Gergonne's Go
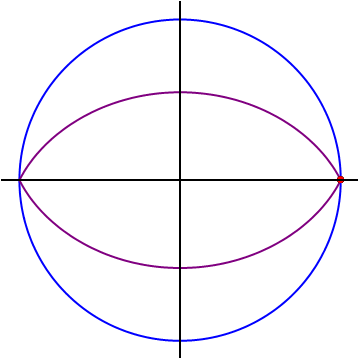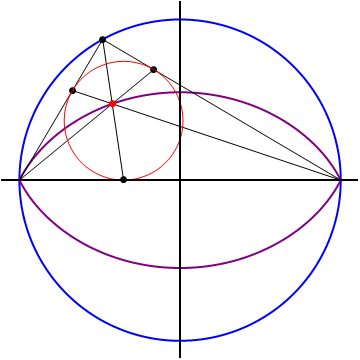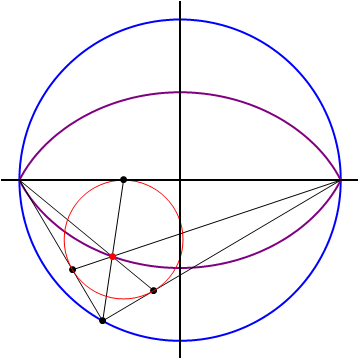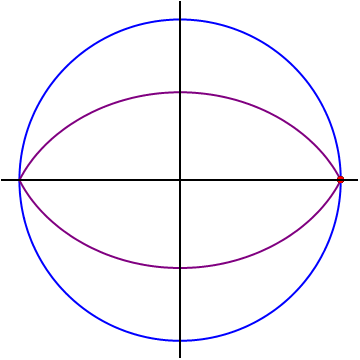 The points
A
,
B
lie on the diameter of a unit circle, and
C
is a third point on that circle, forming a triangle
A
B
C
. The locus of the Gergonne point of the triangle
A
B
C
forms a closed lens-shaped curve (marked in purple on the diagram). It can be shown that the area enclosed by the locus is equal to
−
α
π
+
q
p
β
γ
+
q
p
q
δ
cos
−
1
(
ζ
ε
p
)
where
α
,
β
,
γ
,
δ
,
ε
,
ζ
are positive integers (with
ε
and
ζ
coprime) and
p
,
q
are distinct prime numbers.
The points
A
,
B
lie on the diameter of a unit circle, and
C
is a third point on that circle, forming a triangle
A
B
C
. The locus of the Gergonne point of the triangle
A
B
C
forms a closed lens-shaped curve (marked in purple on the diagram). It can be shown that the area enclosed by the locus is equal to
−
α
π
+
q
p
β
γ
+
q
p
q
δ
cos
−
1
(
ζ
ε
p
)
where
α
,
β
,
γ
,
δ
,
ε
,
ζ
are positive integers (with
ε
and
ζ
coprime) and
p
,
q
are distinct prime numbers.
Find the value of α + β + γ + δ + ε + ζ + p + q .
The answer is 117.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
1 solution
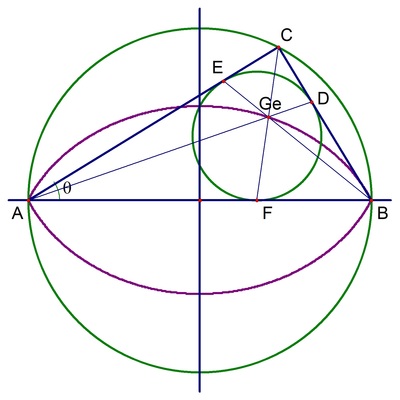 If we let
∠
B
A
C
=
θ
for
0
<
θ
<
2
1
π
(so that
C
is in the upper semicircle), then the vertices of the triangle
A
B
C
are
A
(
−
1
,
0
)
B
(
1
,
0
)
C
(
cos
2
θ
,
sin
2
θ
)
The triangle
A
B
C
has sides
a
,
b
,
c
and semiperimeter
s
where
a
=
2
sin
θ
b
=
2
cos
θ
c
=
2
s
=
1
+
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
If
D
,
E
,
F
are the touch points of the incircle with the sides of the triangle, then
A
F
=
A
E
=
s
−
a
and
B
D
=
s
−
b
, and hence we have coordinates
D
E
F
(
1
−
(
1
+
sin
θ
−
cos
θ
)
sin
θ
,
(
1
+
sin
θ
−
cos
θ
)
cos
θ
)
(
−
1
+
(
1
+
cos
θ
−
sin
θ
)
cos
θ
,
(
1
+
cos
θ
−
sin
θ
)
sin
θ
)
(
cos
θ
−
sin
θ
,
0
)
and the inradius of the triangle
A
B
C
is
r
=
s
−
c
=
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
−
1
. Solving simultaneously the equations for the lines
A
D
and
B
E
, we find that the Gergonne point
G
e
has coordinates
(
X
(
θ
)
,
Y
(
θ
)
)
, where
X
(
θ
)
Y
(
θ
)
=
cos
2
θ
−
3
+
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
2
(
cos
θ
−
sin
θ
)
(
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
−
1
)
=
3
+
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
(
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
−
1
)
(
1
+
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
)
2
By symmetry, the desired area is
Δ
=
2
∫
2
1
π
0
X
′
(
θ
)
Y
(
θ
)
d
θ
=
2
∫
2
1
π
0
(
3
+
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
)
3
(
−
1
+
c
o
s
θ
+
sin
θ
)
(
1
+
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
)
3
(
−
6
+
cos
θ
+
cos
3
θ
+
sin
θ
−
8
sin
2
θ
−
sin
3
θ
)
d
θ
=
−
3
2
∫
0
1
(
1
+
t
2
)
5
(
2
+
t
+
t
2
)
3
(
t
−
1
)
t
(
1
+
t
)
3
(
1
+
9
t
+
8
t
2
−
6
t
3
+
t
4
−
7
t
5
+
2
t
6
)
d
t
using the
t
=
tan
2
1
θ
substitution. This last integrand can be expanded by partial fractions as
