Frequency response 4
Consider the circuit on the image with a voltage source . What is the effective voltage across the capacitor as the frequency of my voltage source goes to infinity?
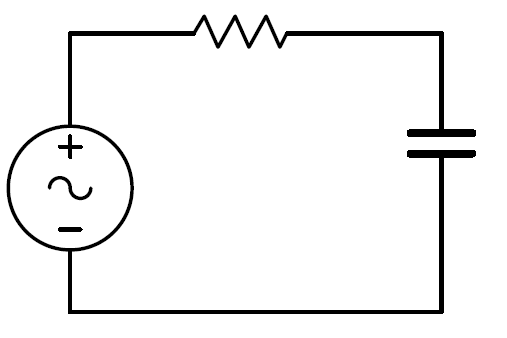
The answer is 0.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
The resistor with the capacitor are a voltage divider. Let's call Z c the capacitor's impedance and R the resistor's impedance, we can calculate the voltage across the capacitor as
V o = V i ⋅ ( R + Z c Z c )
We can calculate Z c in function of the frequency as Z c = 2 π f C − j with j = − 1 . It's easy to see that the capacitor's impedance will go to infinity as the frequency goes to zero, which means that
lim Z c → ∞ ( R + Z c Z c ) = R 0 = 0 so V o = 0