Geometric Probability
Let and be real numbers. Let denote probability that the absolute difference between and will is greater than their average. If the value of is in the form of for coprime positive integers and , find the value of .
The answer is 4.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Rewriting the probability P into a more useful form leads to ∣ a − b ∣ > 2 a + b This implies two equations: a − b a − b > 2 a + b < − 2 a + b Solving in terms of a leads to b < 3 a and b > 3 a . Utilizing geometric probability we can generalize this problem using the unit square as shown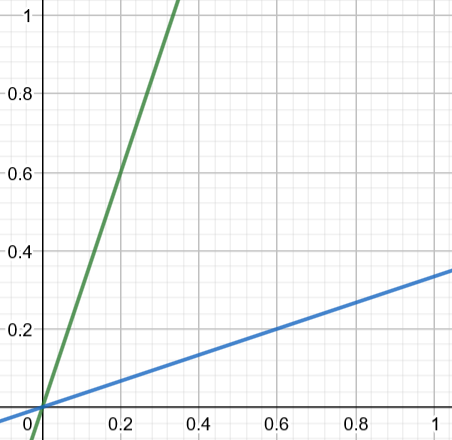 With
b
on the
y
-axis and
a
on the
x
-axis, the regions defined by the previous inequalities are the ones touching their respective axes. Thus, the area covered by the sum of the regions is just the sum of the areas of the two triangles both with lengths
1
and
3
1
. This implies that the total area covered by these equations is
2
(
1
)
(
3
1
)
+
2
(
1
)
(
3
1
)
=
3
1
. Thus, the probability of the absolute difference between
a
and
b
being larger than their average is
3
1
. Therefore, the answer is
x
+
y
=
1
+
3
=
4
With
b
on the
y
-axis and
a
on the
x
-axis, the regions defined by the previous inequalities are the ones touching their respective axes. Thus, the area covered by the sum of the regions is just the sum of the areas of the two triangles both with lengths
1
and
3
1
. This implies that the total area covered by these equations is
2
(
1
)
(
3
1
)
+
2
(
1
)
(
3
1
)
=
3
1
. Thus, the probability of the absolute difference between
a
and
b
being larger than their average is
3
1
. Therefore, the answer is
x
+
y
=
1
+
3
=
4