This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
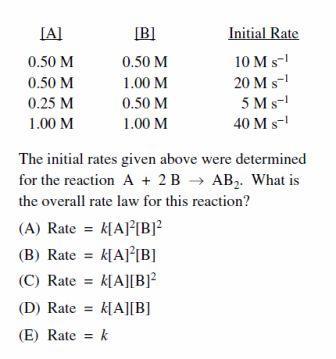
Let us divide the data into four cases C a s e I , I I , I I I , I V respectively. From our reference to C a s e I a n d I I on doubling the concentration of B the rate doubles so we can see that it is of order 1 w.r.t. B and on halving the concentration of A the rate too decreases to half. Again on doubling the concentration of both A and B the rate quadruples .Hence our rate law is R a t e = k [ A ] 1 [ B ] 1