Elliptic Mania.
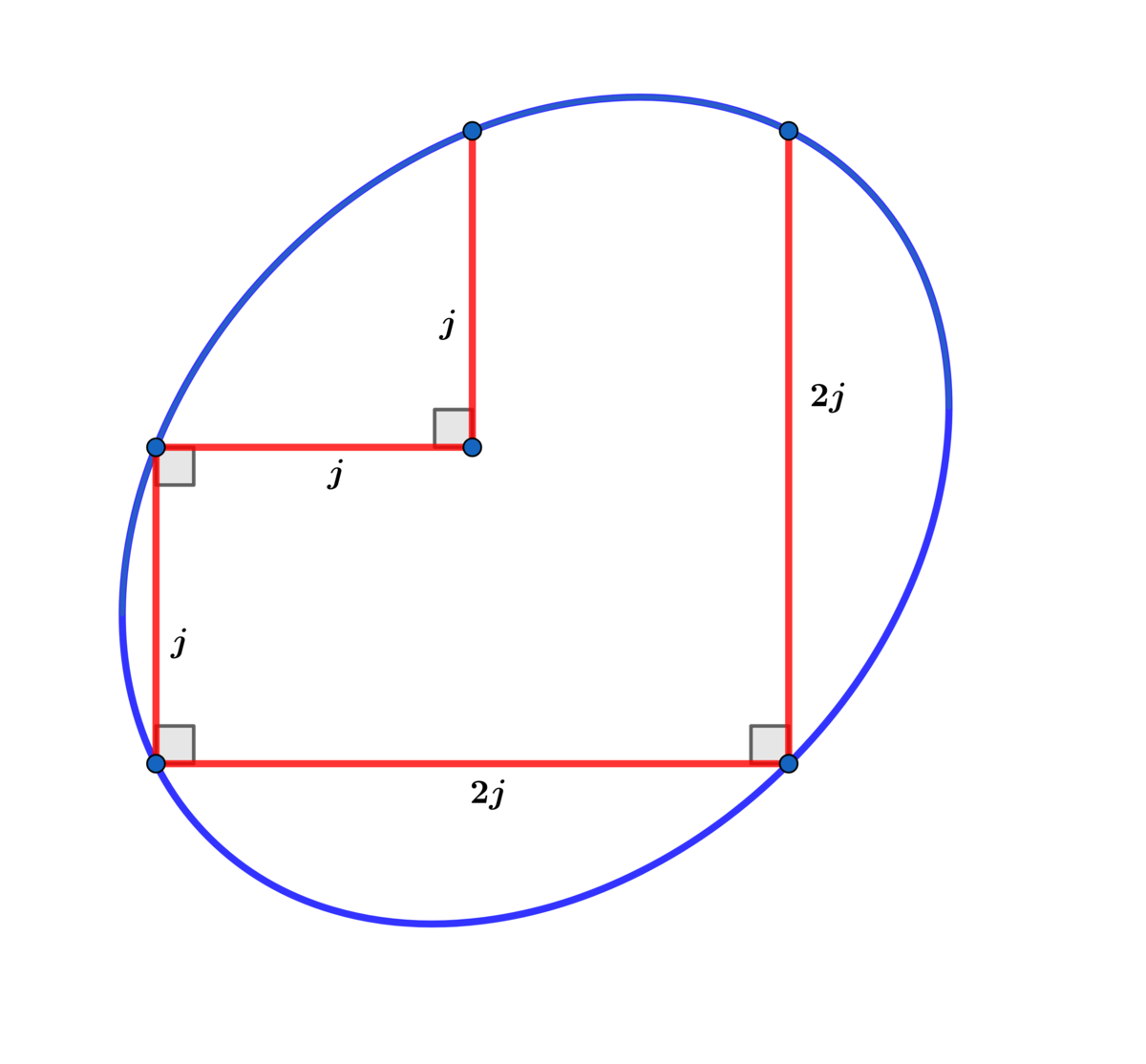
Find the value of j for which the area of the ellipse above is A e = 1 5 2 3 4 7 0 4 π .
