Integral octagon
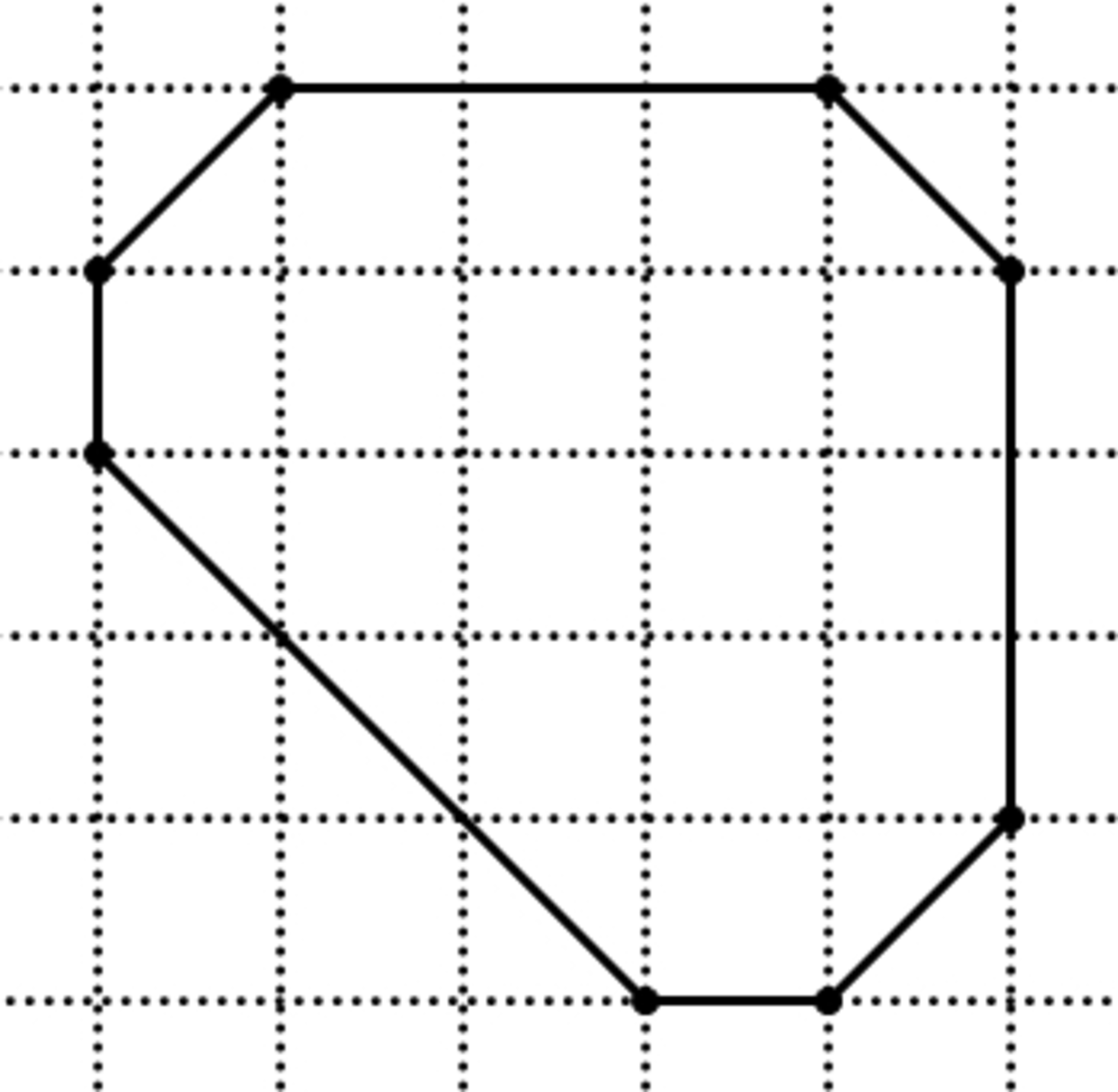
We will say that an octagon is integral if it is equiangular, its vertices are lattice points (i.e., points with integer coordinates), and its area is an integer.
For example, the figure on the above shows an integral octagon of area 19.
Determine the smallest positive integer so that there exists an integral octagon, none of whose sides are parallel to the coordinate axes, that has an area of .
The answer is 35.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
0 solutions
No explanations have been posted yet. Check back later!