Erratic Systematic Wormhole Variance
Chaos has emerged in a
1
×
1
field; The fabric of space will never be healed.
The limits of light have been replaced: All matter is teleported to a random place!
What is the
variance
of the displacement of the points?
Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
This rule of space should not be disregarded: You might teleport to exactly where you started.
You might want to try Finding the expected value first.
I thank Deeparaj Bhat and Bobbym None for helping me solve this.
The answer is 0.061488775.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Say the particle's initial position is (a,b) and the particle's final position is (x,y).
The displacement of the particle would be
( x − a ) 2 + ( y − b ) 2
Since we want to find the variance, we need to first find the average over all possible a, b, x, y:
x = No. of cases ∑ All cases = 1 1 ∫ 0 1 1 1 ∫ 0 1 1 1 ∫ 0 1 1 1 ∫ 0 1 ( x − a ) 2 + ( y − b ) 2 d y d x d a d b = 0 . 5 2 1 4 0 5 4 3 3 3 0 9
Note that numerical methods were used to calculate the integrals.
Now to find the variance:
s 2 = No. of cases ∑ ( All cases − x ) 2 = ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ( ( x − a ) 2 + ( y − b ) 2 − x ) 2 d y d x d a d b = 0 . 0 6 1 4 6 9 7 0 7 4 4 9
Interesting fact: If the question asks for the root mean square, the answer would be exactly 1 / 3 . Also this problem actually has a closed form
What numerical method would you recommend for doing the integral?
Log in to reply
I'm rather bad at coding so I just used Desmos to integrate, which uses Riemann sums to approximate.
Log in to reply
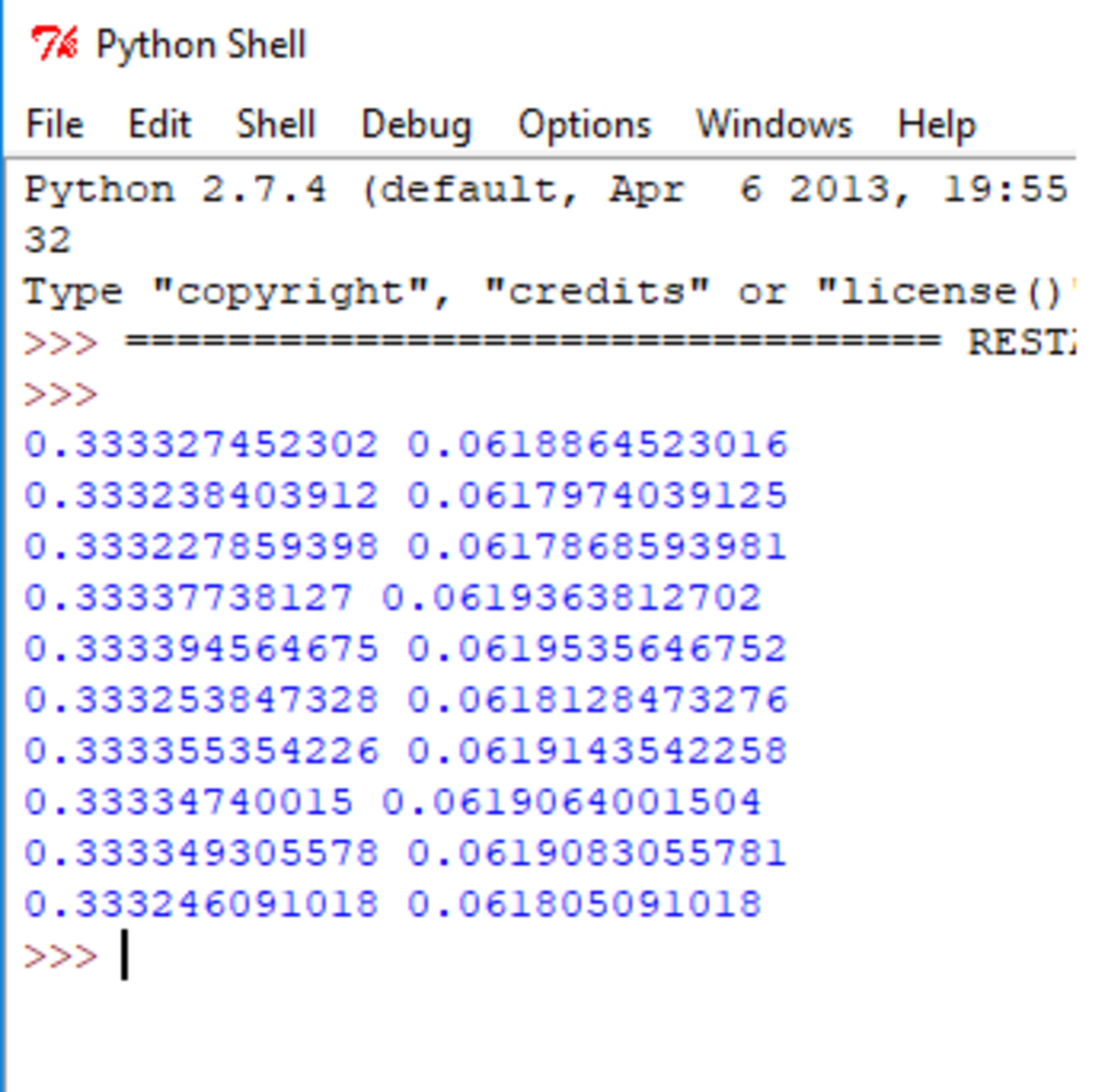
I see. I solved this problem with Monte Carlo methods.
Monte Carlo code
import math
import random
u = 0.521 # from previous problem
for z in range(0,10): # run experiment 10 times
N = 10**7 # 10 million points - Monte Carlo
Dsqav = 0.0
for j in range(0,N):
x1 = random.uniform(0.0,1.0)
y1 = random.uniform(0.0,1.0)
x2 = random.uniform(0.0,1.0)
y2 = random.uniform(0.0,1.0)
Dsq = (x1-x2)**2.0 + (y1-y2)**2.0
Dsqav = Dsqav + Dsq
EDsq = Dsqav / N
print EDsq,(EDsq - u**2.0) # Var = EDsq - u**2.0
It is known that the average distance,
x = ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ( x − y ) 2 + ( z − w ) 2 d x d y d z d w = 1 5 1 ( 2 + 2 + 5 ln ( 1 + 2 ) )
The variance, is
σ 2 = ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ( ( x − y ) 2 + ( z − w ) 2 − x ) 2 d x d y d z d w = ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ( x − y ) 2 + ( z − w ) 2 − 2 x ( x − y ) 2 + ( z − w ) 2 + x 2 d x d y d z d w = ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ( x − y ) 2 + ( z − w ) 2 d x d y d z d w − 2 x ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ( x − y ) 2 + ( z − w ) 2 d x d y d z d w + x 2 = 3 1 − 2 x ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 ( x − y ) 2 + ( z − w ) 2 d x d y d z d w + x 2 = 3 1 − 2 x 2 + x 2 = 3 1 − x 2 = 3 1 − 2 2 5 1 ( 2 + 2 + 5 ln ( 1 + 2 ) ) 2 = 2 2 5 7 5 − ( 2 + 2 + 5 ln ( 1 + 2 ) ) 2 ≈ 0 . 0 6 1 4 6 9 7 0 7