Equivalent resistance
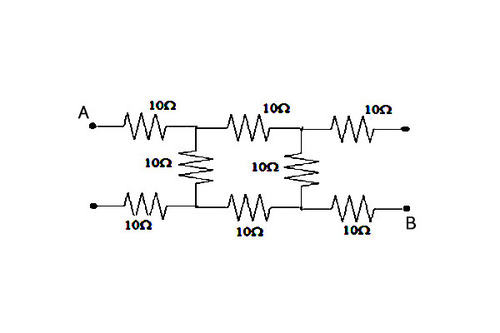 What will be the equivalent resistance between
and
in the above diagram?
What will be the equivalent resistance between
and
in the above diagram?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Since the reference is taken at points A and B , no current flow through the top-right resistor and bottom-right resistor. The two resistors need not to be considered in the calculations. The remaining circuit is ( R = 1 0 Ω ):
R e q = R + ( R + R ) / / ( R + R ) + R
= 1 0 + 2 0 / / 2 0 + 1 0 = 1 0 + 1 0 + 1 0 = 3 0 Ω