Inscribed Trapezoid
As shown above, Trapezoid ABCD is inscribed in a semicircle with a radius of 2 . They share the same base which is A D . The lengths of the line segments A B and D C are both 1 . Find the area of Trapezoid ABCD to three decimal places (round up if necessary with the third decimal place).
The answer is 3.631.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Connect B D , ∠ A B D = 9 0 ∘ ,so B D = 1 5 .
Let E be on A D and ∠ A E B = 9 0 ∘ ,then △ A B E △ A D B .
So, A E = 4 1 , B C = 4 − 4 1 × 2 = 3 . 5 ,and B E = 4 1 5
Hence the area is ( 4 + 3 . 5 ) × 4 1 5 × 2 1 = 1 6 1 5 1 5
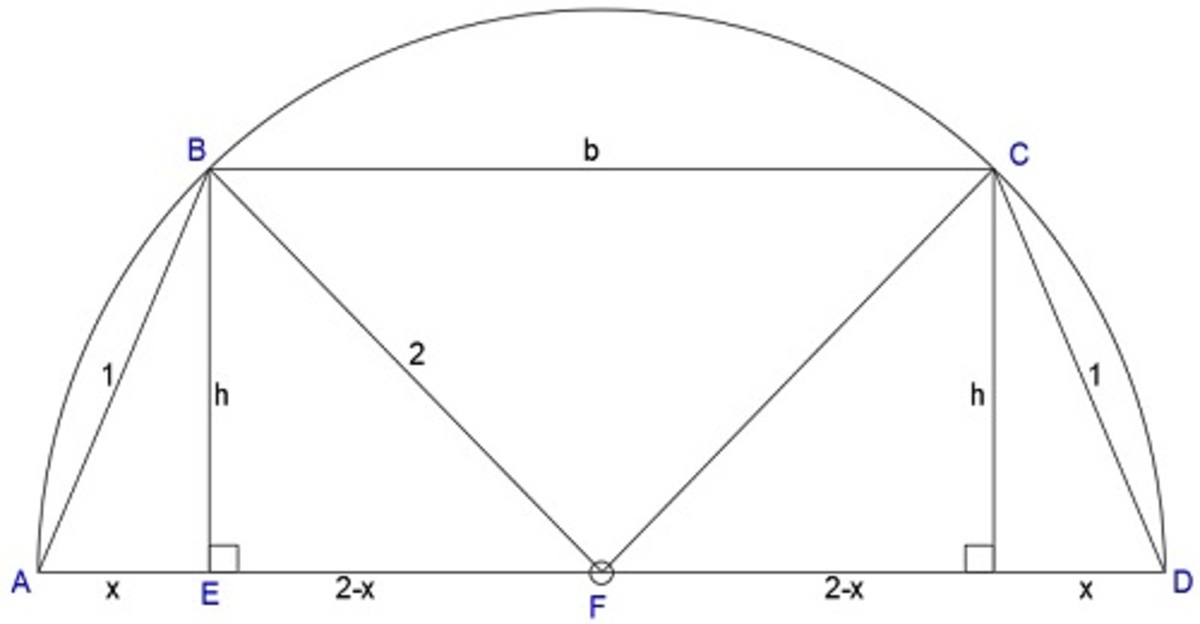
Apply pythagorean theorem on △ A B E . We get
h 2 = 1 − x 2 ( 1 )
Apply pythagorean theorem on △ B E F . We get
h 2 + x 2 − 4 x = 0 ( 2 )
Substituting ( 1 ) in ( 2 ) then simplifying, we get
x = 4 1
It follows that
h = 4 1 5 and b = 2 7
The area of a trapezoid is 2 1 ( b a s e 1 + b a s e 2 ) × h e i g h t . Substitute:
A = 2 1 ( 2 7 + 4 ) ( 4 1 5 ) ≈ 3 . 6 3 1
As shown above, label the center of the semicircle as O , draw radius O C (length 2 ) , draw the altitude to A D from point C to E , label C D as 1 , O E as x , and E D as 2 − x . Begin by observing that altitude C E constructs right triangles O E C and D E C . Using the Pythagorean Theorem , we can solve for x as such:
C E 2 = 2 2 − x 2
C E 2 = 1 2 − ( 2 − x ) 2
∴ 1 2 − ( 2 − x ) 2 = 2 2 − x 2 ⇒ 1 − ( 2 − x 2 = 4 − x 2 ⇒ 1 − ( 2 − x ) ( 2 − x ) = 4 − x 2 ⇒ 1 − ( 4 − 4 x + x 2 ) = 4 − x 2 ⇒ 1 + ( − 4 + 4 x − x 2 ) = 4 − x 2 ⇒ − 3 + 4 x − x 2 + x 2 = 4 ⇒ 4 x = 7 ⇒ x = 4 7
Now that we have solved for x , we can substitute 4 7 for x to solve for altitude C E as such:
C E 2 = 2 2 − ( 4 7 ) 2 ⇒ C E 2 = 4 − 1 6 4 9 ⇒ C E 2 = 1 6 1 5 ⇒ C E = 4 1 5
Now that we have solved for the altitude/height ( C E ) of Trapezoid ABCD , we can solve for the area of Trapezoid ABCD as such:
Area of Trapezoid ⇒ 2 b 1 + b 2 × h
∴ A T r a p e z o i d A B C D = 2 ( A D ) + ( B C ) × ( C E ) ⇒ A T r a p e z o i d A B C D = 2 ( 4 + 7 2 ) × 4 1 5 ⇒ A T r a p e z o i d A B C D = 1 6 1 5 1 5
1 6 1 5 1 5 ≈ 3 . 6 3 1