Dynamic Geometry: P93
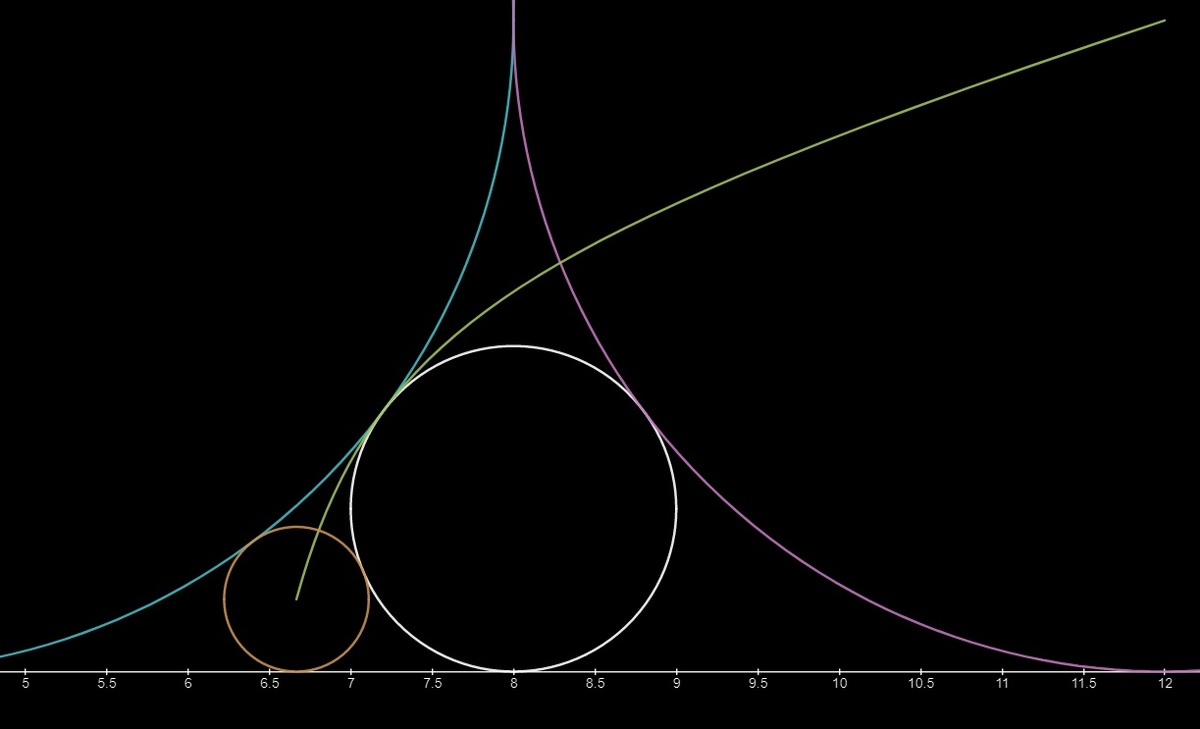
 The diagram shows a cyan circle with radius
4
and a green circle with radius
1
tangent to each other and tangent to a black horizontal line. The yellow circle moves freely so it is tangent to both circles at any moment. Its center bounces between two vertical segments (red and purple). At both segments, the yellow circle is tangent to the black horizontal line. The center of the yellow circle traces a
locus
(blue curve). The area bounded by both vertical segments, the horizontal line and the blue curve can be expressed as:
The diagram shows a cyan circle with radius
4
and a green circle with radius
1
tangent to each other and tangent to a black horizontal line. The yellow circle moves freely so it is tangent to both circles at any moment. Its center bounces between two vertical segments (red and purple). At both segments, the yellow circle is tangent to the black horizontal line. The center of the yellow circle traces a
locus
(blue curve). The area bounded by both vertical segments, the horizontal line and the blue curve can be expressed as:
q p − ln ( q )
where p and q are coprime positive integers. Find p + q .
The answer is 527.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Im proud of this problem. Great solution.
 The center (x,y) and radius
r
of the moving circle, is governed by these two equations
(
x
−
4
)
2
+
(
y
−
4
)
2
=
(
4
+
r
)
2
and
(
x
−
8
)
2
+
(
y
−
1
)
2
=
(
1
+
r
)
2
.