The answer is 7.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
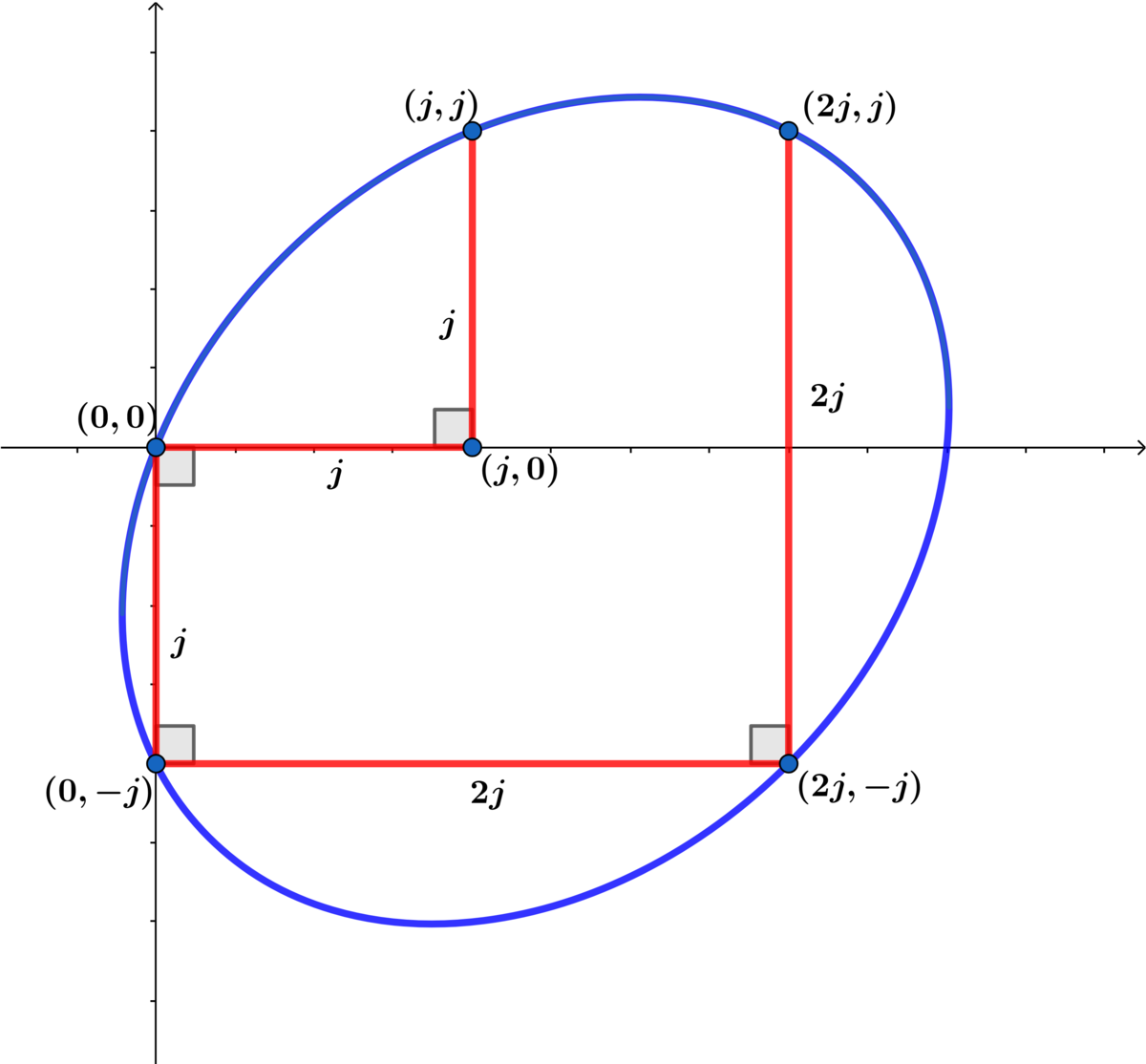
For the area A of the ellipse above
(1) ( j , j ) : j 2 a + j 2 b + j 2 c + j d + j e = 0
(2) ( 0 , − j ) : j c − e = 0 ⟹ c = j e
(3) 2 j , j ) : 4 j 2 a + 2 j 2 b + j 2 c + 2 j d + j e = 0
(4) ( 2 j , − j ) : 4 j 2 a − 2 j 2 b + j 2 c + 2 j d − j e = 0
Subtracting (4) from (3) ⟹ 2 j b + e = 0 ⟹ b = − 2 j e
Replacing c = j e and b = − 2 j e into equations (1) and (3) ⟹
2 j a + 2 d = − 3 e
4 j a + 2 d = − e
⟹ d = − 2 5 e and a = j e
⟹ j 1 x 2 − 2 j 1 x y + j 1 y 2 − 2 5 x + y = 0
⟹ 2 x 2 − x y + 2 y 2 − 5 j x + 2 j y = 0
Solving for y we obtain:
y = 4 1 ( x − 2 j ± 1 5 1 3 8 4 j 2 − ( 1 5 x − 1 8 j ) 2 )
y = 4 1 ( x − 2 j + 1 5 1 3 8 4 j 2 − ( 1 5 x − 1 8 j ) 2 ) for the portion of the ellipse above the line y = 4 x − 2 j .
Setting 3 8 4 j 2 − ( 1 5 x − 1 8 j ) 2 = 0 ⟹ x = 1 5 2 ( 9 ± 4 6 ) j are the points of intersection of the ellipse and the line y = 4 x − 2 j .
