I like Right Triangles
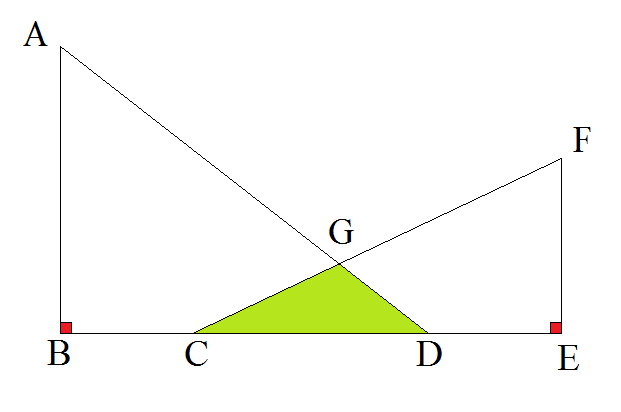
In the above figure, A B = 1 2 , F E = 8 , B C = C D = D E = 3 , A B ⊥ B E , F E ⊥ B E ,
Then find the area of Δ G C D .
The answer is 3.6.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Place the whole diagram on a coordinate plane such that B is ( 0 , 0 ) . Then with the given information, A is ( 0 , 1 2 ) , C is ( 3 , 0 ) , D is ( 6 , 0 ) , E is ( 9 , 0 ) , and F is ( 9 , 8 ) .
Then C F is on y = 3 4 x − 4 and A D is on y = − 2 x + 1 2 , and their intersection at G is ( 5 2 4 , 5 1 2 ) .
Therefore, △ C D G has a base of 3 and a height of 5 1 2 , and an area of A = 2 1 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 5 1 2 = 5 1 8 = 3 . 6 .
Since △ CEF ~ △ CGH
Therefore,
G H F E = C H C E
=> G H 8 = C H 6
=> 8(CH) = 6(GH) (1)
Since △ DAB ~ △ DGH
Therefore, G H A B = H D B D
=> G H A B = C D − C H B D
=> G H 1 2 = 3 − C H 6
=> 12(3-CH) = 6(GH)
=> 36-12(CH) = 6(GH) (2)
Combine (1) and (2) through Transitive Property, we got:
36-12(CH) = 8(CH)
=>36= 20(CH)
=>CH = 1.8
We have that: 8(CH) = 6(GH)
=>8(1.8) = 6(GH)
=>GH= 2.4
Area of △ CGD = 2 C D ∗ G H = 2 3 × 2 . 4 = 3 . 6
C H G H = C E F E
C H G H = 6 8
C H = 4 3 G H
Since △ D G H ∼ △ D A B ,
H D G H = B D A B
H D G H = 6 1 2
H D = 2 1 G H
We know that C H + H D = 3 , so
4 3 G H + 2 1 G H = 3
G H = 5 1 2
The desired area is
A = 2 1 ( C D ) ( G H ) = 2 1 ( 3 ) ( 1 2 5 ) = 3 . 6