The center (x,y) and radius
r
of the moving circle, is governed by these two equations
(
x
−
4
)
2
+
(
y
−
4
)
2
=
(
4
+
r
)
2
and
(
x
−
8
)
2
+
(
y
−
1
)
2
=
(
1
+
r
)
2
.
y solves to 1 4 4 − 2 4 x − 7 x 2 + 2 4 x + 1 4 4 = 2 4 7 x − 2 ( x − 6 ) 3 + 4 3
∫ 3 2 0 1 2 f ( x ) d x = 2 7 5 0 0 − ln 2 7
Let the x -axis be the straight line tangent to both cyan and green circles. And the y -axis be in the middle of the center O of the cyan circle and the center Q of the green circle, and an arbitrary point on the locus, the center of the yellow circle, be P ( x , y ) while its radius is r .
Then by cosine rule ,
P Q 2 ( r + 1 ) 2 ⟹ O P ⋅ cos ∠ P O Q = O P 2 + O Q 2 − 2 ⋅ O P ⋅ O Q ⋅ cos ∠ P O Q = ( r + 4 ) 2 + 5 2 − 1 0 ⋅ O P cos ∠ P O Q = 1 0 ( r + 4 ) 2 + 5 2 − ( r + 1 ) 2 = 5 3 r + 2 0
Note that O P ⋅ cos ∠ P O Q = O N is the projection of O P on O Q . Also note that the gradient of O N is − tan 4 3 and the coordinates of N ( x N , y N ) are x N = 5 4 ⋅ O N − 2 = 2 5 1 2 r + 3 0 and y N = 4 − 5 3 ⋅ O N = 2 5 4 0 − 9 r .
By Pythagorean theorem ,
P N 2 ⟹ P N ⟹ tan ϕ sec 2 ϕ ⟹ sec ϕ x N y N = O P 2 − O N 2 = ( r + 4 ) 2 − ( 5 3 r + 2 0 ) 2 = 2 5 1 6 r 2 + 8 0 r = 5 4 r 2 + 5 r = 2 tan ϕ = 5 2 r 2 + 5 r = tan 2 ϕ + 1 = 2 5 4 r 2 + 2 0 r + 2 5 = ( 5 2 r + 5 ) 2 = 5 2 r + 5 = 2 5 1 2 r + 3 0 = 5 6 ⋅ 5 2 r + 5 = 5 6 sec ϕ = 2 5 4 0 − 9 r = 2 5 4 0 − 1 0 9 ⋅ 5 2 r + 5 + 5 0 4 5 = 2 5 − 1 0 9 sec ϕ
The coordinates of P ( x , y ) :
⎩ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎧ x = x N + 5 3 ⋅ P N = 5 6 sec ϕ + 5 6 tan ϕ y = y N + 5 4 ⋅ P N = 2 5 − 1 0 9 sec ϕ + 5 8 tan ϕ ⎩ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎧ 3 x + 4 y 8 x − 6 y = 1 0 + 1 0 tan ϕ = − 1 5 + 1 5 sec ϕ ⟹ tan ϕ = 1 0 3 x + 4 y − 1 0 ⟹ sec ϕ = 1 5 8 x − 6 y + 1 5 1 + tan 2 ϕ 1 + ( 1 0 3 x + 4 y − 1 0 ) 2 1 + 1 0 0 9 x 2 + 2 4 x y + 1 6 y 2 − 6 0 x − 8 0 y + 1 0 0 ⟹ 7 x 2 − 2 4 x y + 6 0 x − 3 6 ⟹ y = sec 2 ϕ = ( 1 5 8 x − 6 y − 1 5 ) 2 = 2 2 5 6 4 x 2 − 9 6 x y + 3 6 y 2 + 2 4 0 x − 1 8 0 y + 2 2 5 = 0 = 2 4 7 x + 2 5 − 2 x 3
The locus is part of a hyperbola. Note y of the locus is r of the yellow circle, The smallest radius (red vertical line) is given by r min 1 = 1 1 + 4 1 = 2 3 ⟹ r min = 9 4 . From 2 4 7 x + 2 5 − 2 x 3 = 9 4 ⟹ x min = 3 2 . The largest radius (purple vertical line) r max = 4 , when the yellow circle is congruent with the cyan circle; and the x max = 6 . The area under the locus is
A = ∫ 3 2 6 y d x = ∫ 3 2 6 2 4 7 x + 2 5 − 2 x 3 d x = 4 8 7 x 2 + 2 5 x − 2 3 ln x ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ 3 2 6 = 2 7 5 0 0 − ln 2 7
Therefore p + q = 5 0 0 + 2 7 = 5 2 7 .