Find net work done
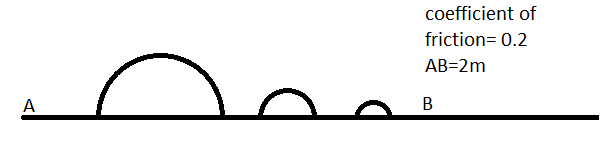 A particle of mass 'm' is moved from point A to B along the track as as shown in the figure
A particle of mass 'm' is moved from point A to B along the track as as shown in the figure
Find the minimum work that has to be done to cause that
DETAILS AND ASSUMPTION
.
coefficient of friction =
Height of first hemisphere =
Height of 2nd hemisphere=
Height of 3rd hemisphere=
The answer is 4.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Net work done = change in potential energy + change in kinetic energy + work done by friction
In case of minimum work done , it means that the particle is not transferred any more energy than needed or that it is slowly moved with practically 0 kinetic energy or speed at all instants
hence change in kinetic energy = 0-0 =0
Now since A and B are at the same height
change in gravitational potential energy = 0
Now work done by friction = net work done
Now consider any arbitary route with slope angle at any particular point as
θ ′ T h e n t h e f r i c t i o n a l f o r c e a c t i n g o n i t i s μ m g c o s θ a n d t h e w o r k d o n e i n a n e l e m e n t a r y d i s p l a c e m e n t ′ d l ′ a l o n g t r a c k i s μ m g c o s θ d l = μ m g ( d l c o s θ ) = μ m g d x i n t e g r a t i n g w e g e t μ m g ( x 2 − x 1 ) w h i c h i n t h i s c a s e i s μ m g A B = ( 0 . 2 ) ( 1 0 ) ( 2 ) = 4 J
Its amazing how work done by friction is independent of path length and only depends on displacement ,, just like the force on any current carrying conductor in magnetic field is same as long it joins the same points no matter how it does