Inspired by Aniket Verma
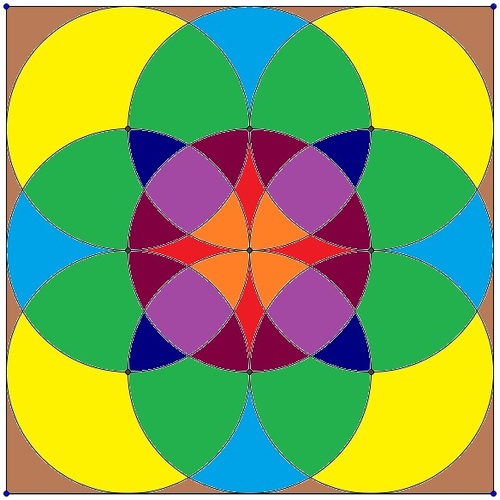 Find the area of
V
i
o
l
e
t
region (four square looking region of central circle) if radius of each circle is 4 units.
Find the area of
V
i
o
l
e
t
region (four square looking region of central circle) if radius of each circle is 4 units.
Inspired by this question.
Image credit goes to Aniket Verma .
The answer is 20.16939.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
I added a image (cropped from the original) of the region that I think you're talking about. Can you confirm if it's accurate?
Log in to reply
@Calvin Lin , would you add another image which explains how Brian gets the sector of 30°, 2 2 sin 1 5 ° and so on because I just can't get it.
Yes, that looks great! Thanks for adding the image. :)
( 3 π − 3 + 1 ) is the important constant.
Log in to reply
Why / How?
Log in to reply
Because it is a ratio of area for the square of 1 sq. unit. Geometry can confirm critical points of interceptions, or extended circles outside the boundary of the square can be judged from trigonometry for a 3 0 ∘ . Get side length of the nearly squared at the middle for an area of smaller square plus 4 segments based on 3 0 ∘ with Δ = 2 1 r 2 ( θ − sin θ ) . The formula of Area = S 2 ( 3 π − 3 + 1 ) is confirmed. Not by plus or minus areas for example square and circle only but it is calculated via partition sums of interceptions.
I don't understand?? As I am in standard 9.
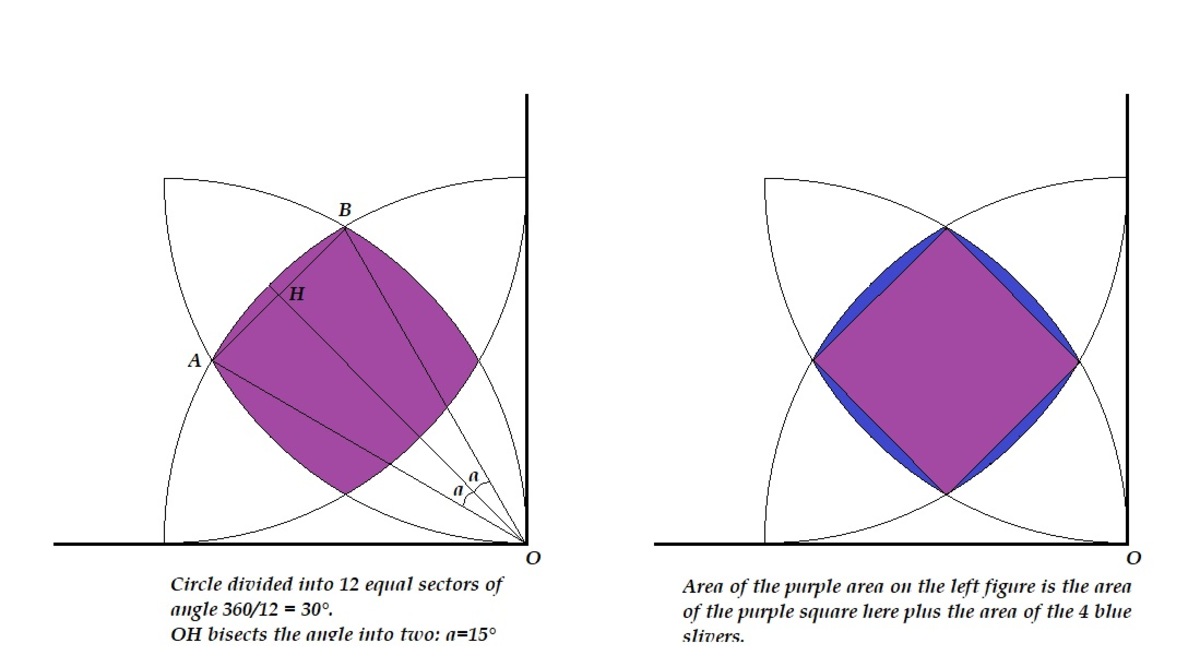
Each purple part could be subdivided into a square and 4 arc slivers extending from each side. Let A 1 be the surface area of the square and A 2 that of the arcs. The total area of all four purple shapes will be: A 0 = 4 A 1 + 1 6 A 2
1 − S q u a r e
To calculate the area of the square, we first calculate the side, segment A B in the image at left.
