Incenter Beast
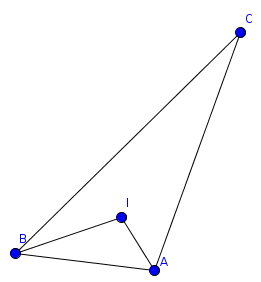
In △ A B C , I is the incenter of the triangle. A C + A I = B C and A B + B I = A C . Find the measure of ∠ A B C , to the nearest degree.
The answer is 51.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Nice problem.Took me quite a long time to solve.Please post more such challenging geometry problems.
Awesome problem! Keep posting such problems :)
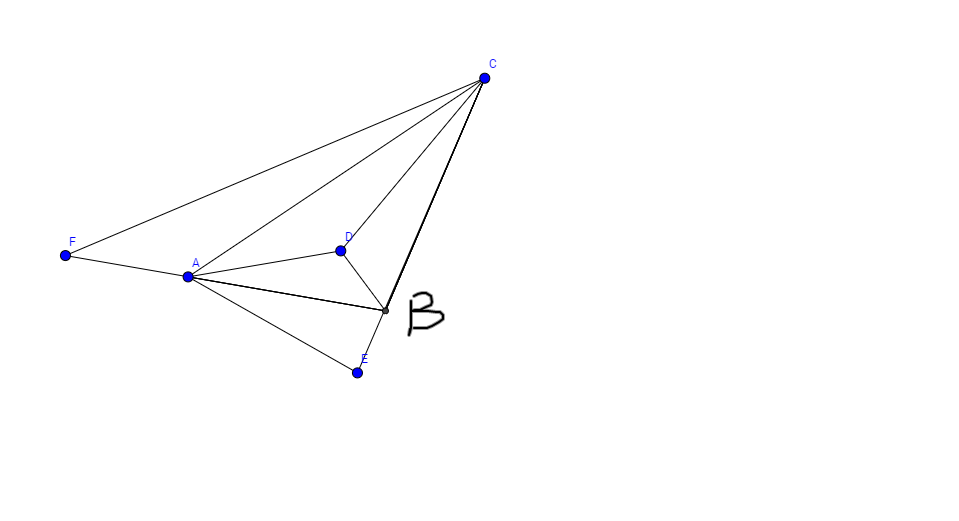 P
r
o
d
u
c
e
C
B
t
o
E
w
h
i
c
h
D
B
=
B
E
.
L
e
t
∠
A
C
B
=
θ
,
∠
C
A
E
=
∠
C
E
A
=
9
0
°
−
2
θ
∵
D
i
s
i
n
c
e
n
t
r
e
.
∠
D
A
B
+
∠
D
B
A
=
9
0
°
−
2
θ
∠
A
D
B
=
9
0
°
+
2
θ
.
∠
A
D
B
+
∠
A
E
B
=
1
8
0
°
∴
A
,
D
,
B
,
E
i
s
c
o
n
c
y
c
l
i
c
.
D
B
=
B
E
⇒
D
A
B
=
B
A
E
=
D
A
C
l
e
t
D
A
B
=
α
⇒
C
A
E
=
C
E
A
=
3
α
.
∠
A
C
E
=
1
8
0
°
−
6
α
⇒
A
C
D
=
D
C
B
=
9
0
°
−
3
α
A
B
C
=
B
A
E
+
A
E
B
=
4
α
P
r
o
d
u
c
e
B
A
t
o
F
w
h
e
r
e
A
F
=
D
A
⇒
B
F
=
B
C
⇒
B
F
C
=
B
C
F
=
9
0
−
2
α
∠
F
C
D
=
F
C
B
−
D
C
B
=
(
9
0
°
−
2
α
)
−
(
9
0
−
3
α
)
=
α
F
C
A
=
9
0
°
−
2
α
−
(
1
8
0
°
−
6
α
)
=
4
α
−
9
0
∠
D
C
F
=
∠
D
A
B
=
α
.
∵
F
C
D
A
i
s
c
o
n
c
y
c
l
i
c
A
F
=
A
D
⇒
∠
F
C
A
=
∠
A
C
D
⇒
4
α
−
9
0
°
=
9
0
°
−
3
α
⇒
α
=
2
5
.
7
1
4
.
.
.
∠
B
A
B
=
2
α
=
5
1
.
4
2
8
.
.
.
P
r
o
d
u
c
e
C
B
t
o
E
w
h
i
c
h
D
B
=
B
E
.
L
e
t
∠
A
C
B
=
θ
,
∠
C
A
E
=
∠
C
E
A
=
9
0
°
−
2
θ
∵
D
i
s
i
n
c
e
n
t
r
e
.
∠
D
A
B
+
∠
D
B
A
=
9
0
°
−
2
θ
∠
A
D
B
=
9
0
°
+
2
θ
.
∠
A
D
B
+
∠
A
E
B
=
1
8
0
°
∴
A
,
D
,
B
,
E
i
s
c
o
n
c
y
c
l
i
c
.
D
B
=
B
E
⇒
D
A
B
=
B
A
E
=
D
A
C
l
e
t
D
A
B
=
α
⇒
C
A
E
=
C
E
A
=
3
α
.
∠
A
C
E
=
1
8
0
°
−
6
α
⇒
A
C
D
=
D
C
B
=
9
0
°
−
3
α
A
B
C
=
B
A
E
+
A
E
B
=
4
α
P
r
o
d
u
c
e
B
A
t
o
F
w
h
e
r
e
A
F
=
D
A
⇒
B
F
=
B
C
⇒
B
F
C
=
B
C
F
=
9
0
−
2
α
∠
F
C
D
=
F
C
B
−
D
C
B
=
(
9
0
°
−
2
α
)
−
(
9
0
−
3
α
)
=
α
F
C
A
=
9
0
°
−
2
α
−
(
1
8
0
°
−
6
α
)
=
4
α
−
9
0
∠
D
C
F
=
∠
D
A
B
=
α
.
∵
F
C
D
A
i
s
c
o
n
c
y
c
l
i
c
A
F
=
A
D
⇒
∠
F
C
A
=
∠
A
C
D
⇒
4
α
−
9
0
°
=
9
0
°
−
3
α
⇒
α
=
2
5
.
7
1
4
.
.
.
∠
B
A
B
=
2
α
=
5
1
.
4
2
8
.
.
.
Nice solution
A more precise answer should be 7 3 6 0 ° ≈ 5 1 . 4 3 ° .
Cut B C into B R and C R , where C R = C A . As A C + A I = B C , A I = B R .
△ A C R is isosceles, with C I as an angle bisector. Therefore, C I is also the perpendicular bisector of A R , meaning that A I = R I , m ∠ C R I = m ∠ C A I .
m ∠ C R I = m ∠ R B I + m ∠ R I B . As R I = I A = R B , m ∠ R B I = m ∠ R I B , then m ∠ C R I = 2 m ∠ R B I = m ∠ R B A .
On the other hand, m ∠ C A I = m ∠ B A I , then m ∠ R B A = m ∠ I A B . △ A B I ≅ △ B A R ( S . A . S . ). Thus m ∠ C A B = 2 m ∠ A B C .
By going through the same process for a second time, we can get B I = I S = C S → △ B I S ≅ △ C S I → m ∠ A B C = 2 m ∠ A C B .
Therefore, m ∠ C A B : m ∠ A B C : m ∠ B C A = 4 : 2 : 1 , making m ∠ A B C = 2 × 7 1 8 0 ° = 7 3 6 0 ° .