Inscribed square
We inscribed the red square into a bigger square, as it is shown in the figure below. The lengths of the bigger square are
.
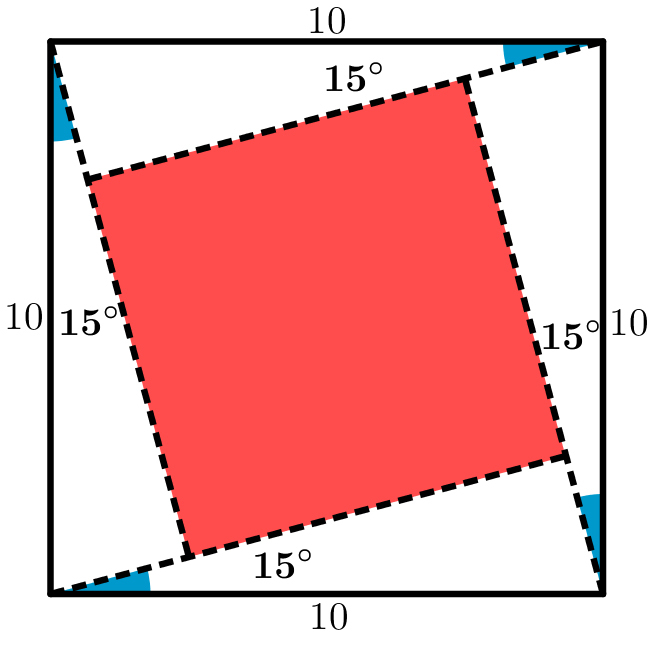
What is the area of the smaller, red square?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
The area of each of the 4 peripheral triangles is 2 1 ( 1 0 sin ( 1 5 ∘ ) ) ( 1 0 cos ( 1 5 ∘ ) ) = 5 0 sin ( 1 5 ∘ ) cos ( 1 5 ∘ ) = 2 5 sin ( 3 0 ∘ ) = 1 2 . 5 ,
where the identity sin ( 2 x ) = 2 sin ( x ) cos ( x ) was used. Thus the sum of the areas of the 4 peripheral triangles is 4 × 1 2 . 5 = 5 0 , and so the area of the red square is 1 0 2 − 5 0 = 5 0 .