Elliptic Mania!
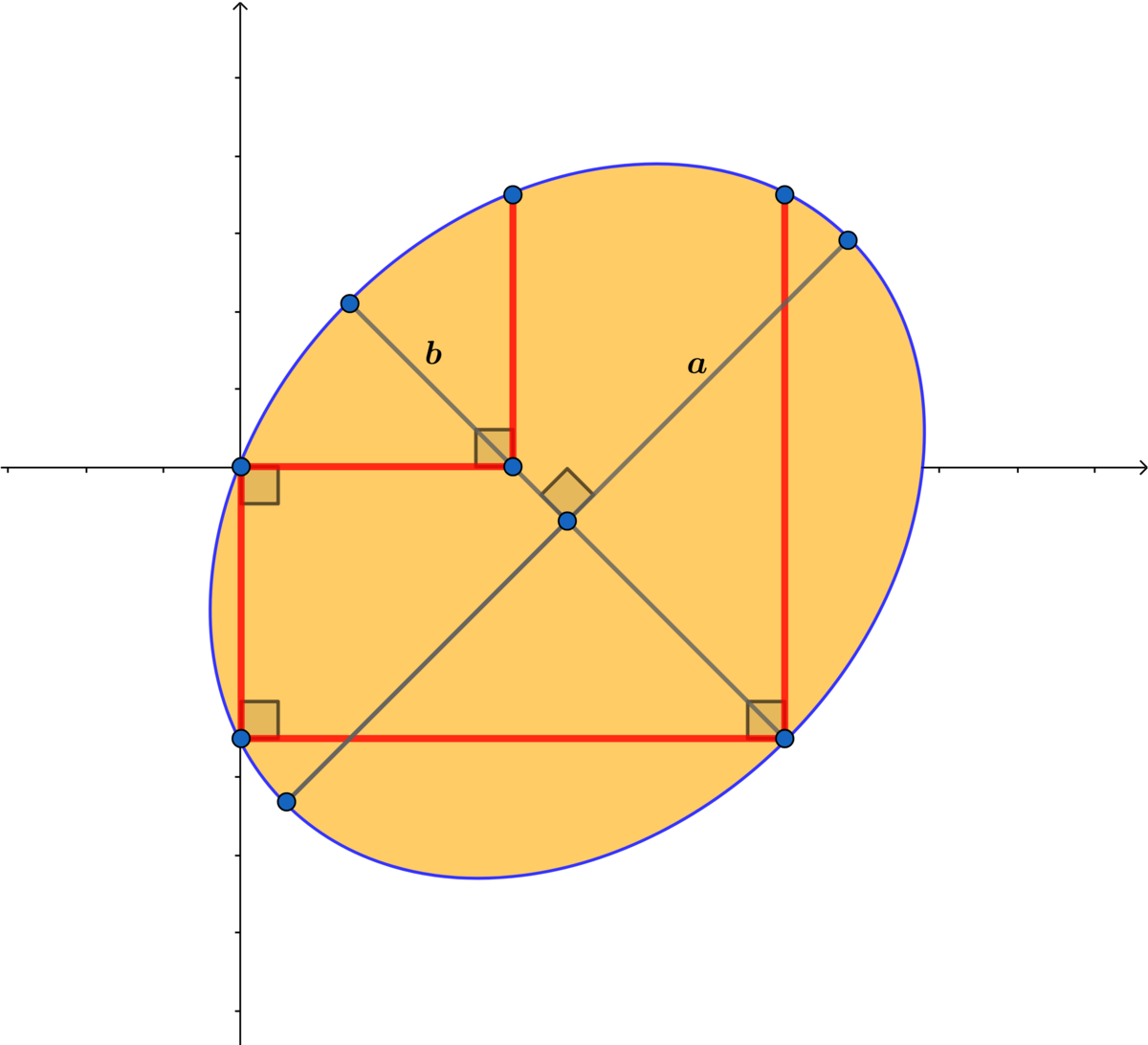
In the ellipse shown, let a and b be the lengths of the semi-major and semi-minor axes, respectively.
