Golden Circles
Two unit circles and are placed tangent to a line and to each other. Then circle is placed tangent to the line and tangent to circles and , and circle is placed tangent to the line and tangent to circles and , and so on, so each new circle is placed tangent to the line and tangent to circles and .
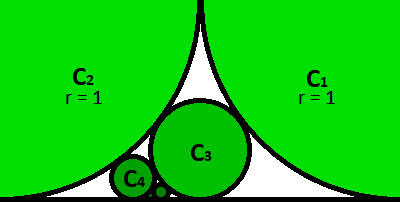
Let be the area of each circle . Then = where is the golden ratio and is an integer.
What is ?
The answer is 4.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Let the radius of circle C n be r n . Then we note that the horizontal distance between centers of C 2 and C 3 is equal to the sum of distance between centers of C 2 and C 4 and distance between centers of C 3 and C 4 and by Pythagorean theorem:
( r 2 + r 3 ) 2 − ( r 2 − r 3 ) 2 2 r 2 r 3 ⟹ r 4 1 = ( r 2 + r 4 ) 2 − ( r 2 − r 4 ) 2 + ( r 3 + r 4 ) 2 − ( r 3 − r 4 ) 2 = 2 r 2 r 4 + 2 r 3 r 4 Divide both sides by 2 r 2 r 3 r 4 = r 3 1 + r 2 1
Then we have:
r 1 1 r 2 1 r 3 1 r 4 1 ⟹ r n 1 = 1 = F 1 = 1 = F 2 = r 2 1 + r 1 1 = 2 = F 3 = r 3 1 + r 2 1 = 3 = F 4 = F n where F n is the n th Fibonacci number.
Then we have:
n → ∞ lim A n + 1 A n = n → ∞ lim π r n + 1 2 π r n 2 = n → ∞ lim ( r n + 1 r n ) 4 = n → ∞ lim ( F n F n + 1 ) 4 = φ 4 where φ is the golden ratio.
Therefore, m = 4 .