Everybody, let's roll!
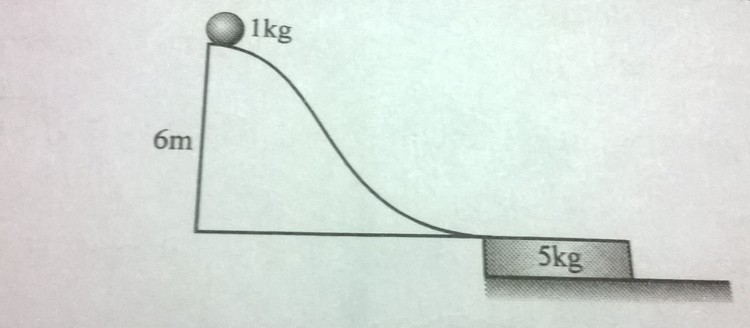 A small disc of mass 1kg slides down a smooth hill of height 6 m without initial velocity and gets onto a plank of mass 5 kg lying on a smooth horizontal plane at the base of hill as shown in the figure. Due to friction between the disc and the plank , disc slows down and after some time moves as one piece with the plank . Find out the magnitude of total work (in joule) performed by the friction forces in this process.
A small disc of mass 1kg slides down a smooth hill of height 6 m without initial velocity and gets onto a plank of mass 5 kg lying on a smooth horizontal plane at the base of hill as shown in the figure. Due to friction between the disc and the plank , disc slows down and after some time moves as one piece with the plank . Find out the magnitude of total work (in joule) performed by the friction forces in this process.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Using Work -Energy theorem ,
W f = K f − K i where
W f =Final work done.
K f =Final kinetic energy.
K i =Initial kinetic energy.
W f = 2 1 ( m + M ) V 2 − 2 1 m v o 2
= 2 − 1 m + M m M v o 2
= − m + M m M g h , since v o 2 = 2 g h
Substituting m=1 kg , M=5 kg , h = 6 and g = 1 0 ,we get W f = − 5 0 J