Inspiratio!
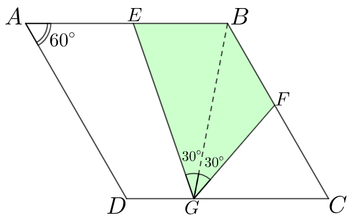
In the rhombus A B C D of interior angle 6 0 ∘ , point G is selected on segment C D , such that D G : C G = 1 : 2 . In addition, ∠ B G E = ∠ B G F = 3 0 ∘ .
If the ratio of the area of the quadrilateral E G F B to area of the rhombus A B C D can be expressed as b a , where a and b are both coprime positive integers, input a + b as your answer.
Challenge: Solve this problem without any trigonometry.
The answer is 25.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Nice and short!
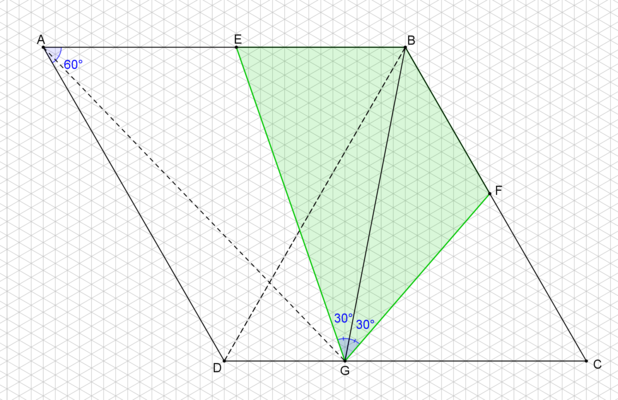 Figure 1
If we use an isometric grid as shown on figure 1, we see that
A
B
E
B
=
B
C
B
F
=
1
5
7
(see at the end of the solution for a more elaborate explanation)
Figure 1
If we use an isometric grid as shown on figure 1, we see that
A
B
E
B
=
B
C
B
F
=
1
5
7
(see at the end of the solution for a more elaborate explanation)
Now, △ G B E and △ G B A share a common height from vertex G , thus, [ G A B ] [ G E B ] = A B E B = 1 5 7 ⇒ [ G E B ] = 1 5 7 [ G A B ] = 1 5 7 [ D A B ] = 1 5 7 ( 2 1 [ A B C D ] ) = 3 0 7 [ A B C D ] ( 1 ) Likewise, △ G B F and △ G B C share a common height from vertex G, thus, [ G B C ] [ G B F ] = B C B F = 1 5 7 ⇒ [ G B F ] = 1 5 7 [ G B C ] ( 2 ) Next, [ D B C ] [ G B C ] = 2 1 C B ⋅ C D ⋅ sin C 2 1 C B ⋅ C G ⋅ sin C = C D C G = 3 2 ⇒ [ G B C ] = 3 2 [ D B C ] ( 3 ) ( 2 ) , ( 3 ) ⇒ [ G B F ] = 1 5 7 ( 3 2 [ D B C ] ) = 4 5 1 4 ( 2 1 [ A B C D ] ) ⇒ [ G B F ] = 4 5 7 [ A B C D ] ( 4 ) Finally, [ E G F B ] = [ G E B ] + [ G B F ] = ( 1 ) , ( 4 ) 3 0 7 [ A B C D ] + 4 5 7 [ A B C D ] = 1 8 7 [ A B C D ] i.e. [ A B C D ] [ E G F B ] = 1 8 7 For the answer, a = 7 , b = 1 8 , thus, a + b = 2 5 .
Details to justify that in the grid, ∠ E G F is indeed 6 0 ∘ and ∠ B G F = 3 0 ∘ , i.e. F and E are the correct (given) points.
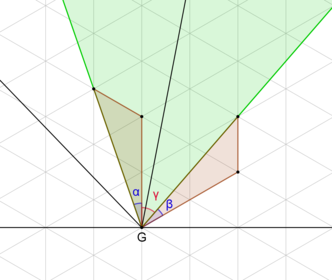 Figure 2
Figure 2
Focusing around point G , triangle congruency verifies that ∠ E G F = α + γ = β + γ = 6 0 ∘ (figure 2).
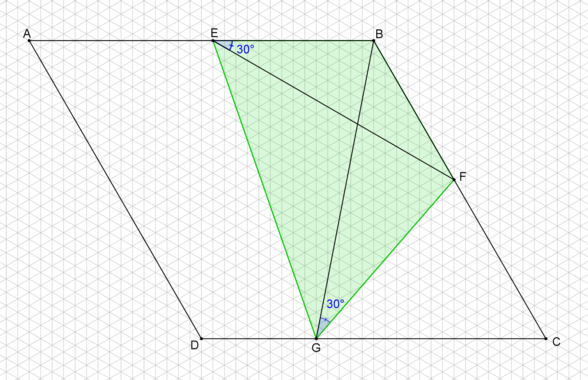 Figure 3
Furthermore, since
∠
E
B
F
+
∠
E
G
F
=
1
2
0
∘
+
6
0
∘
=
1
8
0
∘
,
E
G
F
B
is a cyclic quadrilateral, thus
∠
B
G
F
=
∠
B
E
F
=
3
0
∘
(figure 3).
Figure 3
Furthermore, since
∠
E
B
F
+
∠
E
G
F
=
1
2
0
∘
+
6
0
∘
=
1
8
0
∘
,
E
G
F
B
is a cyclic quadrilateral, thus
∠
B
G
F
=
∠
B
E
F
=
3
0
∘
(figure 3).
The shaded area can be cut and rearranged to fill out 7 out of 1 8 equilateral triangles as follows:
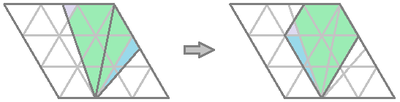
which makes the ratio 1 8 7 , so a = 7 , b = 1 8 , and a + b = 2 5 .
△ B F H is congruent to the △ B E J . △ B G J is congruent to the △ G H I . This means that the area of the quadrilateral EGFB is equal to the area of the equilateral △ B G I . Segment B G = 3 7 D C . Area of the rhombus is twice the area of the equilateral triangle with the same side length. The ratio of the area of the quadrilateral EGFB to area of the rhombus ABCD is 2 ∗ 9 7 = 1 8 7