What is the value of j for which a 2 + b 2 = 1 9 2 0 0 ?
The answer is 75.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
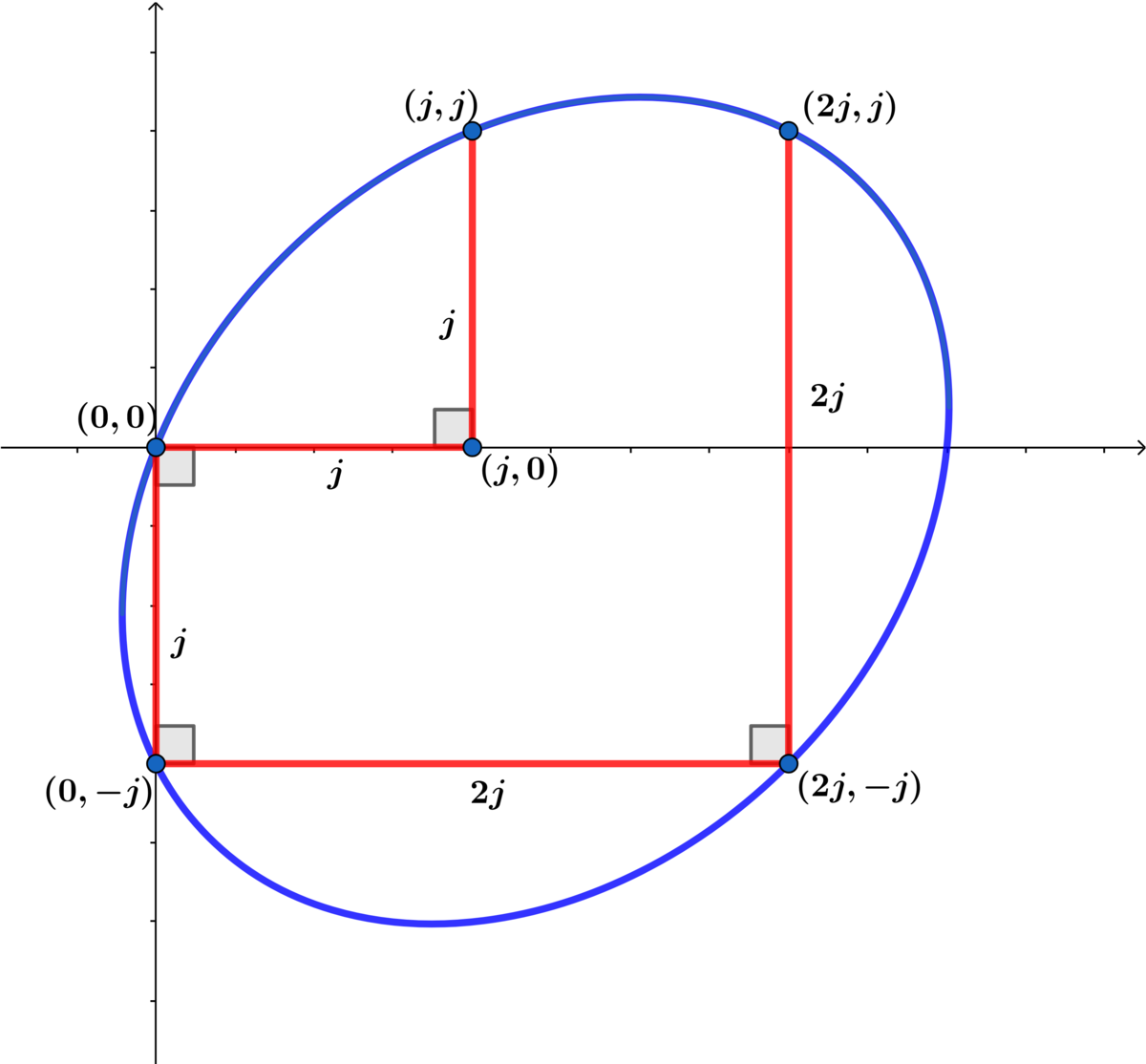
If the area A of the ellipse above
(1) ( j , j ) : j 2 a + j 2 b + j 2 c + j d + j e = 0
(2) ( 0 , − j ) : j c − e = 0 ⟹ c = j e
(3) 2 j , j ) : 4 j 2 a + 2 j 2 b + j 2 c + 2 j d + j e = 0
(4) ( 2 j , − j ) : 4 j 2 a − 2 j 2 b + j 2 c + 2 j d − j e = 0
Subtracting (4) from (3) ⟹ 2 j b + e = 0 ⟹ b = − 2 j e
Replacing c = j e and b = − 2 j e into equations (1) and (3) ⟹
2 j a + 2 d = − 3 e
4 j a + 2 d = − e
⟹ d = − 2 5 e and a = j e
⟹ j 1 x 2 − 2 j 1 x y + j 1 y 2 − 2 5 x + y = 0
⟹ 2 x 2 − x y + 2 y 2 − 5 j x + 2 j y = 0
Let
x = x ′ cos ( θ ) − y ′ sin ( θ )
y = x ′ sin ( θ ) + y ′ cos ( θ )
2 ( x ′ 2 cos 2 ( θ ) − sin ( 2 θ ) x ′ y ′ + y ′ 2 sin 2 ( θ ) ) − ( ( 2 x ′ 2 − y ′ 2 ) sin ( 2 θ ) + cos ( 2 θ ) x ′ y ′ ) + 2 ( x ′ 2 cos 2 ( θ ) ) + sin ( 2 θ ) x ′ y ′ + y ′ 2 sin 2 ( θ ) ) − 5 j ( x ′ cos ( θ ) − y ′ sin ( θ ) ) + 2 j ( x ′ sin ( θ ) + y ′ cos ( θ ) ) = 0
Setting x ′ y ′ terms to zero ⟹ cos ( 2 θ ) = 0 ⟹ θ = 4 π
⟹
x = 2 1 ( x ′ − y ′ )
y = 2 1 ( x ′ + y ′ )
⟹ 3 x ′ 2 + 5 y ′ 2 − 3 2 j x ′ + 7 2 j y ′ = 0 ⟹ 3 ( x ′ − 2 j ) 2 + 5 ( y ′ + 5 2 7 j ) 2 = 5 3 2 j 2
