How fast??
A body of mass 1 kg is placed at the top of a double incline as shown in the figure. What is the speed of the object at the instant when it reaches point C(just at the junction of the two inclines)?
Details and Assumptions:
-
There is no loss of energy at the junction of the two inclines.
-
All the surfaces are frictionless.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Let's begin by naming a few points: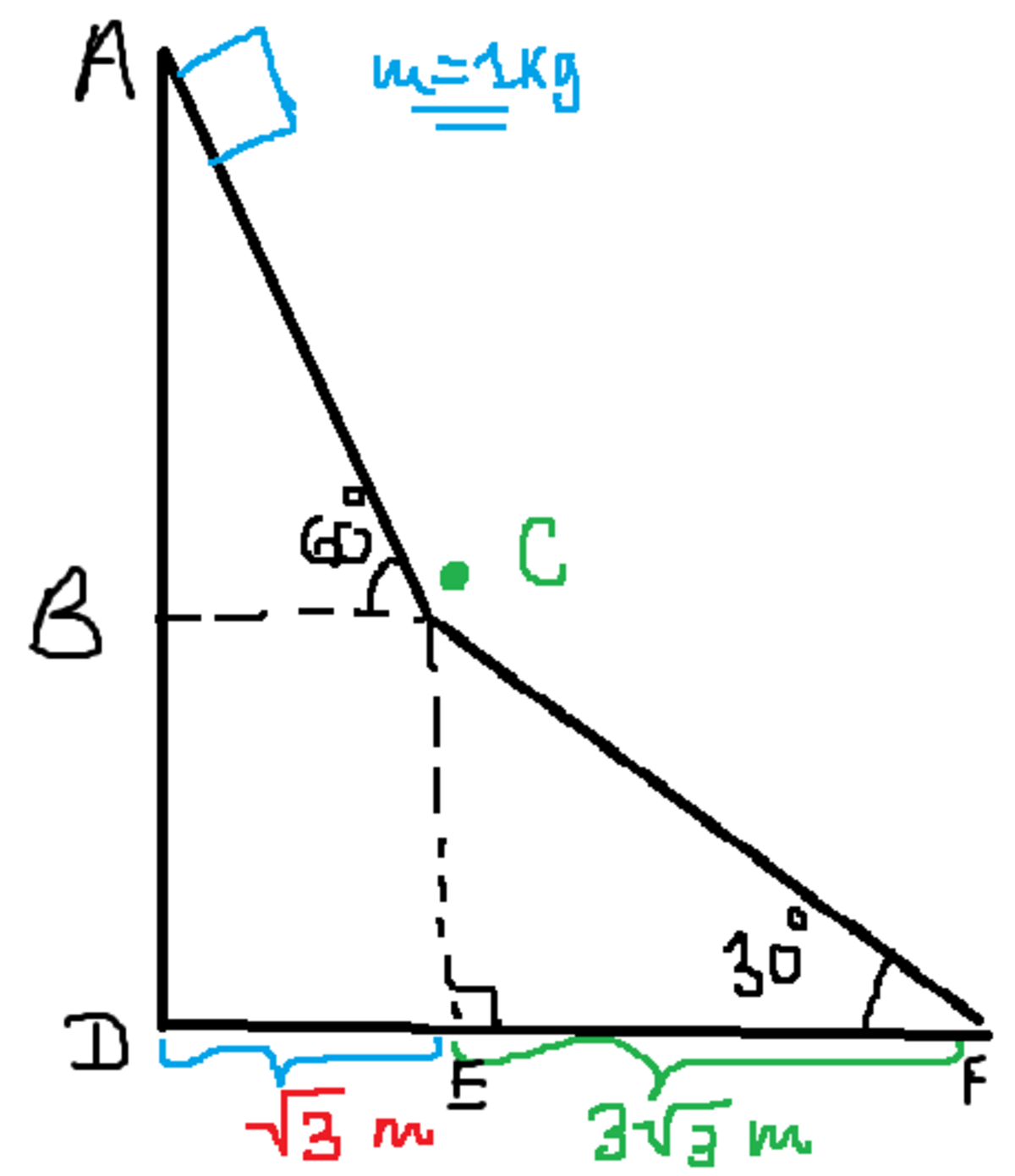
1. Figuring out the height:
In incline CEF:
C E = E F × t a n ( 3 0 ) = 3 3 × 3 1 = 3 m B D = C E = 3 m
Similarly in incline ABC:
B C = D E = 3 m A B = B C × t a n ( 6 0 ) = 3 × 3 = 3 m
Now, H e i g h t ( h ) = A B + B D = 3 m + 3 m = 6 m
2. Figuring out the gravitational potential energy:
G . P . E ( A ) = m g h = 1 k g × 1 0 m / s 2 × 6 m = 6 0 J
3. Applying the LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MECHANICAL ENERGY:
TOTAL MECHANICAL ENERGY AT A = TOTAL MECHANICAL ENERGY AT C
= > G . P . E ( A ) + K . P . E ( A ) = G . P . E ( C ) + K . E ( C )
Since, body is placed over the incline K.P.E(A) can be assumed to be 0.
= > G . P . E ( A ) = G . P . E ( C ) + K . E ( C ) N o t e : h ( C ) = C E = 3 m . T h e r e f o r e : G . P . E ( C ) = m g h ( C ) = 1 k g × 1 0 m / s 2 × 3 m = 3 0 J
Putting in the equation:
6 0 J = 3 0 J + K . E ( C ) = > K . E ( C ) = 3 0 J
4. USING KINETIC ENERGY TO FIGURE OUT THE SPEED:
Now, Kinetic energy has this neat formula:
K E = 2 1 × m × v 2
Where:
m -> Mass of object
v -> Speed of the object
Now, using this formula:
K . E ( C ) = 2 1 × m × v 2 = > 3 0 J = 2 1 × ( 1 k g ) × v 2 = > 1 k g 2 × 3 0 J = v 2 = > v 2 = 6 0 s 2 m 2 = > v = 6 0 s m