Electrochemistry-Level 2
Chemistry
Level
2
 For
assumption and details
, please refer my note from my set
Chemistry Challenge
.
For
assumption and details
, please refer my note from my set
Chemistry Challenge
.
The answer is 1.21.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
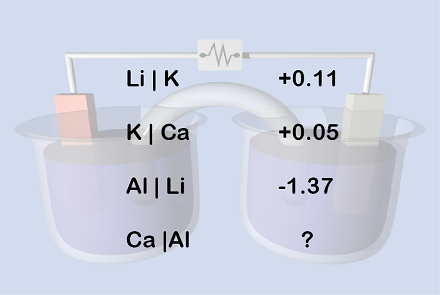
Well obviously we are supposed to find the reduction potential of C a ∣ ∣ A l . Now, E A l ∣ ∣ K = E A l ∣ ∣ L i + E L i ∣ ∣ K , which gives , E A l ∣ ∣ K = − 1 . 3 7 + 0 . 1 1 = − 1 . 2 6 Then, E K ∣ ∣ A l = − ( E A l ∣ ∣ K ) = 1 . 2 6 and, E C a ∣ ∣ K = − ( E K ∣ ∣ C a ) = − 0 . 0 5 Finally we get, E C a ∣ ∣ A l = E C a ∣ ∣ K + E K ∣ ∣ A l = − 0 . 0 5 + 1 . 2 6 = 1 . 2 1
PS: Even im not sure if my solution is ryt so comment if my approach is wrong ;)