⟹ ( 1 5 3 2 j 2 ) ( x ′ − 2 j ) 2 + ( 2 5 3 2 j 2 ) ( y ′ + 5 2 7 j ) 2
⟹ a = 1 5 4 2 j and b = 5 4 2 j ⟹ a 2 + b 2 = 7 5 2 5 6 j 2 = 1 9 2 0 0 ⟹ j = 7 5 .
Find the intersections of line y=x-b with ellipse as (0,-b) and {(2ba^2/(a^2+b^2)), b(a^2-b^2)/(a^2+b^2)}. The length of the chord between these two points is set equal to integer 2j.
Setting a^2+b^2=19200 and defining the i=(√2)b as the new constant , we get the following, Diophantine equation;
i^3=38400(i-j).
Solution is i=120 and j=75.
Answer=75.
The whole diagram is symmetrical in a 4 5 ° line, so we can rotate the whole ellipse and place the bottom right point at ( 0 , 0 ) for a vertical ellipse with a center of ( b , 0 ) , as shown below.
The j and 2 j sides are hypotenuses of isosceles right triangles, and so we can deduce that the other points on the ellipse are ( 2 j , ± 2 j ) and ( 2 3 2 j , ± 2 2 j ) .
Since the equation of a vertical ellipse with center ( b , 0 ) is b 2 ( x − b ) 2 + a 2 y 2 = 1 , we have b 2 ( 2 j − b ) 2 + a 2 ( ± 2 j ) 2 = 1 and b 2 ( 2 3 2 j − b ) 2 + a 2 ( ± 2 2 j ) 2 = 1 .
These two equations and the given equation a 2 + b 2 = 1 9 2 0 0 solve to a = ± 2 0 3 0 , b = 6 0 2 , and j = 7 5 for j > 0 .