Square Inscribed Triangle
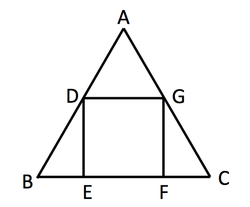 The area of Square
□
D
E
F
G
is
a
b
−
c
, which is inscribed into an equilateral
△
A
B
C
.
The area of Square
□
D
E
F
G
is
a
b
−
c
, which is inscribed into an equilateral
△
A
B
C
.
With a , b , c are all integers and b square free. And The area of the equilateral triangle △ A B C is 1 .
Evaluate b c − a to three decimal places.
The answer is 6.667.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
First, we find the length of the side of the △ . Since A B = A C = B C :
2 1 ( B C ) 2 sin 6 0 ∘ = 1 ( B C ) 2 ( 2 3 ) = 2 ( B C ) 2 = 3 2 1 4 B C = 3 4 1 2
Now, we let the side of the square be q , as shown in the diagram below:
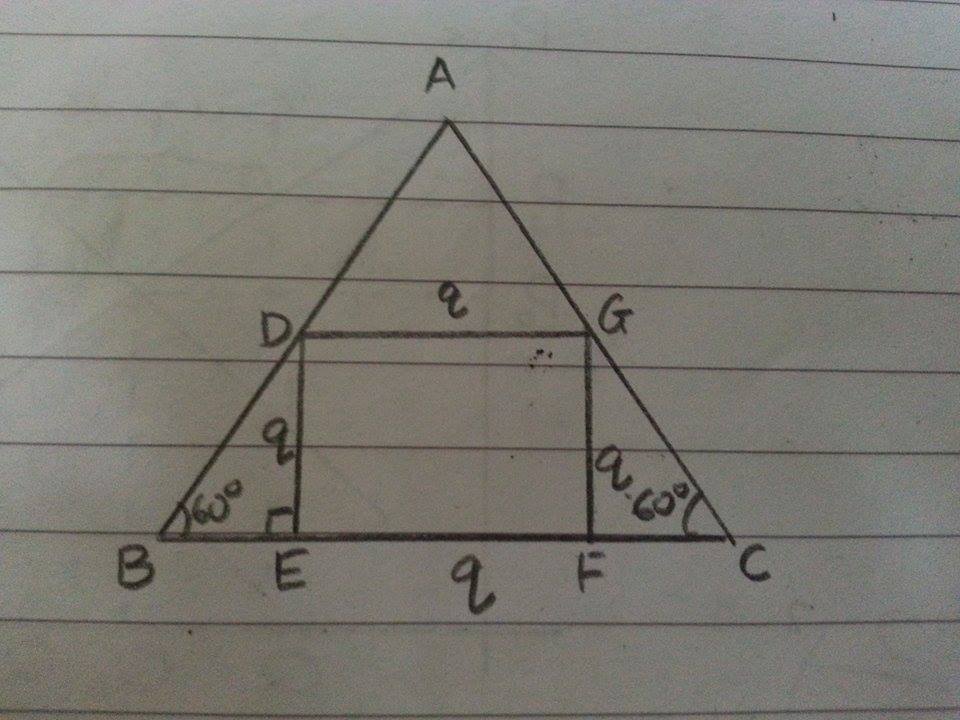
We can find B E = F C in terms of q :
tan 6 0 ∘ = B E D E 3 = B E q B E = 3 q
We know that:
B C = B E + E F + F C 3 4 1 2 = q + 2 3 q 3 2 q + 3 q = 3 4 1 2 q = 3 4 1 ( 2 + 3 ) 2 3 q = 2 + 3 2 ( 3 4 1 )
The area of the square is given as q 2 :
q 2 = ( 2 + 3 2 ( 3 4 1 ) ) 2 = 4 + 4 3 + 3 4 3 = 7 + 4 3 4 3 = ( 7 + 4 3 ) ( 7 − 4 3 ) 4 3 ( 7 − 4 3 ) = 4 9 − 1 6 ( 3 ) 2 8 3 − 1 6 ( 3 ) = 4 9 − 4 8 2 8 3 − 4 8 = 2 8 3 − 4 8
a b − c = 2 8 3 − 4 8 a = 2 8 , b = 3 , c = 4 8 b c − a = 3 4 8 − 2 8 = 3 2 0 = 6 . 6 6 7
Collection of shapes and spaces equate total the One
Call A, B are edges of square and equilateral triangles. [ A B C ] = 4 B 2 3 = 1 ⇒ B 2 = 3 4 A 3 2 + A = B A = 3 + 2 3 B A 2 = 7 + 4 3 3 B 2 = 2 8 3 − 4 8 b c − a = 3 2 0 = 6 . 6 6 7
cant understand.... make it easy
Log in to reply
Angle B is 60 and Angle DGB is 90. So we can use trigonometry to find BG In terms of side of the square. What we get will be equal to CF as EFC and DGB are congruent. BG+GF+CF = side of triangle ABC(which we can find from the area). So we will get side of the square and hence we can find the area,
Let the side length of the triangle A B = B C = C A = x and and that of the square D E = E F = F G = G D = h .
We can see that A G = G D = h and that:
G C sin 6 0 ∘ ( C A − A G ) sin 6 0 ∘ ( x − h ) sin 6 0 ∘ x sin 6 0 ∘ = G F = G F = h = ( 1 + sin 6 0 ∘ ) h
We note that the area of △ A B C is 2 1 x 2 sin 6 0 ∘ = 1 ⇒ x 2 sin 6 0 ∘ = 2 .
x sin 6 0 ∘ x 2 sin 2 6 0 ∘ 2 sin 6 0 ∘ 3 4 3 = ( 1 + sin 6 0 ∘ ) h = ( 1 + sin 6 0 ∘ ) 2 h 2 = ( 1 + 2 sin 6 0 ∘ + sin 2 6 0 ∘ ) h 2 = ( 1 + 3 + 4 3 ) h 2 = ( 7 + 4 3 ) h 2
We note that the area of the square is:
A = h 2 = 7 + 4 3 4 3 = 1 ( 4 3 ) ( 7 − 4 3 ) = 2 8 3 − 4 8
⇒ b c − a = 3 4 8 − 2 8 = 3 2 0 = 6 . 6 6 7