Exponential Integration
Above shows an indefinite integral for some non-constant function and arbitrary constant .
If the minimum value of is equal to , then find the value of .
Join the Brilliant Classes and enjoy the excellence.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
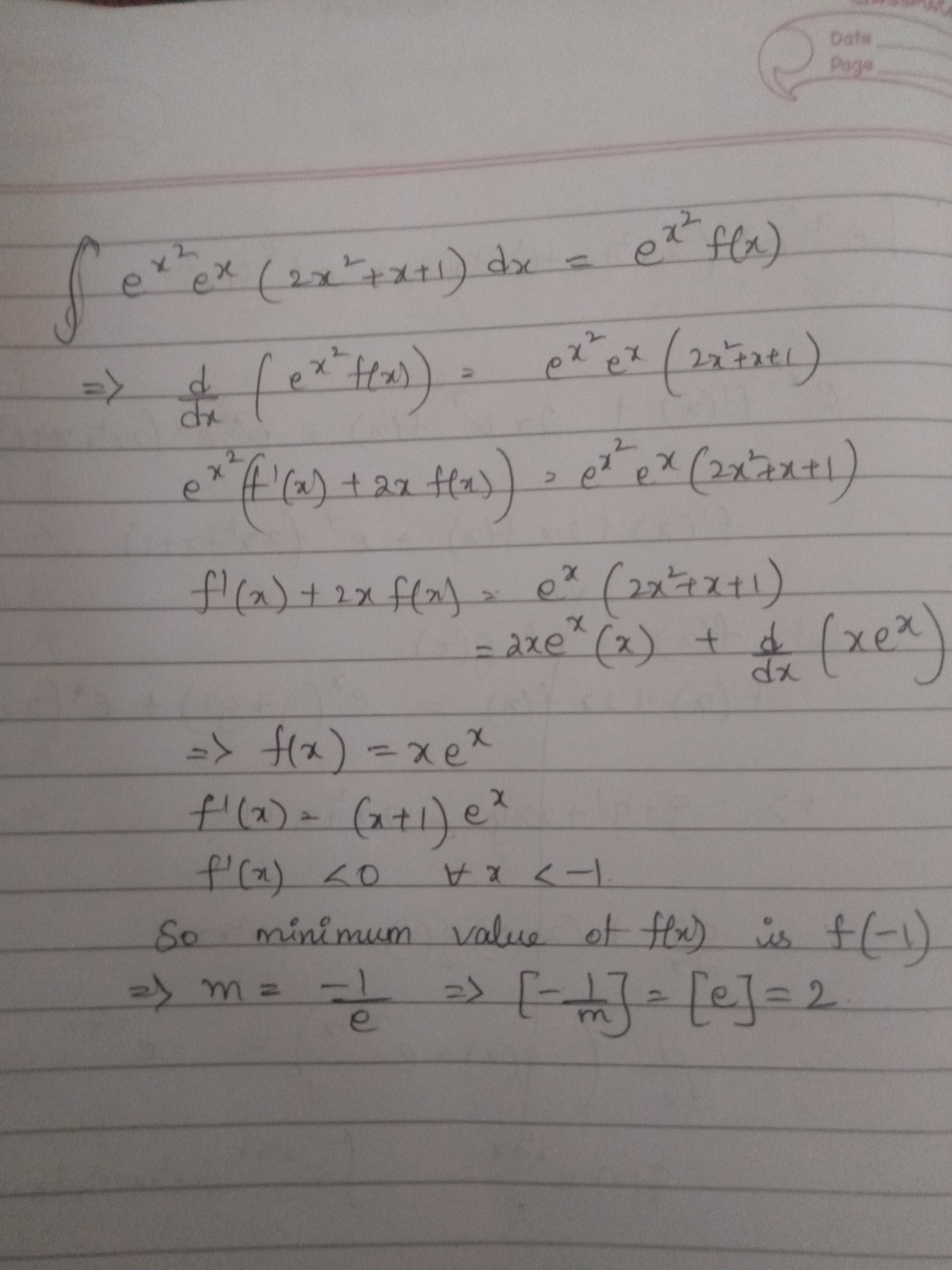
∫ e x 2 + x ( x ( 2 x + 1 ) + 1 )
using ∫ e f ( x ) ( g ( x ) × f ′ ( x ) + g ′ ( x ) ) = g ( x ) . e f ( x ) + c
the integral is x . e x 2 + x + c
ϕ ( x ) = x e x
on differentiating and equating to zero we get
x = − 1 and the double derivative gives a positive value at x = − 1
hence the minimum value is m = e − 1
and [ m − 1 ] = [ e ]
[ e ] = [ 2 . 7 ] = 2