Can you reverse the process?
∫ 1 a x + x x − 1 d x = 4
Let a > 1 be a constant satisfying the equation above. What is the value of a 2 + a + 1 ?
The answer is 91.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
Moderator note:
You always post the neatest solutions. Lovely flow of work and your reasoning are simple to understand. Fantastic work. Keep it up! It's a blessing to have you here!
Start by making the substitution x = u 2 . We do this because it will eliminate the square root in the denominator, which tend to be unmanageable to integrate. With the substitution x = u 2 , we have that d x = 2 u d u , which converts the integral from ∫ 1 a x + x x − 1 d x to ∫ 1 a u 2 + u ( u 2 − 1 ) 2 u d u .
Simplifying the integrand on the right reduces it to ∫ 1 a ( 2 u − 2 ) d u = u 2 − 2 u ∣ ∣ ∣ 1 a = ( a − 2 a ) − ( − 1 ) = 4
The only solution to a − 2 a + 1 = 4 is a = 9 . Therefore, a 2 + a + 1 = 9 1 .
do a little bit of algebraic manipulation:
-
x − 1 = ( x − 1 ) ( x + 1 )
-
x + ( x ) = ( x ) ( ( x ) + 1 )
do some cancelation and evaluate the integral!
Moderator note:
Check your working again.
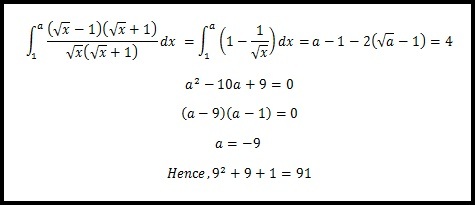
∫ 1 a x + x x − 1 d x = ∫ 1 a x ( x + 1 ) ( x ) 2 − 1 2 d x = ∫ 1 a x ( x + 1 ) ( x − 1 ) ( x + 1 ) d x = ∫ 1 a x x − 1 d x = ∫ 1 a 1 − x 1 d x = ∫ 1 a 1 − x − 2 1 d x = [ x − 2 x 2 1 ] x = 1 x = a = a − 2 a − ( 1 − 2 ) = a − 2 a − 3 = ( a − 3 ) ( a + 1 ) = a = 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 0 0 3 , − 1
But a ≥ 0 and a > 1 Hence, a = 3 ⇒ a = 9
Thus, a 2 + a + 1 = 9 2 + 9 + 1 = 8 1 + 1 0 = 9 1