Geometry or calculus? II
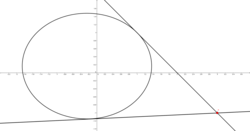 Given a ellipse with equation
2
x
2
+
3
y
2
+
x
−
y
−
5
=
0
and a point
P
(
3
,
−
1
)
, there are two lines passing through
P
that are also tangent to the ellipse. One line is represented by the equation
a
x
+
b
y
−
c
=
0
and the other one is
d
x
−
e
y
−
f
=
0
, where
a
,
b
,
c
,
d
,
e
,
f
>
0
,
g
cd
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
=
1
and
g
cd
(
d
,
e
,
f
)
=
1
. Find
a
+
b
+
c
d
+
e
+
f
−
2
.
Given a ellipse with equation
2
x
2
+
3
y
2
+
x
−
y
−
5
=
0
and a point
P
(
3
,
−
1
)
, there are two lines passing through
P
that are also tangent to the ellipse. One line is represented by the equation
a
x
+
b
y
−
c
=
0
and the other one is
d
x
−
e
y
−
f
=
0
, where
a
,
b
,
c
,
d
,
e
,
f
>
0
,
g
cd
(
a
,
b
,
c
)
=
1
and
g
cd
(
d
,
e
,
f
)
=
1
. Find
a
+
b
+
c
d
+
e
+
f
−
2
.
The answer is 104.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Factorisation is really tough part ...it takes much time
Log in to reply
You can make it a quadratic in y and solve for y to get the two factors.
Log in to reply
Ahh ... I missed That ... Thanks I will use it in future
I just did via general approach and it has taken 3 pages to get the answer :D...
L e t t h e e q u a t i o n ( s ) o f t h e l i n e ( s ) t a n g e n t t o 2 x 2 + 3 y 2 + x − y − 5 = 0 b e y = m x + b S i n c e y = m x + b p a s s e s t h r o u g h P ( 3 , − 1 ) , y = m ( x − 3 ) − 1 L e t A = x − 3 S u b s t i t u t e y = m A − 1 t o 2 x 2 + 3 y 2 + x − y − 5 = 0 , 2 x 2 + 3 ( m A − 1 ) 2 + x − m A + 1 − 5 = 0 2 x 2 + 3 ( m 2 A 2 − 2 m A + 1 ) + x − m A − 4 = 0 2 x 2 + 3 m 2 A 2 − 7 m A + x − 1 = 0 2 x 2 + 3 m 2 ( x 2 − 6 x + 9 ) − 7 m ( x − 3 ) + x − 1 = 0 2 x 2 + 3 m 2 x 2 − 1 8 m 2 x + 2 7 m 2 − 7 m x + 2 1 m + x − 1 = 0 x 2 ( 2 + 3 m 2 ) + x ( − 1 8 m 2 − 7 m + 1 ) + 2 7 m 2 + 2 1 m − 1 = 0 S i n c e t h e l i n e i s t a n g e n t t h e d i s c r i m i n a n t , D , i s e q u a l t o 0 D = ( − 1 8 m 2 − 7 m + 1 ) 2 − 4 ( 2 + 3 m 2 ) ( 2 7 m 2 + 2 1 m − 1 ) = ( 3 2 4 m 4 + 2 5 2 m 3 + 1 3 m 2 − 1 4 m + 1 ) − 4 ( 8 1 m 4 + 6 3 m 3 + 5 1 m 2 + 4 2 m − 2 ) = 1 3 m 2 − 2 0 4 m 2 − 1 4 m − 1 6 8 m + 1 + 8 = − 1 9 1 m 2 − 1 8 2 m + 9 = 0 − 1 9 1 m 2 − 1 8 2 m + 9 = 0 1 9 1 m 2 + 1 8 2 m − 9 = 0 m = 1 9 1 − 9 1 ± 8 2 8 1 + 1 7 1 9 m = 1 9 1 − 9 1 + 1 0 0 , 1 9 1 − 9 1 − 1 0 0 m = 1 9 1 9 , − 1 S i n c e y = m ( x − 3 ) − 1 , S u b s t i t u t i n g m = 1 9 1 9 , y = 1 9 1 9 x − 1 9 1 2 7 − 1 1 9 1 y = 9 x − 2 7 − 1 9 1 − 9 x + 1 9 1 y = − 2 1 8 9 x − 1 9 1 y − 2 1 8 = 0 T h e e q u a