be expressed as
b
a
where
a
and
b
are coprime positive integers. Find
2
a
−
5
b
.
The answer is 3.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Thank you for posting !
Talk about a "duh" moment! I feel I've taken an absolutely atrocious route to the solution...well done!
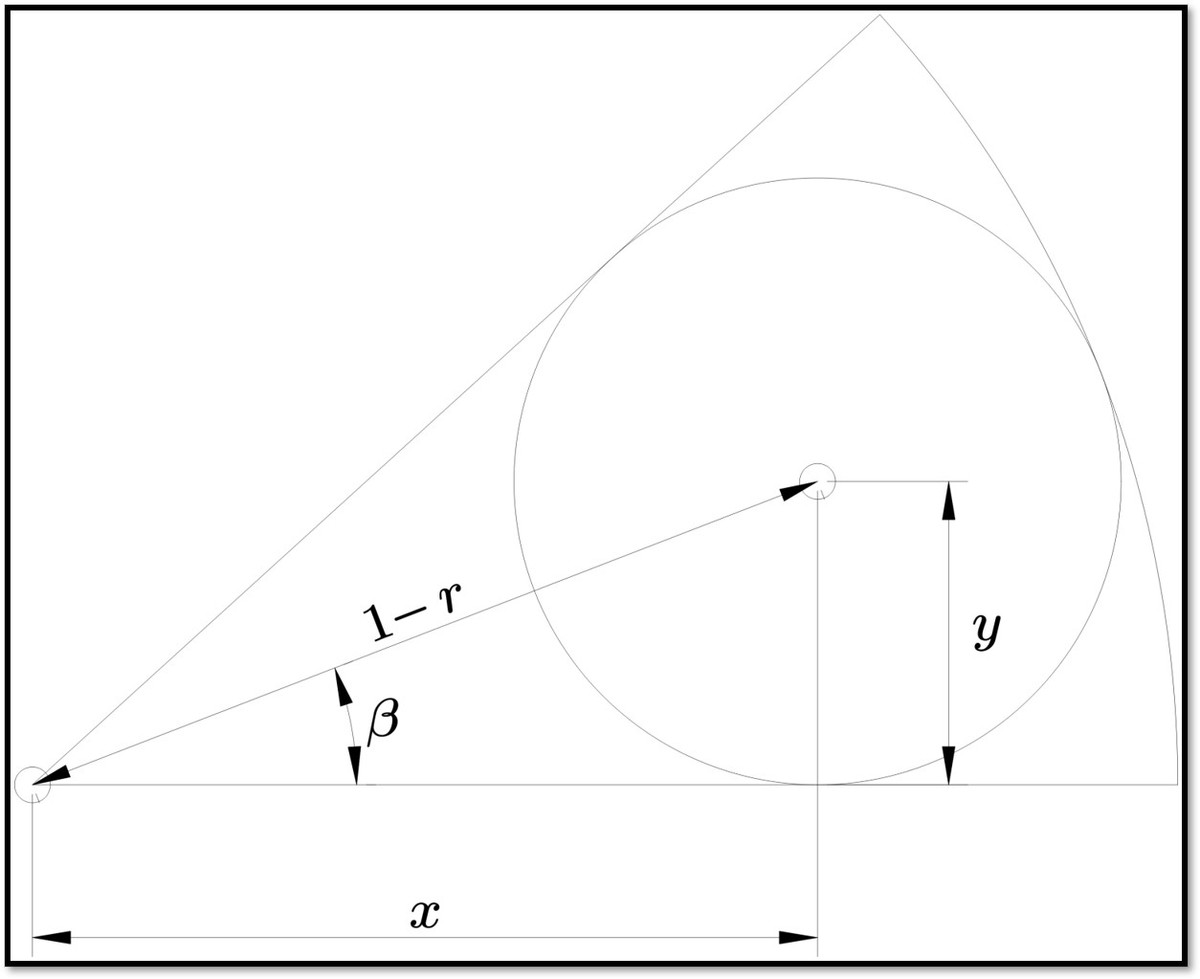
y d = ( 1 − r ) sin β Eq1 = x 2 + y 2 Eq2
We are given:
y x = 7 2 4 Eq3
We can deduce from the geometry and the given coordinate ratio locating the center of the circle:
y x sin β = r Eq4 = 7 2 4 r Eq5 = ( 7 2 4 ) 2 + 1 1 Eq6
Let:
φ = ( 7 2 4 ) 2 + 1 Eq7
Next , substitute Eq4, Eq5 → Eq2 , then Eq7 → Eq2 and let the result be Eq2’ :
d = ( 7 2 4 ) 2 r 2 + r 2 = r ( 7 2 4 ) 2 + 1 = r φ Eq2’
Substitute Eq7 → Eq6 → Eq1 and followed by Eq4 → Eq1 and let the result be Eq1’ :
r = ( 1 − r ) φ 1
⇒
r = 1 + φ 1 Eq8
Finally, substitute Eq8 → Eq2’
d = φ + 1 φ = 3 2 2 5 = b a
Thus;
a − 5 b = 5 − 2 = 3
In right-triangle O D P , O D 2 + P D 2 ( 7 2 4 r ) 2 + r 2 4 9 5 7 6 r 2 + r 2 ⟹ 5 7 6 r 2 + 9 8 r − 4 9 = O P 2 = ( 1 − r ) 2 = 1 − 2 r + r 2 = 0 Solving the above quadratic, we have, r = 3 2 7 ⟹ ∣ O P ∣ = 1 − r = 3 2 2 5 .
Therefore, a = 2 5 , b = 3 2 ⟹ 2 a − 5 b = 5 − 2 = 3