−
3
2
⎝
⎜
⎜
⎛
(
1
+
t
2
)
5
1
6
+
(
1
+
t
2
)
4
4
(
3
t
−
1
1
)
−
(
1
+
t
2
)
3
2
(
1
4
t
−
1
9
)
+
(
1
+
t
2
)
2
1
6
t
−
5
+
(
1
+
t
2
)
3
−
(
2
+
t
+
t
2
)
3
1
4
(
t
−
1
)
−
(
2
+
t
+
t
2
)
2
1
9
t
+
3
3
−
(
2
+
t
+
t
2
)
3
⎠
⎟
⎟
⎞
Since each of these terms can be integrated using either
t
=
tan
φ
or
t
+
2
1
=
tan
φ
as substitution, we deduce that
Δ
=
−
4
3
π
+
7
3
6
8
+
7
3
2
0
0
cos
−
1
(
8
5
2
)
=
−
4
3
π
+
7
2
4
×
2
3
+
7
2
7
×
2
5
cos
−
1
(
8
5
2
)
so that
α
=
4
3
,
β
=
4
,
γ
=
2
3
,
δ
=
2
5
,
ε
=
5
,
ζ
=
8
,
p
=
2
and
q
=
7
, so that
α
+
β
+
γ
+
δ
+
ε
+
ζ
+
p
+
q
=
1
1
7
.
If we let
∠
B
A
C
=
θ
for
0
<
θ
<
2
1
π
(so that
C
is in the upper semicircle), then the vertices of the triangle
A
B
C
are
A
(
−
1
,
0
)
B
(
1
,
0
)
C
(
cos
2
θ
,
sin
2
θ
)
The triangle
A
B
C
has sides
a
,
b
,
c
and semiperimeter
s
where
a
=
2
sin
θ
b
=
2
cos
θ
c
=
2
s
=
1
+
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
If
D
,
E
,
F
are the touch points of the incircle with the sides of the triangle, then
A
F
=
A
E
=
s
−
a
and
B
D
=
s
−
b
, and hence we have coordinates
D
E
F
(
1
−
(
1
+
sin
θ
−
cos
θ
)
sin
θ
,
(
1
+
sin
θ
−
cos
θ
)
cos
θ
)
(
−
1
+
(
1
+
cos
θ
−
sin
θ
)
cos
θ
,
(
1
+
cos
θ
−
sin
θ
)
sin
θ
)
(
cos
θ
−
sin
θ
,
0
)
and the inradius of the triangle
A
B
C
is
r
=
s
−
c
=
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
−
1
. Solving simultaneously the equations for the lines
A
D
and
B
E
, we find that the Gergonne point
G
e
has coordinates
(
X
(
θ
)
,
Y
(
θ
)
)
, where
X
(
θ
)
Y
(
θ
)
=
cos
2
θ
−
3
+
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
2
(
cos
θ
−
sin
θ
)
(
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
−
1
)
=
3
+
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
(
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
−
1
)
(
1
+
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
)
2
By symmetry, the desired area is
Δ
=
2
∫
2
1
π
0
X
′
(
θ
)
Y
(
θ
)
d
θ
=
2
∫
2
1
π
0
(
3
+
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
)
3
(
−
1
+
c
o
s
θ
+
sin
θ
)
(
1
+
cos
θ
+
sin
θ
)
3
(
−
6
+
cos
θ
+
cos
3
θ
+
sin
θ
−
8
sin
2
θ
−
sin
3
θ
)
d
θ
=
−
3
2
∫
0
1
(
1
+
t
2
)
5
(
2
+
t
+
t
2
)
3
(
t
−
1
)
t
(
1
+
t
)
3
(
1
+
9
t
+
8
t
2
−
6
t
3
+
t
4
−
7
t
5
+
2
t
6
)
d
t
using the
t
=
tan
2
1
θ
substitution. This last integrand can be expanded by partial fractions as
−
3
2
⎝
⎜
⎜
⎛
(
1
+
t
2
)
5
1
6
+
(
1
+
t
2
)
4
4
(
3
t
−
1
1
)
−
(
1
+
t
2
)
3
2
(
1
4
t
−
1
9
)
+
(
1
+
t
2
)
2
1
6
t
−
5
+
(
1
+
t
2
)
3
−
(
2
+
t
+
t
2
)
3
1
4
(
t
−
1
)
−
(
2
+
t
+
t
2
)
2
1
9
t
+
3
3
−
(
2
+
t
+
t
2
)
3
⎠
⎟
⎟
⎞
Since each of these terms can be integrated using either
t
=
tan
φ
or
t
+
2
1
=
tan
φ
as substitution, we deduce that
Δ
=
−
4
3
π
+
7
3
6
8
+
7
3
2
0
0
cos
−
1
(
8
5
2
)
=
−
4
3
π
+
7
2
4
×
2
3
+
7
2
7
×
2
5
cos
−
1
(
8
5
2
)
so that
α
=
4
3
,
β
=
4
,
γ
=
2
3
,
δ
=
2
5
,
ε
=
5
,
ζ
=
8
,
p
=
2
and
q
=
7
, so that
α
+
β
+
γ
+
δ
+
ε
+
ζ
+
p
+
q
=
1
1
7
.
@Mark Hennings So that means that it is equal to the phrases, 'so as to', and 'in order to'.