t i o n 9 x − 1 9 1 y − 2 1 8 = 0 i s i n t h e f o r m d x − e y − f = 0 w h e r e d > 0 , e > 0 , f > 0 , a n d g c d ( d , e , f ) = 1 d = 9 , e = 1 9 1 , f = 2 1 8 S u b s t i t u t i n g m = − 1 , y = − x + 3 − 1 y = − x + 2 x + y − 2 = 0 T h e e q u a t i o n x + y − 2 = 0 i s i n t h e f o r m a x + b y − c = 0 w h e r e a > 0 , b > 0 , c > 0 , a n d g c d ( a , b , c ) = 1 a = 1 , b = 1 , c = 2 ⎩ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎧ a = 1 b = 1 c = 2 d = 9 e = 1 9 1 f = 2 1 8 a + b + c d + e + f − 2 = 4 9 + 1 9 1 + 2 1 8 − 2 = 4 4 1 6 = 1 0 4 T h e r e f o r e , a + b + c d + e + f − 2 = 1 0 4
Considere r : a x + b y − c = 0 e s : d x − e y − f = 0 ,
Da figura conclui-se que ( 2 , 0 ) ∈ r , segue que:
∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ x 2 3 y 0 − 1 1 1 1 ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ = 0 − x + 2 y + 2 − 3 y = 0 − x − y + 2 = 0
Ora, a = 1 , b = 1 e c = 2 .
Dado o ponto ( 3 , − 1 ) ∈ s , temos que y = m ( x − 3 ) − 1 é a equação da tangente à elipse.
Substituindo a equação da reta s na equação da elipse, devemos encontrar apenas um ponto (tangente) de intersecção, ou seja, Δ = 0 . Segue que,
2 x 2 + 3 [ m ( x − 3 ) − 1 ] 2 + x − [ m ( x − 3 ) − 1 ] − 5 = 0 ( 3 m 2 + 2 ) x 2 + ( 1 − 7 m − 1 8 m 2 ) x + ( 2 7 m 2 + 2 1 m − 1 ) = 0
Anulando o discriminante,
1 9 1 m 2 + 1 8 2 m − 9 = 0 ( m + 1 ) ( m − 1 9 1 9 ) = 0
Se fizeres m = − 1 , então e < 0 ; portanto, m = 1 9 1 9
Segue que,
y = 1 9 1 9 ⋅ ( x − 3 ) − 1 9 x − 1 9 1 y − 2 1 8 = 0 ⎩ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎧ d = 9 e = 1 9 1 f = 2 1 8
Com efeito,
a + b + c d + e + f − 2 = 4 4 1 6 = 1 0 4
A very well known result will greatly help us here that is :
Combined equations of tangents from a point ( u , v ) to a conic
a x 2 + 2 h x y + b y 2 + 2 g x + 2 f y + c = 0
is given by :
T 2 = S S 1
where T = a u x + h ( x v + y u ) + b v y + g ( x + u ) + f ( y + v ) + c
S = a x 2 + 2 h x y + b y 2 + 2 g x + 2 f y + c
S 1 = a u 2 + 2 h u v + b v 2 + 2 g u + 2 f v + c
In this question we have :
u = 3 , v = − 1 , a = 2 , h = 0 , b = 3 , g = 2 1 , h = − 2 1 , c = − 5
Writing the equation we have :
( 2 1 3 x − 7 y − 6 ) 2 = 2 0 . ( 2 x 2 + 3 y 2 + x − y − 5 )
Simplifying it we get :
9 x 2 − 1 9 1 y 2 − 2 3 6 x + 1 6 4 − 1 8 2 x y + 4 3 6 = 0
Factorising it we get :
− ( 9 x − 1 9 1 y − 2 1 8 ) ( x + y − 2 ) = 0
We can simply say that the lines are :
x + y − 2 = 0
9 x − 1 9 1 y − 2 1 8
So we get :
a = b = 1 , c = 2 , d = 9 , e = 1 9 1 , f = 2 1 8
Finally we get :
a + b + c d + e + f − 2 = 1 0 4