This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Let D C = x
Now,notice,
△ A D C ∼ △ B A C
Therefore,
B C A C = A C D C
⇒ 8 + x 4 3 = 4 3 x
⇒ 4 8 = x 2 + 8 x
Solving the equation.we get,
x = -12 , 4
Since length of side cannot be negative, So,
DC = 4
Now, in △ A D C
A D 2 = A C 2 − D C 2
⇒ A D 2 = 4 8 − 1 6 = 3 2
⇒ A D = 3 2 = 4 2
From Leg Corollary to the Right Angle Altitude Theorem, (8+DC)/AB=AB/BD. AB= sqrt(8+y)^2-(4sqrt3)^2 from Phythagorean Theorem. Hence, DC= 4 From Hypotenuse Corollary to the Right Traingle Altitide Theorem, BD/AD=AD/DC. Therefore, 8/AD=AD/4 AD= 4sqrt2
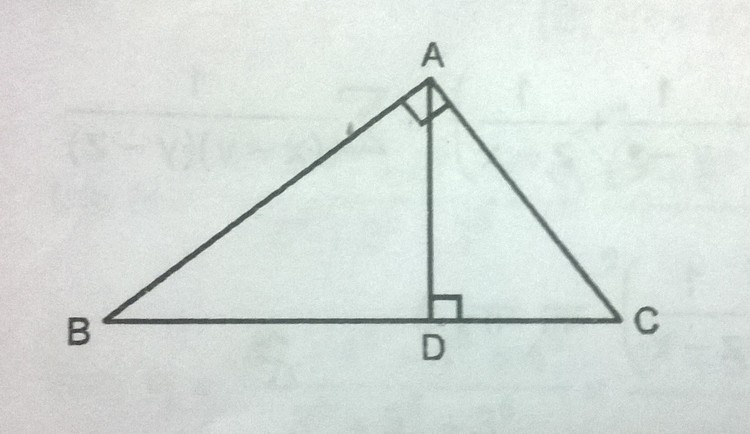
tan θ = 8 h = h D C ⟹ 8 h = h D C ⟹ h 2 = 8 D C
Apply pythagorean theorem on triangle A D C , h 2 = ( 4 3 ) 2 − ( D C ) 2 = 4 8 − ( D C ) 2
h 2 = h 2
4 8 − ( D C ) 2 = 8 D C
( D C ) 2 + 8 D C − 4 8 = 0
( D C + 1 2 ) ( D C − 4 ) = 0
D C = − 1 2 or D C = 4 (disregard the negative value)
Therefore,
h 2 = 8 D C = 8 ( 4 ) = 3 2
h = 3 2 = 1 6 ( 2 ) = 4 2