I don' think questions should be given names.
If x + x 1 = 3 , find the value of x 1 8 + x 1 2 + x 6 + 1 .
The answer is 0.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
7 solutions
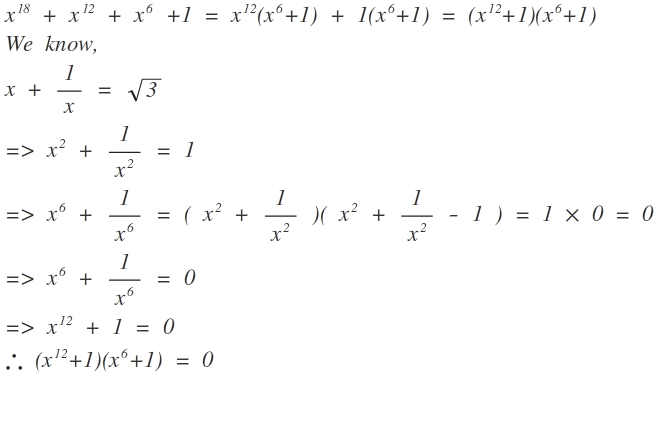
Moderator note:
Yes, well done.
Nice method you got there. Here's another way to look at it:
Take the required expression as S . From the given equation, we can see that x = 0 , 1 . So, we can regroup our required expression and use finite GP sum formula.
S = x 1 8 + x 1 2 + x 6 + 1 = r = 0 ∑ 3 ( x 6 ) r = x 6 − 1 ( x 6 ) 4 − 1
Back to our given equation, cube both sides and with a bit of manipulation, you'll get that,
x 3 + x 3 1 = 0 ⟹ x 6 + 1 = 0 ⟹ x 6 = ( − 1 )
Use this value of x 6 to evaluate S as follows:
S = ( − 1 ) − 1 ( − 1 ) 4 − 1 = − 2 1 − 1 = 0
I believe there is an error in this method. Specifically, you rely on this line for your solution:
x 6 + x 6 1 = ( x 2 + x 2 1 ) ( x 2 + x 2 1 − 1 )
A quick glance shows that the leading term for the result of the right is actually x 4 , not x 6 . Working it through completely, you will find that:
( x 2 + x 2 1 ) ( x 2 + x 2 1 − 1 ) = x 4 + x 4 1 − ( x 2 + x 2 1 ) + 2 = x 4 + x 4 1 + 1
And
x 6 + x 6 1 = x 4 + x 4 1 + 1
But you do have a good start. Try this out:
x + x 1 = x x 2 + 1 = 3 = > x 2 ( x 2 + 1 ) 2 = 3 = x 2 x 4 + 2 x 2 + 1 = x 2 + 2 + x 2 1 = 3 x 2 + x 2 1 = 1
Next we need x 4 + x 4 1 :
1 2 = ( x 2 + x 2 1 ) 2 = ( x 2 x 4 + 1 ) 2 = x 4 + 2 + x 4 1 = 1 = > x 4 + x 4 1 = − 1
Now:
x 2 ( x 4 + x 4 1 ) = ( − 1 ) ( x 2 ) = > x 6 + x 2 1 = ( − 1 ) ( x 2 ) = > x 6 = ( − 1 ) ( x 2 + x 2 1 ) = > x 6 = ( − 1 ) ( 1 ) = − 1
Now to plug into our equation: x 1 8 + x 1 2 + x 6 + 1 = ( x 6 ) 3 + ( x 6 ) 2 + x 6 + 1 = ( − 1 ) 3 + ( − 1 ) 2 + ( − 1 ) + 1 = − 1 + 1 − 1 + 1 = 0 ∴ x 1 8 + x 1 2 + x 6 + 1 = 0
Given, x + x 1 = 3
Solving for x , we get that x = 2 3 ± 2 i
Multiplying through out by i ,
⇒ i x = 2 i 3 ± 2 − 1
⇒ i x = ω o r − ω
⇒ x = i ω o r − i ω
Substituting the values of x in x 1 8 + x 1 2 + x 6 + 1 , we get,
− 1 + 1 − 1 + 1 = 0
Note: ω i s t h e c u b e r o o t o f u n i t y and i = − 1 .