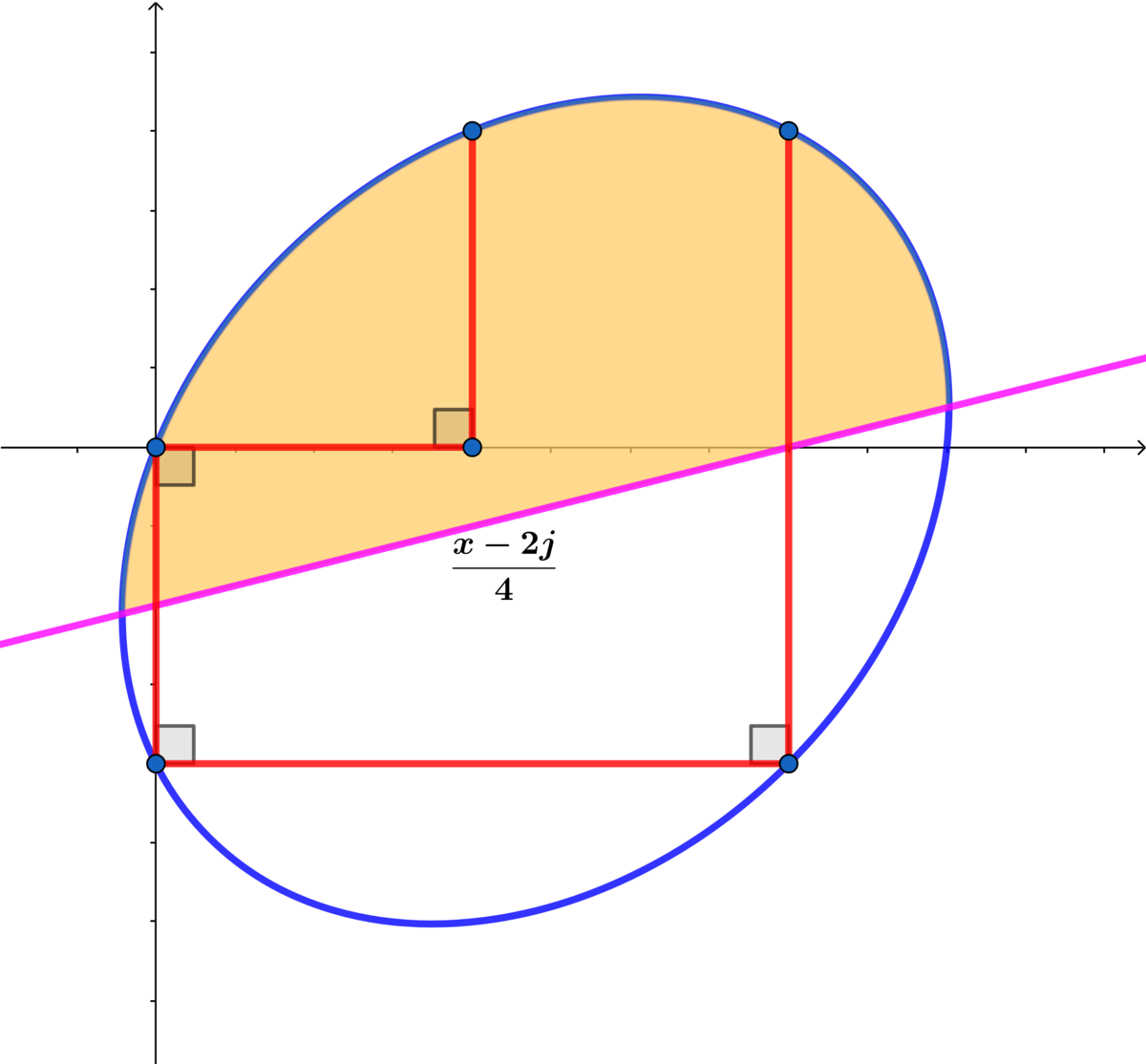
Letting a = 1 5 2 ( 9 − 4 6 ) j and b = 1 5 2 ( 9 + 4 6 ) j the area of the ellipse is A e = 4 1 5 2 ∫ a b 3 8 4 j 2 − ( 1 5 x − 1 8 j ) 2 )
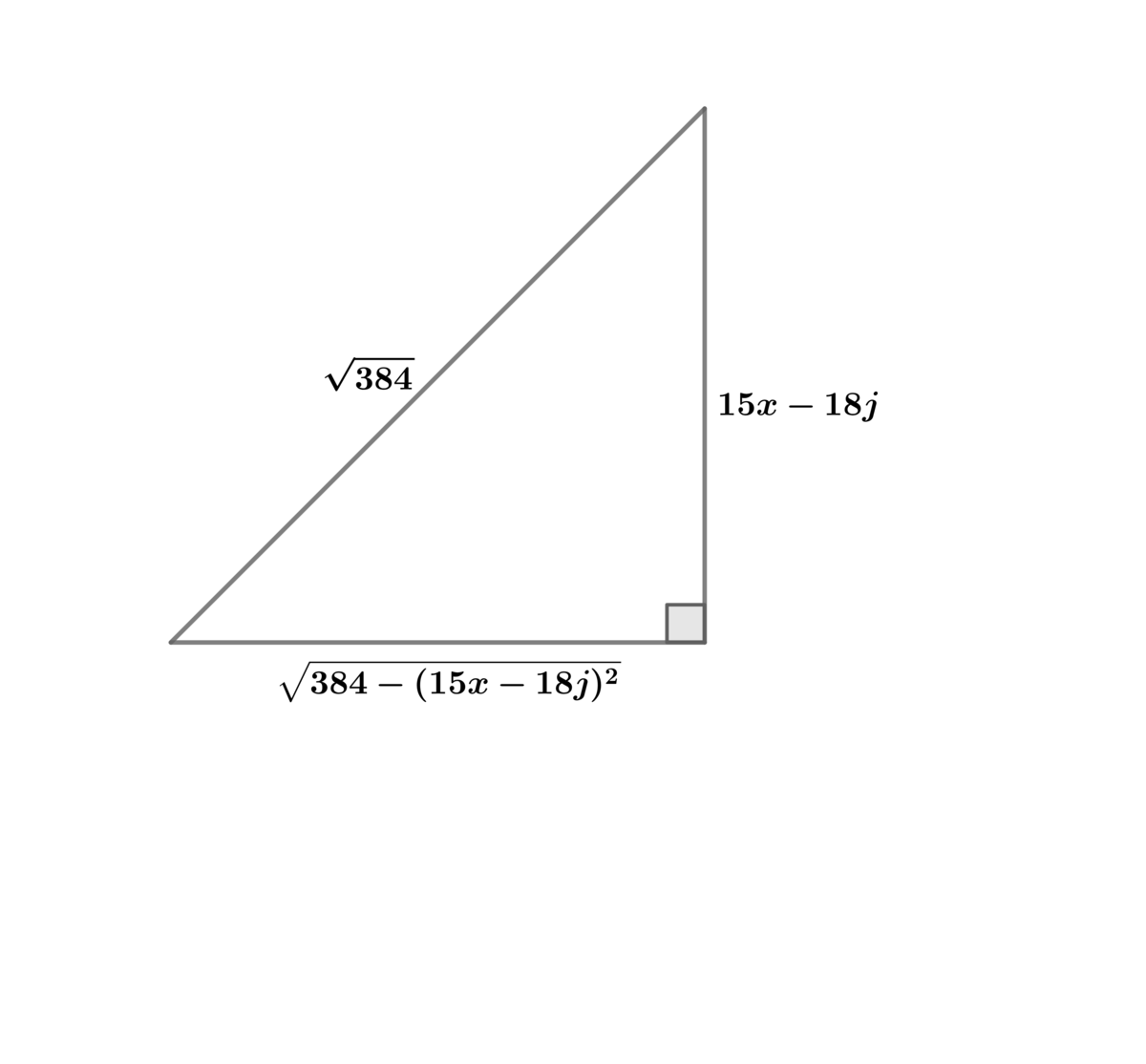
Letting 1 5 x − 1 8 j = 3 8 4 j sin ( θ ) ⟹ d x = 1 5 3 8 4 j cos ( θ ) ⟹
I ( θ ) = 1 5 3 8 4 j 2 ∫ cos 2 ( θ ) d θ = 3 0 3 8 4 j 2 ∫ ( 1 + cos ( 2 θ ) ) d θ = 1 5 1 9 2 j 2 ( θ + sin ( θ ) cos ( θ ) )
⟹ A e = 1 5 2 3 9 6 j 2 ( arcsin ( 3 8 4 1 5 x − 1 8 j ) + 3 8 4 ( 1 5 x − 1 8 j ) 3 8 4 j 2 − ( 1 5 x − 1 8 j ) 2 ) ) ∣ a b = 1 5 2 3 9 6 π j 2 = 1 5 2 3 4 7 0 4 π ⟹ j = 7
Great problems! I use a different approach. First I do like you (but use matrices) to obtain the implicit equation of the ellipse (avoiding letting it pass through origo though). Then I use a general formula, which is rather easily proven, that the area of an ellipse A x 2 + B x y + C y 2 + D x + E x = 1 equals ( 4 A C − B 2 ) 3 / 2 2 π ( A C − B 2 + A E 2 + C D 2 − B D E ) .
In this case (with origin at the point inside the elllipse) it yielded 7 5 3 2 1 5 π k 2 = 1 5 1 5 4 7 0 4 π ⟹ k = 7 )