Half-disc: Area ratios
The diagram shows the half disc x 2 + y 2 ≤ 1 for y ≥ 0 . In the region A , all points have − cos θ ≤ x ≤ sin θ .
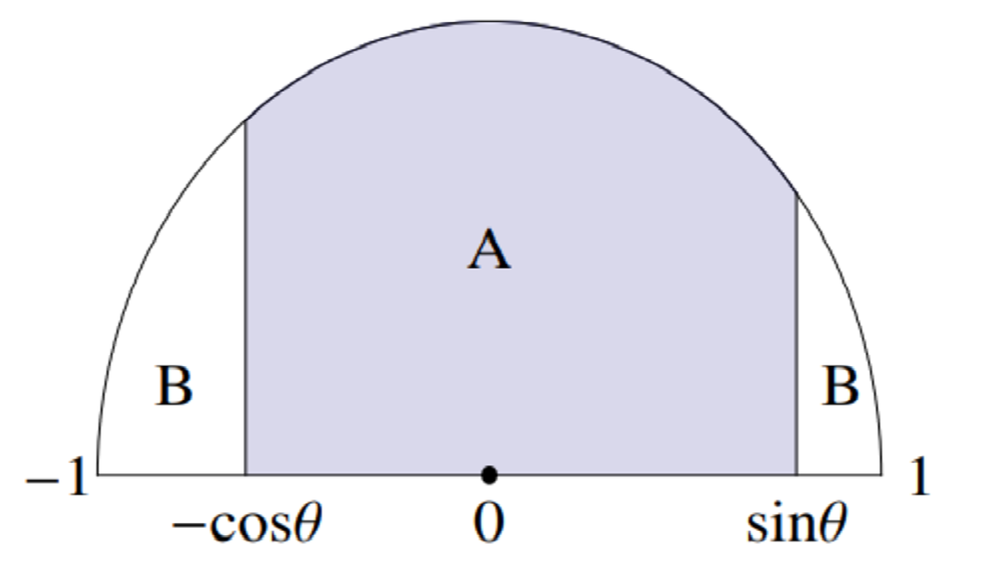
For θ ∈ ( 0 , 2 π ) , what is the maximum value of Area of B Area of A ?
Notes:
- The area of B includes the regions either side of A combined.
- Problem sourced from a University of Oxford admissions test (2013): here .
The answer is 4.503876788.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Let the area of region marked A be A and that marked B be B . Then B is the area of semicircle with radius 1 less A or B = 2 π − A . Then the ratio B A = 2 π − A A = A A π − 1 1 . Then B A is maximum, when A is maximum.
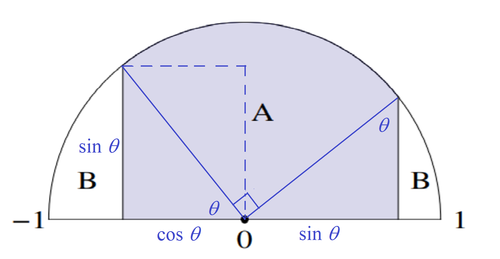
We can see from the figure that A is equal to a quarter circle with radius 1 plus a rectangle with side lengths sin θ and cos θ or A = 4 π + sin θ cos θ = 4 π + 2 sin ( 2 θ ) . ⟹ max ( A ) = 4 π + 2 max ( sin ( 2 θ ) ) = 4 π + 2 1 .
Therefore max ( B A ) = 2 π − A max A max = 4 π − 2 1 4 π + 2 1 = π − 2 π + 2 ≈ 4 . 5 0 .
Adding to the diagram, we have the following:
With the altitudes of the two new triangles being perpendicular to the line y = 0 . The angle defining the sector within A is 1 8 0 ° − θ − ( θ − 9 0 ° ) = 9 0 ° .
A comprises a quarter circle of area 1 2 ⋅ π × 4 1 = 4 π and two congruent triangles of area 2 sin θ cos θ each.
This is because on the edge of the disc we have sin 2 θ + y 2 = 1 ⟸ y = cos θ for the right-hand triangle, since sin 2 x + cos 2 x ≡ 1 . For the left-hand triangle we have ( − cos θ ) 2 = 1 ⟸ y = sin θ .
The area of A = 4 π + 2 ⋅ 2 sin θ cos θ = 4 π + sin θ cos θ .
Evidently, since the half-disk has radius 1, area of A + area of B = 2 π , so the area of B = 2 π − 4 π − sin θ cos θ = 4 π − sin θ cos θ .
Area of B Area of A = 4 π − sin θ cos θ 4 π + sin θ cos θ
If we put 4 π : = k and sin θ cos θ : = x then k − x k + x is a (strictly) increasing function for ∣ x ∣ < k , so the maximum value of the ratio that we require is at the maximum value of x = sin θ cos θ .
We have that x = 2 sin 2 θ ≤ 2 1 .
Alternatively, note that r 2 ≥ 0 ∀ r ∈ R ⟹ ( sin θ − cos θ ) 2 ≥ 0 , so 1 − 2 sin θ cos θ ≥ 0 which gives the same result.
The maximum value of Area of B Area of A = 4 π − 2 1 4 π + 2 1 = π − 2 π + 2 = 4 . 5 0 (3 s.f.)