Moderator note:
Good work!
@challenge master, Didn't get your point....Would you please explain? How could x be cube root of unity?
Log in to reply
Sorry, typo. I misinterpreted the question. Well done!
Uhmm, @Calvin Lin Sir, There is a typo in the Challenge Master Note
x + x 1 = 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 = 0 x = 2 3 ± i 2 1 We can take any value ⇒ x = cos ( 3 0 ) + i sin ( 3 0 )
Now We will apply De Moivre's Theorem to evaluate
x 1 8 + x 1 2 + x 6 + 1 = ( cos ( 3 0 ) + i sin ( 3 0 ) ) 1 8 + ( cos ( 3 0 ) + i sin ( 3 0 ) ) 1 2 + ( cos ( 3 0 ) + i sin ( 3 0 ) ) 6 + 1 Applying theorem we get = cos ( 1 8 × 3 0 ) + i sin ( 1 8 × 3 0 ) + cos ( 1 2 × 3 0 ) + i sin ( 1 2 × 3 0 ) + cos ( 6 × 3 0 ) + i sin ( 6 × 3 0 ) + 1 = − 1 + 0 + 1 + 0 − 1 + 0 + 1 0
Moderator note:
You can have a slight improvement. Hint: all the powers of x are a multiple of 6 .
x 1 8 + x 1 2 + x 6 + 1 = ( x 1 2 + 1 ) ( x 6 + 1 ) = x 9 ( x 6 + x 6 1 ) ( x 3 + x 3 1 ) Then, given: x + x 1 = 3 x x 2 + 1 = 3 x 3 ( x 2 + 1 ) 3 = 3 3 x 3 x 6 + 3 x 4 + 3 x 2 + 1 = 3 3 x 3 + 3 x + x 3 + x 3 1 = 3 3 x 3 + x 3 1 = 0 ⇒ x 1 8 + x 1 2 + x 6 + 1 = 0
Moderator note:
It's easier to start with cubing the equation x + x 1 = 3 . Most people opted for the complex number approach, and you didn't. Nicely done!
x + x 1 = 3 . ∴ x = 0 . ( x + x 1 ) 3 = x 3 + x 3 1 + 3 ∗ 1 ∗ ( x + x 1 ) . ⟹ x 3 + x 3 1 + 3 ∗ 1 ∗ 3 = 3 3 . ∴ x 3 + x 3 1 = 0 . ∴ x 6 = − 1 , x 1 2 = 1 , x 1 8 = − 1 . ∴ x 1 8 + x 1 2 + x 6 + 1 = − 1 + 1 − 1 + 1 = 0
We are given : x + x 1 = 3 . . . ( 1 ) Required expression : x 1 8 + x 1 2 + x 6 + 1 = ( x 6 + 1 ) ( x 1 2 + 1 ) = x 3 ( x 3 + x 3 1 ) ( x 1 2 + 1 ) . . . ( 2 ) Cubing both the sides of (1), ( x + x 1 ) 3 = ( 3 ) 3 ⇒ x 3 + x 3 1 + 3 ( x ) ( x 1 ) ( x + x 1 ) = 3 3 Using (1), ⇒ x 3 + x 3 1 = 0 . . . ( 3 ) Therefore, using (3), the value of required expression (2) = x 3 ( x 3 + x 3 1 ) ( x 1 2 + 1 ) = 0
:D
x + x 1 = 3
x 2 + 1 = 3 x
( x 2 + 1 ) 2 = 3 x 2
x 4 + 2 x 2 + 1 = 3 x 2
x 4 − x 2 + 1 = 0
Let z = x 2
z 2 − z + 1 = 0
z = ( − 1 ) 3 1
x = ( − 1 ) 6 1
There are other solutions for z and x , however this one does give a real valued solution as needed. Plug in the value of x just found to get 0