Law of cosines: A B 2 = O A 2 + O B 2 − 2 . O A . O B . c o s ( 3 0 ∘ )
A B 2 = r 2 + r 2 − 2 . r 2 . 3 / 2 ⇒ A B = r 2 − 3
A 1 = r 2 ( 2 − 3 )
2 − A r c s
The surface area of a blue arc is the surface of the circular sector, A 2 1 minus the surface of triangle O A B , A 2 2
A 2 1 = 1 2 π r 2
A 2 2 = O H . A B / 2
cos 1 5 ∘ = O H / O A ⇒ O H = r ( 6 + 2 ) / 4
A 2 2 = r 2 ( 2 − 3 ) ( 6 + 2 ) / 8 = r 2 / 4 (It's a fun little factoring exercise)
A 2 = A 2 1 − A 2 2 = 1 2 π r 2 − 4 r 2 ⇒ A 2 = r 2 ( 1 2 π − 4 1 )
T o t a l
A 0 = 4 A 1 + 1 6 A 2 = 4 r 2 ( 2 − 3 ) + 1 6 r 2 ( 1 2 π − 4 1 ) ⇒ A 0 = 4 r 2 ( 1 − 3 + 3 π )
For r = 4 , A 0 = 2 0 . 1 6 9
I use calculus to solve this. Please refer to picture for reference. I first calculate area A by integrating y=4-sqrt(8x-x^2) from 2 to 4. This function is the circle to the top right. A= 0.34711.
Next, calculate area B. This is just simply the quarter circle minus half of the 4x4 square. Therefore, area B= 1/4 pi 16-8=4.566370
Next, calculate area C. It is 8 -Area B= 8=4.566370=3.43363
Now, we can calculate D. D= C- 4*Area A= 3.43363- 4(0.34711)=2.04519
Hence, E( violet area) = 4* (2
AreaB) -2
(AreaD)= 4*(9.13274-4.09038)=20.16944
A quarter of one of the four regions is confined by x² + y² = 16; y = 2 and x = 2. This yields to dA = ( sqrt(16 - x²) - 2)dx. Integrating from x = 2 tot x = sqrt(12) yields to the surface of this area. Multiply by 16 to get the answer.
We'll focus first on the square S formed by the centers of the four circles in the upper left of the main square. The violet region is then that region of S common to the four quarter-circles centered at each of the four corners of S .
Now divide this violet region into four identical portions with vertical and horizontal lines acting as axes of symmetry, (each of which pass through the center of the violet region).
Looking at top right portion, we see that it's area is found by first starting with a sector of the lower left circle that subtends an angle of 3 0 ∘ , and then subtracting the areas of two congruent triangles each with a base length of 4 and a height of 2 2 sin ( 1 5 ∘ ) = 3 − 1 . This portion then has an area of
2 1 ∗ 4 2 ∗ 6 π − 2 ∗ 2 1 ∗ 4 ∗ ( 3 − 1 ) = 3 4 π − 4 3 + 4 .
Now the four "whole" violet regions will then be composed of 1 6 of these portions, and hence the desired area value is
6 4 ∗ ( 3 π − 3 + 1 ) = 2 0 . 1 6 9 to 3 decimal places.