Infinite Grid Resitance
There is hexagonal infinite grid resitance. Each segment has resistance
.
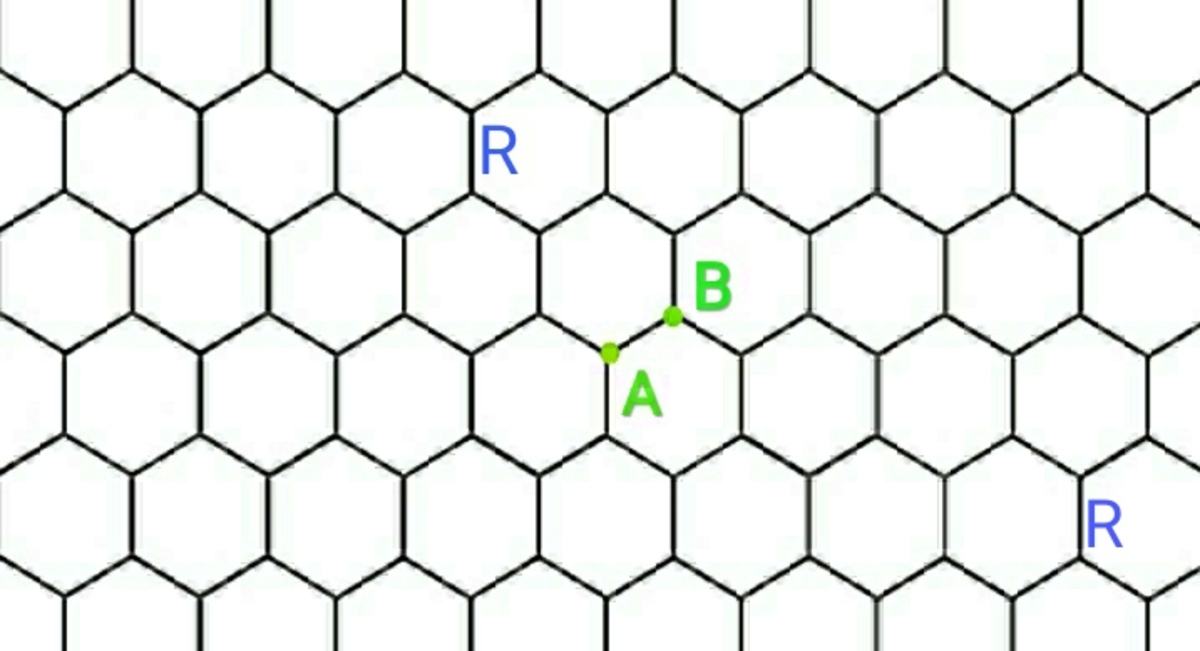 Find the equivalent
between
and
Find the equivalent
between
and
If your answer comes in the the form of
Find
The problem is purely original
The answer is 0.667.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
A hexagonal analog of problem number 3.153 from I. E. Irodov's book "Problems in General Physics". Apply the principle of symmetry to get an equation for the P. D. between points A and B :
V A B = I R e q = I 0 R , where I is the current flowing through the lead wires, I 0 is the current flowing through the section A B , R e q is the equivalent resistance between points A and B to be determined.
Applying the principle of superposition, current enters into any node through three wires. So,
I 0 = 2 × 3 I , the factor 2 arises because of the fact that if current I flowed into A and spread all over the grid, the wire A B would carry a current 3 I . Similarly, if the current flowed into the grid from infinity and left the grid through B , the wire A B would also carry the current 3 I .
Hence, R e q = 3 2 R , and α = 3 2 ≈ 0 . 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 .