Fractional Integral
∫ 0 1 { n x } 1 / 3 d x
The integral above has a closed form when n is a positive integer, find this closed form.
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
Notation : { ⋅ } denotes the fractional part function .
The answer is 0.75.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
∫
0
1
{
n
x
}
3
1
d
x
=
∫
0
1
/
n
{
n
x
}
3
1
d
x
+
⋯
+
∫
(
n
−
1
)
/
n
1
{
n
x
}
3
1
d
x
=
n
∫
0
1
/
n
(
n
x
)
3
1
d
x
(periodic property)
=
n
3
4
∫
0
1
/
n
x
3
1
d
x
=
n
3
4
[
4
3
x
3
4
]
∣
0
1
/
n
=
4
3
=
0
.
7
5
Thats great ! Some other solutions are also present but this one is the most fundamental.
Log in to reply
I have a graph in my mind first and I present the solution in this way :)
In the domain [0,1],
the value of fractional part of 'nx' is 'nx' itself..
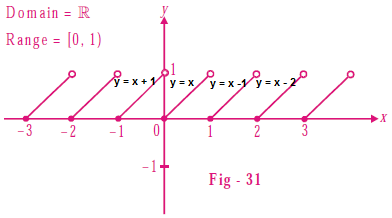
Therefore it is simply an integration of ( n x ) 3 1 from 0 to 1.
Thank you for sharing your approach!
I would like to point out that
{
n
x
}
is equal to
n
x
in the domain
[
0
,
1
)
only if
n
≤
1
. It is not true for
n
>
1
.
For example, consider
{
3
x
}
. It is equal to
3
x
in the interval
[
0
,
3
1
)
, it is
3
x
−
1
in the interval
[
3
1
,
3
2
)
, and
3
x
−
2
in the interval
[
3
2
,
1
)
.
Log in to reply
Put n x = y then,
I = n 1 ∫ 0 n { y } 3 1 d y = n 1 k = 0 ∑ n − 1 ∫ k k + 1 ( y − k ) 3 1 d y
Put y − k = u , I = n 1 k = 0 ∑ n − 1 ∫ 0 1 u 3 1 d y
I = 4 3 = 0 . 7 5